Detailed explanation of Java's memory mechanism (pictures and text)
This article mainly introduces the relevant knowledge of Java's memory mechanism, which has a very good reference value. Let's take a look at it with the editor
Java divides memory into two types: one One is stack memory, and the other is heap memory. Some basic types of variables and object reference variables defined in the function are allocated in the stack memory of the function. When a variable is defined in a block of code, Java allocates memory space for the variable on the stack. When the scope of the variable is exceeded (for example, when function B is called in function A and variable a is defined in function B, the scope of variable a is only function B. After function B runs, variable a will be automatically destroyed. Assigned to Its memory will be recycled), Java will automatically release the memory space allocated for the variable, and the memory space can be used for other purposes immediately.
Heap memory is used to store the memory array created by new. The memory allocated in the heap is managed by the automatic garbage collector of the Java virtual machine. After generating an array or object in the heap, you can also define a special variable in the stack so that the value of the variable in the stack is equal to the first address of the array or object in the heap memory. The variable in the stack becomes After obtaining the reference variable of the array or object, you can use the variable in the stack to access the array or object in the heap in the program. The reference variable is equivalent to giving a name to the array or object. Reference variables are ordinary variables that are allocated on the stack when defined. The reference variables are released after the program runs outside other scopes. Arrays and objects are allocated in the heap. Even if the program runs outside the code block where the array or object statement generated by new is located, the memory occupied by the array and object will not be released. Arrays and objects only become garbage when there are no reference variables pointing to them and can no longer be used. They will be collected (released) by the garbage collector at an unspecified time later. This is also the reason why Java takes up more memory. In fact, variables in the stack point to variables in the heap memory, which are pointers in Java.
Code example Demo1: Single object creation
class Person {
String name ;
int age ;
public void tell() {
System.out.println("姓名:"+name+",年龄:"+age);
}
}
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person per = new Person() ;
}
}In the above program, an object per is instantiated. During the instantiation process, space needs to be opened up in the memory. This includes stack memory and heap memory. The specific memory allocation is shown in the following figure:
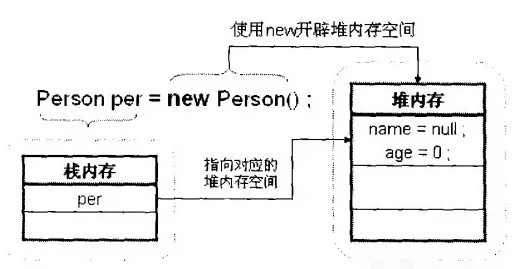
## Figure 1-1 Object instantiation process
We can find from the above picture that the object name per is saved in the stack memory (more accurately, the access address of the heap memory space is saved in the stack memory), and the specific content of the object , such asattributesname and age, are saved in heap memory. Because the per object has only been instantiated and has not been assigned a specific value, it has default values. The default value of string is null, and the default value of type int is 0. As mentioned earlier, the heap memory space must be opened using the new keyword.
Code example Demo2: multiple objects created
class Person {
String name ;
int age ;
public void tell() {
System.out.println("姓名:"+name+",年龄:"+age);
}
}
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person per1 = new Person() ;
Person per2 = new Person() ;
per1.name="张三" ;
per1.age=30 ;
per2.age=33 ;
per1.tell();
per2.tell();
}
}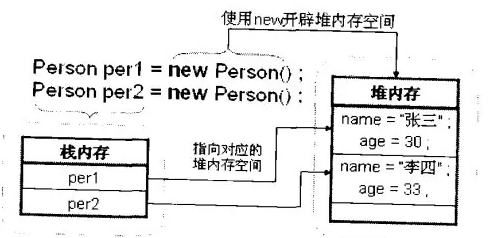
Figure 1-2 Instantiate two objects
Key concepts: Classes, like arrays, are reference types. Reference types mean that the same heap memory can be pointed to by multiple stack memories. Let's take a look at a simple example of reference transfer.Code example Demo3: Object reference transfer 1
class Person {
String name ;
int age ;
public void tell() {
System.out.println("姓名:"+name+",年龄:"+age);
}
}
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person per1 = new Person() ;
Person per2 = per1 ;//-------注意--------
per1.name="张三" ;
per1.age=30 ;
per2.age=33 ;
per1.tell();
per2.tell();
}
}
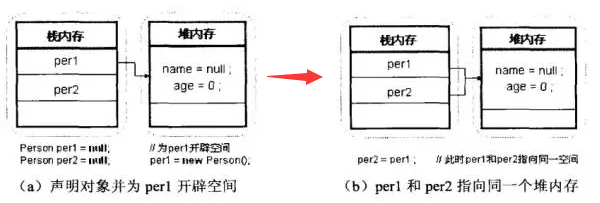
Figure 1-3 Transfer memory allocation of object reference
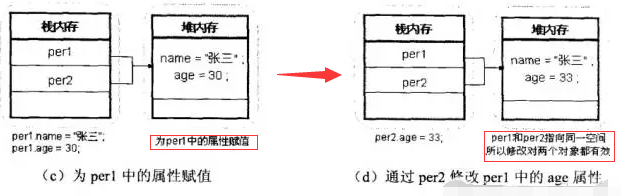
Figure 1-3 Transfer memory allocation of object reference (continued)
Note: In the above example, the object per2 has no heap memory space. This is because the object per2 only Declaration operations are performed, and no instantiation operations are performed. Just use the new keyword, and there will be heap memory space after instantiationCode example Demo4: Object reference transfer 2
class Person {
String name ;
int age ;
public void tell() {
System.out.println("姓名:"+name+",年龄:"+age);
}
}
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person per1 = new Person() ;
Person per2 = new Person() ;
per1.name="张三" ;
per1.age=30 ;
per2.name="李四" ;
per2.age=33 ;
per2=per1 ;//-----注意----
per1.tell();
per2.tell();
}
}
It can be found from the output of the program that it is similar to Demo3. However, some changes have occurred in memory allocation, as shown below:

Figure 1-4 (Garbage Object) Generation
Notes:
1. Java itself provides a garbage collection mechanism (Garbage Collection, GC), which will release unused memory space from time to time. As long as the object is no longer used, it will wait for the GC to release the space. , such as name="李思";age=33 in the heap memory above.
2. A stack memory can only point to one heap memory space. If you want to point to another heap memory space, you must first disconnect the existing pointer before allocating a new pointer.
Common memory areas in Java
There are mainly 4 memory spaces in Java. The names and functions of these memories are as follows:
1. Stack memory space: Saves the names of all objects.
2. Heap memory space: saves the specific attribute content of each object.
3. Global data area: Save static type attribute values.
4. Global code area: saves all method definitions.
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Java's memory mechanism (pictures and text). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1677
1677
 14
14
 1431
1431
 52
52
 1334
1334
 25
25
 1279
1279
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 Composer: Aiding PHP Development Through AI
Apr 29, 2025 am 12:27 AM
Composer: Aiding PHP Development Through AI
Apr 29, 2025 am 12:27 AM
AI can help optimize the use of Composer. Specific methods include: 1. Dependency management optimization: AI analyzes dependencies, recommends the best version combination, and reduces conflicts. 2. Automated code generation: AI generates composer.json files that conform to best practices. 3. Improve code quality: AI detects potential problems, provides optimization suggestions, and improves code quality. These methods are implemented through machine learning and natural language processing technologies to help developers improve efficiency and code quality.
 H5: Key Improvements in HTML5
Apr 28, 2025 am 12:26 AM
H5: Key Improvements in HTML5
Apr 28, 2025 am 12:26 AM
HTML5 brings five key improvements: 1. Semantic tags improve code clarity and SEO effects; 2. Multimedia support simplifies video and audio embedding; 3. Form enhancement simplifies verification; 4. Offline and local storage improves user experience; 5. Canvas and graphics functions enhance the visualization of web pages.
 How to use MySQL functions for data processing and calculation
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:21 PM
How to use MySQL functions for data processing and calculation
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:21 PM
MySQL functions can be used for data processing and calculation. 1. Basic usage includes string processing, date calculation and mathematical operations. 2. Advanced usage involves combining multiple functions to implement complex operations. 3. Performance optimization requires avoiding the use of functions in the WHERE clause and using GROUPBY and temporary tables.
 Discuss situations where writing platform-specific code in Java might be necessary.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Discuss situations where writing platform-specific code in Java might be necessary.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Reasons for writing platform-specific code in Java include access to specific operating system features, interacting with specific hardware, and optimizing performance. 1) Use JNA or JNI to access the Windows registry; 2) Interact with Linux-specific hardware drivers through JNI; 3) Use Metal to optimize gaming performance on macOS through JNI. Nevertheless, writing platform-specific code can affect the portability of the code, increase complexity, and potentially pose performance overhead and security risks.
 How to use type traits in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
How to use type traits in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
typetraits are used in C for compile-time type checking and operation, improving code flexibility and type safety. 1) Type judgment is performed through std::is_integral and std::is_floating_point to achieve efficient type checking and output. 2) Use std::is_trivially_copyable to optimize vector copy and select different copy strategies according to the type. 3) Pay attention to compile-time decision-making, type safety, performance optimization and code complexity. Reasonable use of typetraits can greatly improve code quality.
 How to configure the character set and collation rules of MySQL
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:06 PM
How to configure the character set and collation rules of MySQL
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:06 PM
Methods for configuring character sets and collations in MySQL include: 1. Setting the character sets and collations at the server level: SETNAMES'utf8'; SETCHARACTERSETutf8; SETCOLLATION_CONNECTION='utf8_general_ci'; 2. Create a database that uses specific character sets and collations: CREATEDATABASEexample_dbCHARACTERSETutf8COLLATEutf8_general_ci; 3. Specify character sets and collations when creating a table: CREATETABLEexample_table(idINT
 How to rename a database in MySQL
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:00 PM
How to rename a database in MySQL
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:00 PM
Renaming a database in MySQL requires indirect methods. The steps are as follows: 1. Create a new database; 2. Use mysqldump to export the old database; 3. Import the data into the new database; 4. Delete the old database.
 How to implement singleton pattern in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
How to implement singleton pattern in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
Implementing singleton pattern in C can ensure that there is only one instance of the class through static member variables and static member functions. The specific steps include: 1. Use a private constructor and delete the copy constructor and assignment operator to prevent external direct instantiation. 2. Provide a global access point through the static method getInstance to ensure that only one instance is created. 3. For thread safety, double check lock mode can be used. 4. Use smart pointers such as std::shared_ptr to avoid memory leakage. 5. For high-performance requirements, static local variables can be implemented. It should be noted that singleton pattern can lead to abuse of global state, and it is recommended to use it with caution and consider alternatives.




