Introduction to examples of positioning background images using CSS
Another example:

These small pictures are the parts after the whole picture is divided. Put each part on one picture instead of storing them separately. We all know the purpose of pictures is to reduce the number of http requests and save time and bandwidth.
So how to realize that only part of a picture is displayed in different places? This uses the positioning problem of the background picture we are going to talk about today. I believe many people have been depressed about this problem, and friends often ask me, so today I will explain it systematically:
We know that when using an image as a background, the css should be written like this, take the div container as an example , it can also be the background of body, td, p, etc., the principle is the same.
Code:
div{ background:#FFF url(image) no-repeat fixed x y;}
The background attribute values here are in sequence It is:
#FFF Background color: (color value, the area not covered by the background image, or the background color when there is no background image)
image Background image: (Here is the address of the image)
no-repeat Whether to repeat: (When the picture is smaller than the size of the container, the picture will be arranged repeatedly to fill the container by default. no-repeat means no repetition. Only at this time will the subsequent positioning coordinates be useful.)
fixed Whether the background is random Container scrolling: (There are two optional values, scroll scrolling, fixed does not scroll, the default is scroll)
x y Positioning of the background image : (Note that positioning is meaningful only under no-repeat . This is the focus of today)
We need to clarify a few points in background image positioning:
1. The first one of the two values is the horizontal positioning, which we call the x-axis direction. position. The latter value is the longitudinal positioning, which we call the y-axis positioning. If there is only one value, the default is the x-axis direction. At this time, the y-axis direction defaults to aligning up and down, which is center.
2. The origin of the coordinate axis is the left vertex of the corresponding container.
3. The y-axis arrow of this coordinate points downward, that is, the values of x and y in the lower right corner (inside the container) are all positive.
4. The x and y values respectively represent the value of the left vertex of the background image relative to the coordinate origin (that is, the left vertex of the container).
5. The value of x y can be expressed in percentage or px.
6, x y can also be aligned using the five alignment methods of "left, right, top, bottom, center" Representation, but note: when expressed with "left, right, top, bottom, center", the alignment rules are applied, not the coordinate rules. When x is left, it means the left side of the picture is aligned with the left side of the container. When it is right, it means the right side of the picture is aligned with the right side of the container. When y is top, it means the top of the picture is aligned with the top of the container. When it is bottom, it means the top of the picture is aligned. The bottom is aligned with the bottom of the container. When x y is equal to center, it means centered alignment.
7. When x y is expressed in percentage or px, its value can be a negative number. We can easily understand the meaning of negative numbers by applying the coordinate rules. When x is a negative number, it means that the left vertex of the picture is to the left of the left vertex of the container. When y is a negative number, it means that the left vertex of the picture is above the left fixed point of the container. That is, to the left and up beyond the scope of the container.
Below I use a few illustrations to illustrate several situations. The blue block represents the picture, and the dotted box represents the container (it can be div, td, or directly body). Note that only the background image is in the container. In order to be visible, I use white to represent the visible part, and what is beyond the scope of the container is invisible, so I use gray to represent it. The coordinates of the left fixed point of the container are (0, 0).
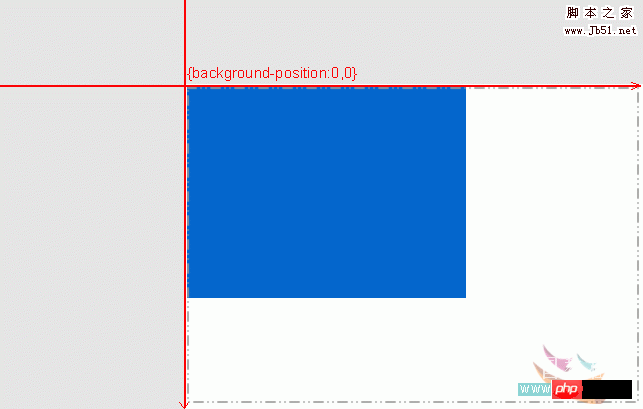
The first one, the background image is aligned with the top left of the content, 0px 0px can also be written as left top
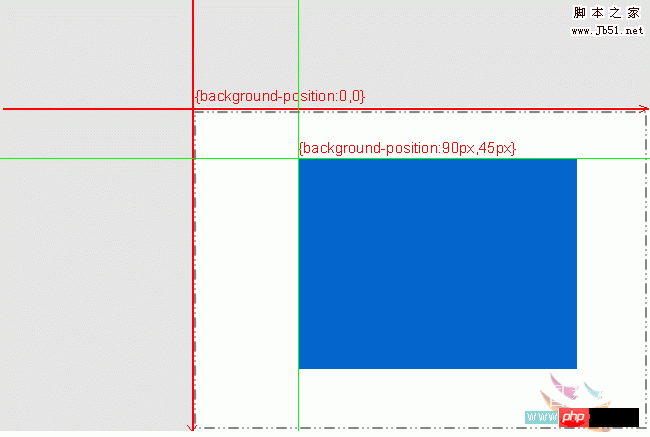
Two pictures, the background image is in the middle of the container, and the fixed point coordinates are positive values
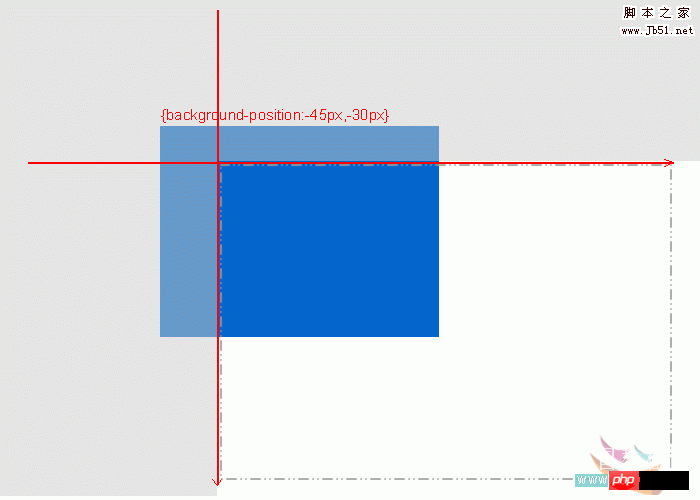
The third picture, the background image is on the upper left side of the container, and the fixed point coordinates are negative values
---------------- -------------------------------------------------- ---------
At this point we may understand how to use the positioning value in the background to accurately locate a background image. Go back and take a look at the two images introduced at the beginning. We can Use these two properties: background positioning and only visible within the container to freely call a certain part of the entire image.
But for the convenience of calling, we need to pay attention to some rules when arranging these small pictures. For example: the distance between small pictures is usually the size of the container that calls the small pictures, or the distance is larger, so that This can avoid images we don’t want to display in the container!
In addition, if the positioning uses percentages, the algorithm is rather special. Let me give you an example:
Code:
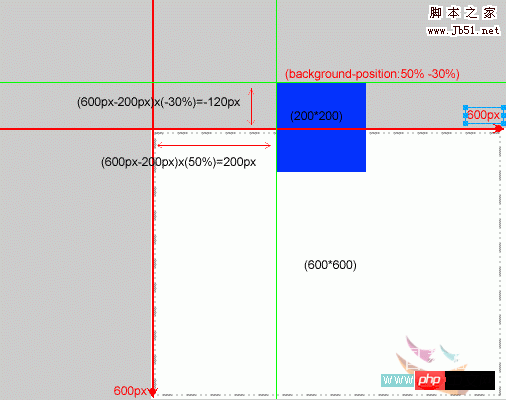
background:#FFF url(image) no-repeat fixed 50% -30%;
At this time the image should be in the container What position? The algorithm formula is as follows:
The coordinate position of the left vertex of the picture from the left vertex of the container is
x: (width of the container - width of the picture) x50%
y: (height of the container -Height of the picture) If the difference is negative and the percentage is negative, the result is positive. All in all, this is the
operatorcombination algorithm here. By bringing the result of the operation into the coordinate rule, you can get the position of the picture. For example: the container is
width: 600px; height: 600px; and the picture is width: 200px; height: 200px; We use the above style to get the picture The position is:
x: (600px-200px)*50%
y: (600px-200px)*(-30%)
As shown below:
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to examples of positioning background images using CSS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1654
1654
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1306
1306
 25
25
 1252
1252
 29
29
 1225
1225
 24
24
 Google Fonts Variable Fonts
Apr 09, 2025 am 10:42 AM
Google Fonts Variable Fonts
Apr 09, 2025 am 10:42 AM
I see Google Fonts rolled out a new design (Tweet). Compared to the last big redesign, this feels much more iterative. I can barely tell the difference
 How to Create an Animated Countdown Timer With HTML, CSS and JavaScript
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:29 AM
How to Create an Animated Countdown Timer With HTML, CSS and JavaScript
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:29 AM
Have you ever needed a countdown timer on a project? For something like that, it might be natural to reach for a plugin, but it’s actually a lot more
 HTML Data Attributes Guide
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:50 AM
HTML Data Attributes Guide
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:50 AM
Everything you ever wanted to know about data attributes in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
 How to select a child element with the first class name item through CSS?
Apr 05, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
How to select a child element with the first class name item through CSS?
Apr 05, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
When the number of elements is not fixed, how to select the first child element of the specified class name through CSS. When processing HTML structure, you often encounter different elements...
 Why are the purple slashed areas in the Flex layout mistakenly considered 'overflow space'?
Apr 05, 2025 pm 05:51 PM
Why are the purple slashed areas in the Flex layout mistakenly considered 'overflow space'?
Apr 05, 2025 pm 05:51 PM
Questions about purple slash areas in Flex layouts When using Flex layouts, you may encounter some confusing phenomena, such as in the developer tools (d...
 A Proof of Concept for Making Sass Faster
Apr 16, 2025 am 10:38 AM
A Proof of Concept for Making Sass Faster
Apr 16, 2025 am 10:38 AM
At the start of a new project, Sass compilation happens in the blink of an eye. This feels great, especially when it’s paired with Browsersync, which reloads
 In front-end development, how to use CSS and JavaScript to achieve searchlight effects similar to Windows 10 settings interface?
Apr 05, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
In front-end development, how to use CSS and JavaScript to achieve searchlight effects similar to Windows 10 settings interface?
Apr 05, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
How to implement Windows-like in front-end development...
 How We Created a Static Site That Generates Tartan Patterns in SVG
Apr 09, 2025 am 11:29 AM
How We Created a Static Site That Generates Tartan Patterns in SVG
Apr 09, 2025 am 11:29 AM
Tartan is a patterned cloth that’s typically associated with Scotland, particularly their fashionable kilts. On tartanify.com, we gathered over 5,000 tartan




