Java NIO系列教程3: Buffer的基本用法
Java NIO中的Buffer用于和NIO通道进行交互。如你所知,数据是从通道读入缓冲区,从缓冲区写入到通道中的。
缓冲区本质上是一块可以写入数据,然后可以从中读取数据的内存。这块内存被包装成NIO Buffer对象,并提供了一组方法,用来方便的访问该块内存。
下面是NIO Buffer相关的话题列表:
Buffer的基本用法
Buffer的capacity,position和limit
Buffer的类型
Buffer的分配
向Buffer中写数据
flip()方法
从Buffer中读取数据
clear()与compact()方法
mark()与reset()方法
equals()与compareTo()方法
Buffer的基本用法
使用Buffer读写数据一般遵循以下四个步骤:
写入数据到Buffer
调用
flip()方法从Buffer中读取数据
调用
clear()方法或者compact()方法
当向buffer写入数据时,buffer会记录下写了多少数据。一旦要读取数据,需要通过flip()方法将Buffer从写模式切换到读模式。在读模式下,可以读取之前写入到buffer的所有数据。
一旦读完了所有的数据,就需要清空缓冲区,让它可以再次被写入。有两种方式能清空缓冲区:调用clear()或compact()方法。clear()方法会清空整个缓冲区。compact()方法只会清除已经读过的数据。任何未读的数据都被移到缓冲区的起始处,新写入的数据将放到缓冲区未读数据的后面。
下面是一个使用Buffer的例子:
01 |
RandomAccessFile
aFile = new RandomAccessFile("data/nio-data.txt", "rw");
|
02 |
FileChannel
inChannel = aFile.getChannel(); |
03 |
04 |
//create
buffer with capacity of 48 bytes |
05 |
ByteBuffer
buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
|
06 |
07 |
int bytesRead
= inChannel.read(buf); //read
into buffer.
|
08 |
while (bytesRead
!= -1)
{
|
09 |
10 |
buf.flip(); //make
buffer ready for read
|
11 |
12 |
while(buf.hasRemaining()){
|
13 |
System.out.print((char)
buf.get()); //
read 1 byte at a time
|
14 |
}
|
15 |
16 |
buf.clear(); //make
buffer ready for writing
|
17 |
bytesRead
= inChannel.read(buf);
|
18 |
} |
19 |
aFile.close(); |
Buffer的capacity,position和limit
缓冲区本质上是一块可以写入数据,然后可以从中读取数据的内存。这块内存被包装成NIO Buffer对象,并提供了一组方法,用来方便的访问该块内存。
为了理解Buffer的工作原理,需要熟悉它的三个属性:
capacity
position
limit
position和limit的含义取决于Buffer处在读模式还是写模式。不管Buffer处在什么模式,capacity的含义总是一样的。
这里有一个关于capacity,position和limit在读写模式中的说明,详细的解释在插图后面。
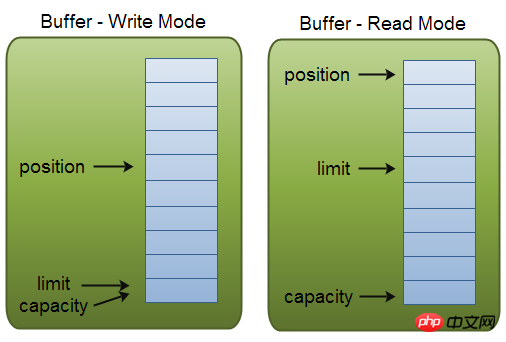
capacity
作为一个内存块,Buffer有一个固定的大小值,也叫“capacity”.你只能往里写capacity个byte、long,char等类型。一旦Buffer满了,需要将其清空(通过读数据或者清除数据)才能继续写数据往里写数据。
position
当你写数据到Buffer中时,position表示当前的位置。初始的position值为0.当一个byte、long等数据写到Buffer后, position会向前移动到下一个可插入数据的Buffer单元。position最大可为capacity – 1.
当读取数据时,也是从某个特定位置读。当将Buffer从写模式切换到读模式,position会被重置为0. 当从Buffer的position处读取数据时,position向前移动到下一个可读的位置。
limit
在写模式下,Buffer的limit表示你最多能往Buffer里写多少数据。 写模式下,limit等于Buffer的capacity。
当切换Buffer到读模式时, limit表示你最多能读到多少数据。因此,当切换Buffer到读模式时,limit会被设置成写模式下的position值。换句话说,你能读到之前写入的所有数据(limit被设置成已写数据的数量,这个值在写模式下就是position)
Buffer的类型
Java NIO 有以下Buffer类型
ByteBuffer
MappedByteBuffer
CharBuffer
DoubleBuffer
FloatBuffer
IntBuffer
LongBuffer
ShortBuffer
p<>
如你所见,这些Buffer类型代表了不同的数据类型。换句话说,就是可以通过char,short,int,long,float 或 double类型来操作缓冲区中的字节。
MappedByteBuffer 有些特别,在涉及它的专门章节中再讲。
Buffer的分配
要想获得一个Buffer对象首先要进行分配。 每一个Buffer类都有一个allocate方法。下面是一个分配48字节capacity的ByteBuffer的例子。
1 |
ByteBuffer
buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
|
这是分配一个可存储1024个字符的CharBuffer:
1 |
CharBuffer
buf = CharBuffer.allocate(1024);
|
向Buffer中写数据
写数据到Buffer有两种方式:
从Channel写到Buffer。
通过Buffer的put()方法写到Buffer里。
从Channel写到Buffer的例子
1 |
int bytesRead
= inChannel.read(buf); //read
into buffer.
|
通过put方法写Buffer的例子:
1 |
buf.put(127);
|
put方法有很多版本,允许你以不同的方式把数据写入到Buffer中。例如, 写到一个指定的位置,或者把一个字节数组写入到Buffer。 更多Buffer实现的细节参考JavaDoc。
flip()方法
flip方法将Buffer从写模式切换到读模式。调用flip()方法会将position设回0,并将limit设置成之前position的值。
换句话说,position现在用于标记读的位置,limit表示之前写进了多少个byte、char等 —— 现在能读取多少个byte、char等。
从Buffer中读取数据
从Buffer中读取数据有两种方式:
从Buffer读取数据到Channel。
使用get()方法从Buffer中读取数据。
从Buffer读取数据到Channel的例子:
1 |
//read
from buffer into channel. |
2 |
int bytesWritten
= inChannel.write(buf);
|
使用get()方法从Buffer中读取数据的例子
1 |
byte aByte
= buf.get();
|
get方法有很多版本,允许你以不同的方式从Buffer中读取数据。例如,从指定position读取,或者从Buffer中读取数据到字节数组。更多Buffer实现的细节参考JavaDoc。
rewind()方法
Buffer.rewind()将position设回0,所以你可以重读Buffer中的所有数据。limit保持不变,仍然表示能从Buffer中读取多少个元素(byte、char等)。
clear()与compact()方法
一旦读完Buffer中的数据,需要让Buffer准备好再次被写入。可以通过clear()或compact()方法来完成。
如果调用的是clear()方法,position将被设回0,limit被设置成 capacity的值。换句话说,Buffer 被清空了。Buffer中的数据并未清除,只是这些标记告诉我们可以从哪里开始往Buffer里写数据。
如果Buffer中有一些未读的数据,调用clear()方法,数据将“被遗忘”,意味着不再有任何标记会告诉你哪些数据被读过,哪些还没有。
如果Buffer中仍有未读的数据,且后续还需要这些数据,但是此时想要先先写些数据,那么使用compact()方法。
compact()方法将所有未读的数据拷贝到Buffer起始处。然后将position设到最后一个未读元素正后面。limit属性依然像clear()方法一样,设置成capacity。现在Buffer准备好写数据了,但是不会覆盖未读的数据。
mark()与reset()方法
通过调用Buffer.mark()方法,可以标记Buffer中的一个特定position。之后可以通过调用Buffer.reset()方法恢复到这个position。例如:
1 |
buffer.mark(); |
2 |
3 |
//call
buffer.get() a couple of times, e.g. during parsing. |
4 |
5 |
buffer.reset(); //set
position back to mark.
|
equals()与compareTo()方法
可以使用equals()和compareTo()方法两个Buffer。
equals()
当满足下列条件时,表示两个Buffer相等:
有相同的类型(byte、char、int等)。
Buffer中剩余的byte、char等的个数相等。
Buffer中所有剩余的byte、char等都相同。
如你所见,equals只是比较Buffer的一部分,不是每一个在它里面的元素都比较。实际上,它只比较Buffer中的剩余元素。
compareTo()方法
compareTo()方法比较两个Buffer的剩余元素(byte、char等), 如果满足下列条件,则认为一个Buffer“小于”另一个Buffer:
第一个不相等的元素小于另一个Buffer中对应的元素 。
所有元素都相等,但第一个Buffer比另一个先耗尽(第一个Buffer的元素个数比另一个少)。
相关文章:
相关视频:
The above is the detailed content of Java NIO系列教程3: Buffer的基本用法. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Is the company's security software causing the application to fail to run? How to troubleshoot and solve it?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
Is the company's security software causing the application to fail to run? How to troubleshoot and solve it?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
Troubleshooting and solutions to the company's security software that causes some applications to not function properly. Many companies will deploy security software in order to ensure internal network security. ...
 How do I convert names to numbers to implement sorting and maintain consistency in groups?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How do I convert names to numbers to implement sorting and maintain consistency in groups?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Solutions to convert names to numbers to implement sorting In many application scenarios, users may need to sort in groups, especially in one...
 How to simplify field mapping issues in system docking using MapStruct?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 06:21 PM
How to simplify field mapping issues in system docking using MapStruct?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 06:21 PM
Field mapping processing in system docking often encounters a difficult problem when performing system docking: how to effectively map the interface fields of system A...
 How to elegantly obtain entity class variable names to build database query conditions?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:42 PM
How to elegantly obtain entity class variable names to build database query conditions?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:42 PM
When using MyBatis-Plus or other ORM frameworks for database operations, it is often necessary to construct query conditions based on the attribute name of the entity class. If you manually every time...
 How does IntelliJ IDEA identify the port number of a Spring Boot project without outputting a log?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
How does IntelliJ IDEA identify the port number of a Spring Boot project without outputting a log?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
Start Spring using IntelliJIDEAUltimate version...
 How to safely convert Java objects to arrays?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to safely convert Java objects to arrays?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Conversion of Java Objects and Arrays: In-depth discussion of the risks and correct methods of cast type conversion Many Java beginners will encounter the conversion of an object into an array...
 E-commerce platform SKU and SPU database design: How to take into account both user-defined attributes and attributeless products?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
E-commerce platform SKU and SPU database design: How to take into account both user-defined attributes and attributeless products?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
Detailed explanation of the design of SKU and SPU tables on e-commerce platforms This article will discuss the database design issues of SKU and SPU in e-commerce platforms, especially how to deal with user-defined sales...
 How to elegantly get entity class variable name building query conditions when using TKMyBatis for database query?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 09:51 PM
How to elegantly get entity class variable name building query conditions when using TKMyBatis for database query?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 09:51 PM
When using TKMyBatis for database queries, how to gracefully get entity class variable names to build query conditions is a common problem. This article will pin...






