
No matter which language, there will definitely be the concept of collection. The simplest and most intuitive collection should be an array. An array is a continuous space in memory. Take a look at the definition of array
in C#.
1. int[] intArry;
intArry= new int[6];
Here declares an int array type variable intArry and saves an int array object with 6 units;
int [,] intArry2 = new int[3, 4];
Declare an int two-dimensional array type variable and initialize an array object with 3 rows and 4 columns;
int[][] intArry3 = new int[9 ][];
Declare an array unit as an array variable of int array type. Each array element is an object reference of int array type.
Because it is an object-oriented language, references and objects are mentioned above. In fact:
1. The .net Frameword array is not a simple data structure, but a type, called an array type;
2. The array variable in the .net Framework stores references to array type objects. That is to say, the array is an object.
All .net Framework arrays (int[], string[], object[]) are subclasses inherited from Array. Generally, the Array class is not used directly, because various languages under the .net Framework, including C# of course, map array objects to their own special syntax, such as int[], string[].
Look at a piece of contact code:
public class MyArray
{
/// <summary>
/// 定义数组测试
/// </summary>
public void TestInt()
{
int[] intArry1 = null;
intArry1 = new int[6];
int[,] intArry2 = new int[3, 4];
int[][] intArry3 = new int[9][];
}
/// <summary>
/// 值类型数组转引用类型数组测试
/// </summary>
/// <param name="array"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static object[] Int32ToArrayOfObject(int[] array)
{
object[] objArray = new object[array.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
{
objArray[i] = array[i];
}
return objArray;
}
/// <summary>
/// 数组的主要特性测试
/// </summary>
public static void MainTest()
{
//声明一个包含是个元素的字符串型数组
string[] sArray = new string[10];
//访问数组
//赋值
for (int i = 0; i < sArray.Length; i++)
{
sArray[i] = @"string" + i;
}
ConsoleToClientString(sArray);
//另一种方式声明数组,所谓的枚举法
sArray = new string[] { "TestString0", "TestString1", "TestString2" };
ConsoleToClientString(sArray);
//数组复制
string[] newSArray = sArray.Clone() as string[];
ConsoleToClientString(newSArray);
//使用Array的CreateInstance方法声明10元素的整形数组
int[] intArray = Array.CreateInstance(typeof(int), 10) as int[];
for (int i = 0; i < intArray.Length; i++)
{
intArray[i] = i;
}
ConsoleToClientInt(intArray);
//数组之间的复制,指定位置,指定长度
int[] newIntArray = new int[20];
Array.Copy(intArray, 3, newIntArray, 4, intArray.Length - 3);
ConsoleToClientInt(newIntArray);
object[] objArray = sArray;
ConsoleToClientObject(objArray);
objArray = Int32ToArrayOfObject(intArray);
ConsoleToClientObject(objArray);
//数组的数组
int[][] intArrayArray = new int[9][];
Console.WriteLine("数组长度:" + intArrayArray.Length);
//赋值
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
{
intArrayArray[i - 1] = new int[i];
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
{
intArrayArray[i - 1][j - 1] = i * j;
}
}
ConsoleToClientArrayArrayInt(intArrayArray);
//二维数组
int[,] intArray2D = new int[9, 9];
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("二维数组 长度:{0},维数:{1}*{2}", intArray2D.Length,
intArray2D.GetLength(0), intArray2D.GetLength(1)));
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
{
intArray2D[i - 1, j - 1] = i * j;
}
}
int count = 0;
foreach (int item in intArray2D)
{
if (item > 0)
{
Console.Write("{0,2}", item);
}
if (++count >= 9)
{
Console.WriteLine();
count = 0;
}
}
}
static void ConsoleToClientArrayArrayInt(int[][] intArrayArray)
{
foreach (int[] item1 in intArrayArray)
{
foreach (int item2 in item1)
{
Console.Write("{0,2}", item2);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void ConsoleToClientString(string[] sArray)
{
foreach (string item in sArray)
{
Console.Write(item + @",");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void ConsoleToClientInt(int[] intArray)
{
foreach (int item in intArray)
{
Console.Write(item + @",");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void ConsoleToClientObject(object[] objArray)
{
foreach (object item in objArray)
{
Console.Write(item.ToString() + @",");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
} class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyArray.MainTest();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}You can know from the above: 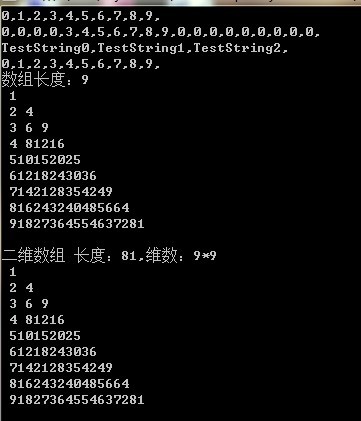 The array has a reference Type array and value type array. For reference type array, the element is used to save the reference of the object, and the initialization value is null; for value type array, the element saves the value of the
The array has a reference Type array and value type array. For reference type array, the element is used to save the reference of the object, and the initialization value is null; for value type array, the element saves the value of the
object, and for the numeric type, the initialization value is 0.
, and the multidimensional array is an array in which each element is an array object.
The above is the compilation of C# basic knowledge: Basic knowledge (14) Array content. For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (www.php.cn)!




