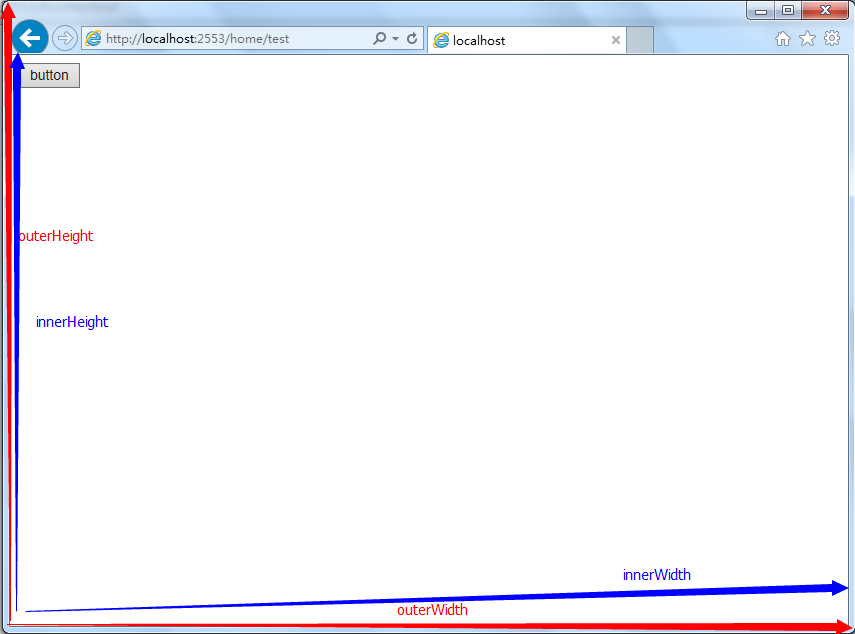
In Javascript, you can use OuterWidth and OuterHeight to get the size of the browser. Use innerWidth and innerHeight to get the size of the window (excluding the browser border). For IE6 and previous versions, it is necessary to distinguish between standard mode and mixed mode. Standard mode uses document.documentElement.clientWidth, document.documentElement.clientHeight; mixed mode uses document.body's clientWidth, clientHeight.
(function () {
var pageWidth = window.innerWidth;
var pageHeight = window.innerHeight;
var broswerWidth = window.outerWidth;
var broswerHeight = window.outerHeight;
alert(pageWidth " " pageHeight);
alert(broswerWidth " " broswerHeight);
If (typeof pageWidth != "number") {
If (document.compatMode == "CSS1Compat") { //The standard mode
pageWidth = document.documentElement.clientWidth;
pageHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight;
} else {
pageWidth = document.body.clientWidth;
pageHeight = document.body.clientHeight;
}
})();
Get the position of the window: IE, chrome, Safari, use screenLeft, screenTop to get the position of the window from the left side of the screen and the top of the screen. Firefox does not support this attribute. Firefox uses screenXP and screenY to achieve the same effect.
(function btnFun() {
var leftPos = (typeof window.screenLeft == "number") ? window.screenLeft :
window.screenX;
var topPos = (typeof window.screenTop == "number") ? window.screenTop :
window.screenY;
alert(leftPos " " topPos);
//alert(window.screenLeft " " window.screenTop);
})();






