Detailed explanation of Apache's object replication example tutorial
BeanUtils.copyProperties and PropertyUtils.copyProperties
Both tool classes process properties with the same name that previously existed in two beans, whether it is the source bean or the target bean. None of the attributes are processed.
The principle is to use the JDK's own reflection mechanism to dynamically get and set, thereby converting our classes.
But we should pay attention to the data types they support. Another thing is that if a class is written inside a class, which is generally called an inner class, conversion of such a class will not be successful.
The biggest difference between the two is:
1.BeanUtils.copyProperties will perform type conversion, but PropertyUtils.copyProperties will not.
Since type conversion is performed, BeanUtils.copyProperties is not as fast as PropertyUtils.copyProperties.
Therefore, the scope of application of PropertyUtils.copyProperties is slightly narrower. It only copies properties with the same name and type. If the name is the same but the type is different, it will report an error.
2. Handling of null: PropertyUtils supports null scenarios; BeanUtils does not support null scenarios for some properties, specifically as follows:
1), date type is not supported ;
2), Boolean, Ineger, Long, Short, Float, Double, etc. are not supported: Convert to false, 0;
3), string: supported, keep null;
There are several things to note when using BeanUtils:
1. For attributes of type Boolean/Short/Integer/Float/Double, it will be converted to false, 0:
1 public class User {
2 3 private Integer intVal;
4 5 private Double doubleVal;
6 7 private Short shortVal;
8 9 private Long longVal;
10 11 private Float floatVal;
12 13 private Byte byteVal;
14 15 private Boolean booleanVal;
16 }
17 18 User src = new User();
19 User dest = new User();
20 BeanUtils.copyProperties(dest, src);
21 System.out.println(src);
22 System.out.println(dest);
23 24 //输出结果: 25 User [intVal=null, doubleVal=null, shortVal=null, longVal=null, floatVal=null, byteVal=null, booleanVal=null]
26 User [intVal=0, doubleVal=0.0, shortVal=0, longVal=0, floatVal=0.0, byteVal=0, booleanVal=false]The explanation is that these types have corresponding basic types. When performing type conversion, it is possible When encountering a conversion similar to Integer -> int, it is obvious that the attribute of type int cannot be assigned a value of null, so it is uniformly converted to 0.
How to prevent it from turning to 0? It can be like this:

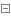
1 import org.apache.commons.beanutils.converters.IntegerConverter; 2 3 IntegerConverter converter = new IntegerConverter(null); //默认为null,而不是0 4 BeanUtilsBean beanUtilsBean = new BeanUtilsBean(); 5 beanUtilsBean.getConvertUtils().register(converter, Integer.class);
2. For java.util.Date/BigDecimal/java.sql For the .Date/java.sql.Timestamp/java.sql.Time classes, if the value is null, an exception will be thrown during copying, and the corresponding Conveter needs to be used:
1 public class User2 {
2 3 private java.util.Date javaUtilDateVal;
4 5 private java.sql.Date javaSqlDateVal;
6 7 private java.sql.Timestamp javaSqlTimeStampVal;
8 9 private BigDecimal bigDecimalVal;
10 11 private java.sql.Time javaSqlTime;
12 13 }
14 15 User2 src = new User2();
16 User2 dest = new User2();
17 18 BeanUtilsBean beanUtilsBean = new BeanUtilsBean();
19 20 //如果没有下面几行,则在转换null时会抛异常,例如:org.apache.commons.beanutils.ConversionException: No value specified for 'BigDecimal'
21 //在org.apache.commons.beanutils.converters这个包下面有很多的Converter,可以按需要使用 22 beanUtilsBean.getConvertUtils().register(new BigDecimalConverter(null), BigDecimal.class);
23 beanUtilsBean.getConvertUtils().register(new DateConverter(null), java.util.Date.class);
24 25 beanUtilsBean.getConvertUtils().register(new SqlTimestampConverter(null), java.sql.Timestamp.class);
26 beanUtilsBean.getConvertUtils().register(new SqlDateConverter(null), java.sql.Date.class);
27 beanUtilsBean.getConvertUtils().register(new SqlTimeConverter(null), java.sql.Time.class);
28 29 beanUtilsBean.copyProperties(dest, src);
30 System.out.println(src);
31 System.out.println(dest); Assume it is copied from A to B:
Requirement 1: If a field in B has a value (not null), then the field is not copied; that is, When the field in B has no value, it will be copied, which is suitable for supplementing the value of B.


1 import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtilsBean;
2 import org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils;
3 4 public class CopyWhenNullBeanUtilsBean extends BeanUtilsBean{
5 6 @Override
7 public void copyProperty(Object bean, String name, Object value)
8 throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
9 try {
10 Object destValue = PropertyUtils.getSimpleProperty(bean, name);
11 if (destValue == null) {
12 super.copyProperty(bean, name, value);
13 }
14 } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
15 throw new RuntimeException(e);
16 }
17 }
18 19 }Requirement 2: If a field in A has no value (is null), then the field will not be copied, that is, do not copy null is copied to B.
1 import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtilsBean;
2 3 public class CopyFromNotNullBeanUtilsBean extends BeanUtilsBean {
4 5 @Override
6 public void copyProperty(Object bean, String name, Object value) throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
7 if (value == null) {
8 return;
9 }
10 super.copyProperty(bean, name, value);
11 }
12 }The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Apache's object replication example tutorial. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to set the cgi directory in apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:18 PM
How to set the cgi directory in apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:18 PM
To set up a CGI directory in Apache, you need to perform the following steps: Create a CGI directory such as "cgi-bin", and grant Apache write permissions. Add the "ScriptAlias" directive block in the Apache configuration file to map the CGI directory to the "/cgi-bin" URL. Restart Apache.
 What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
When the Apache 80 port is occupied, the solution is as follows: find out the process that occupies the port and close it. Check the firewall settings to make sure Apache is not blocked. If the above method does not work, please reconfigure Apache to use a different port. Restart the Apache service.
 How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Apache connects to a database requires the following steps: Install the database driver. Configure the web.xml file to create a connection pool. Create a JDBC data source and specify the connection settings. Use the JDBC API to access the database from Java code, including getting connections, creating statements, binding parameters, executing queries or updates, and processing results.
 How to view your apache version
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:15 PM
How to view your apache version
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:15 PM
There are 3 ways to view the version on the Apache server: via the command line (apachectl -v or apache2ctl -v), check the server status page (http://<server IP or domain name>/server-status), or view the Apache configuration file (ServerVersion: Apache/<version number>).
 How to view the apache version
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:00 PM
How to view the apache version
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:00 PM
How to view the Apache version? Start the Apache server: Use sudo service apache2 start to start the server. View version number: Use one of the following methods to view version: Command line: Run the apache2 -v command. Server Status Page: Access the default port of the Apache server (usually 80) in a web browser, and the version information is displayed at the bottom of the page.
 How to configure zend for apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure zend for apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure Zend in Apache? The steps to configure Zend Framework in an Apache Web Server are as follows: Install Zend Framework and extract it into the Web Server directory. Create a .htaccess file. Create the Zend application directory and add the index.php file. Configure the Zend application (application.ini). Restart the Apache Web server.
 How to delete more than server names of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:09 PM
How to delete more than server names of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:09 PM
To delete an extra ServerName directive from Apache, you can take the following steps: Identify and delete the extra ServerName directive. Restart Apache to make the changes take effect. Check the configuration file to verify changes. Test the server to make sure the problem is resolved.
 How to solve the problem that apache cannot be started
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:21 PM
How to solve the problem that apache cannot be started
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:21 PM
Apache cannot start because the following reasons may be: Configuration file syntax error. Conflict with other application ports. Permissions issue. Out of memory. Process deadlock. Daemon failure. SELinux permissions issues. Firewall problem. Software conflict.






