Data types
There are 5 simple data types (also called basic data types) in JavaScript: Undefined, Null, Boolean, Number and String. There is also a complex data type - Object. Object is essentially composed of a set of unordered name-value pairs.
typeof operator
Since JavaScript is loosely typed, there needs to be a way to detect the data type of a given variable - typeof is the operator responsible for providing provider-side information. Using the typeof operator on a value may return one of the following strings:
● "undefined" - if the value is undefined;
● "boolean" - if the value is Boolean Value;
● "string"--if the value is a string;
● "number"--if the value is a numeric value;
● "object"- —If the value is an object or null;
● "function"——If the value is a function;
Undefined type
The Undefined type has only one value, the special undefined. When a variable is declared using var but not initialized, the value of the variable is undefined, for example:
var message;
alert(message == undefined) //true
Null type
Null type is the second one with only one value Data type, this special value is null. From a logical point of view, the null value represents a null object pointer, and this is why "object" is returned when using the typeof operator to detect null, for example:
var car = null;
alert(typeof car); // "object"
If the defined variable is going to be used to save objects in the future, it is best to initialize the variable to null rather than to another value. In this way, you can know whether the corresponding variable has saved a reference to an object by directly detecting the null value, for example:
if(car != null)
{
//Perform certain operations on the car object
}
In fact, the undefined value is derived from the null value, so ECMA-262 stipulates that their equality test must return true.
alert(undefined == null); //true
Although null and undefined have this relationship, their uses are completely different. Under no circumstances is it necessary to explicitly set the value of a variable to undefined, but the same rule does not apply to null. In other words, as long as a variable that is intended to hold an object does not actually hold an object, you should explicitly let the variable hold a null value. Doing so not only reflects the convention of null as a null object pointer, but also helps to further distinguish null and undefined.
Boolean type
This type has only two literal values: true and false. These two values are not the same thing as numeric values, so true does not necessarily equal 1 and false does not necessarily equal 0.
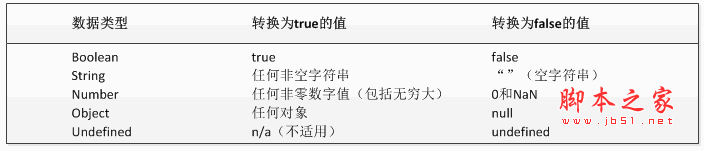
Although there are only two literal values of the Boolean type, all types of values in JavaScript have values equivalent to these two Boolean values. To convert a value to its corresponding Boolean value, you can call the type conversion function Boolean(), for example:
var message = 'Hello World';
var messageAsBoolean = Boolean(message);
In this example, the string message is converted to A Boolean value is stored in the messageAsBoolean variable. The Boolean() function can be called on a value of any data type and will always return a Boolean value. As for whether the returned value is true or false, it depends on the data type of the value to be converted and its actual value. The following table gives the conversion rules for various data types and their objects.

These conversion rules are very important to understand flow control statements (such as if statements) and automatically perform corresponding Boolean conversions, for example:
var message = 'Hello World';
if(message)
{
alert("Value is true");
}
Running this example will display a warning box because the string message is automatically converted to the corresponding Boolean value (true). Because of this automatically performed Boolean conversion, it is crucial to know exactly what variables are used in flow control statements.
Number type
This type is used to represent integers and floating-point values, and there is also a special value, NaN (Not a Number). This value is used to indicate that an operand that is supposed to return a value does not return a value (so that an error is not thrown). For example, in other programming languages, dividing any numeric value by zero results in an error that stops code execution. But in JavaScript, any value divided by 0 will return NaN, so it will not affect the execution of other code.
NaN itself has two extraordinary characteristics. First, any operation involving NaN (such as NaN/10) will return NaN, which may cause problems in multi-step calculations. Second, NaN is not equal to any value, including NaN itself. For example, the following code returns false.
alert(NaN == NaN); //false
There is an isNaN() function in JavaScript. This function accepts a parameter, which can be of any type, and the function will help us determine whether the parameter is "not value". After isNaN() receives a value, it will try to convert the value into a numeric value. Some values that are not numeric are converted directly to numeric values, such as the string "10" or a Boolean value. Any value that cannot be converted to a numeric value will cause this function to return true. For example:
alert(isNaN(NaN)); // true
alert(isNaN(10)); //false(10 is a numerical value)
alert(isNaN("10")); //false(may be converted to a numerical value 10)
alert( isNaN("blue")); //true (cannot be converted to a numerical value)
alert(isNaN(true)); //false (may be converted to a numerical value 1)
Yes 3 functions can convert non-numeric values into numeric values: Number(), parseInt() and parseFloat(). The first function, the conversion function Number(), can be used for any data type, while the other two functions are specifically used to convert strings into numbers. These three functions will return different results for the same input.
The conversion rules of the Number() function are as follows:
● If it is a Boolean value, true and false will be replaced with 1 and 0 respectively
● If it is a numeric value, it is simply passed in and returned
● If it is a null value, return 0
● If it is undefined, return NaN
● If it is a string, follow the following rules:
○ If the string only contains numbers, convert it to decimal Numeric value, that is, "1" will become 1, "123" will become 123, and "011" will become 11 (leading 0 is ignored)
○ If the string contains a valid floating point format, such as "1.1", then convert it to the corresponding floating point number (also, leading 0 will be ignored)
○ If the string contains a valid hexadecimal format, such as "0xf", then convert it to the same Decimal integer value of size
○ If the string is empty, convert it to 0
○ If the string contains characters other than the above format, convert it to NaN
● If If it is an object, call the valueOf() method of the object, and then convert the returned value according to the previous rules. If the result of the conversion is NaN, the toString() method of the object is called, and then the returned string value is converted according to the previous rules.
var num1 = Number("Hello World"); / /NaN
var num2 = Number(""); //0
var num3 = Number("000011"); //11
var num4 = Number(true); //1
Since the Number() function is complex and unreasonable when converting strings, the parseInt() function is more commonly used when processing integers. When the parseInt() function converts a string, it depends more on whether it conforms to the numerical pattern. It ignores leading spaces in the string until it finds the first non-space character. If the first string is not a numeric character or a negative sign, parseInt() will return NaN; that is, using parseInt() to convert an empty string will return NaN. If the first character is a numeric character, praseInt() will continue parsing the second character until all subsequent characters have been parsed or a non-numeric character is encountered. For example, "1234blue" will be converted to 1234, and "22.5" will be converted to 22, because the decimal point is not a valid numeric character.
If the first character in the string is a numeric character, parseInt() can also recognize various integer formats (i.e. decimal, octal, hexadecimal). In order to better understand the conversion rules of the parseInt() function, some examples are given below
var num1 = parseInt("1234blue"); //1234
var num2 = parseInt(""); //NaN
var num3 = parseInt("0xA"); //10 (Hex)
var num4 = parseInt("22.5"); //22
var num5 = parseInt("070"); //56 (octal)
var num6 = parseInt(" 70"); //70
var num7 = parseInt("10",2); //2 (parsed in binary)
var num8 = parseInt("10",8); //8(parsed in binary Octal parsing)
var num9 = parseInt("10",10); //10 (parsed in decimal format)
var num10 = parseInt("10",16); //16 (parsed in hexadecimal format) Parsing)
var num11 = parseInt("AF"); //56 (octal)
var num12 = parseInt("AF",16); //175
with parseInt () function is similar, parseFloat() also parses each character starting from the first character (position 0). And it is parsed until the end of the string, or until an invalid floating-point numeric character is encountered. That is to say, the first decimal point in the string is valid, but the second decimal point is invalid, so the string after it will be ignored. For example, "22.34.5" will be converted to 22.34.
The second difference between parseFloat() and parseInt() is that it always ignores leading zeros. Since parseFloat() values parse decimal values, it has no usage of specifying the base with the second parameter.
var num1 = parseFloat("1234blue"); // 1234
var num2 = parseFloat("0xA"); //0
var num3 = parseFloat("22.5"); //22.5
var num4 = parseFloat("22.34.5"); // 22.34
var num5 = parseFloat("0908.5"); //908.5
String type String type is used to represent zero or more 16-bit Unicode A character sequence composed of characters, that is, a string. Strings can be represented by single quotes (') or double quotes (").
var str1 = "Hello";
var str2 = 'Hello';
The length of any string can be obtained by accessing its length attribute
alert(str1.length); //Output 5
There are two ways to convert a value to a string. The first is to use the toString() method that is available on almost every value.
The code is as follows: var age = 11; var ageAsString = age.toString(); //String "11" var found = true;
var foundAsString = found.toString(); //String "true"
Numeric, Boolean, object and string values all have toString() method, but null. There is no such method for undefined values. In most cases, there is no need to pass parameters when calling the toString() method. However, when calling the toString() method of a value, you can pass a parameter:
Copy code
The code is as follows:
alert(num.toString(16)); //"a"
As you can see from this example, by specifying the base, the toString() method will change the output value. The value 10 can be converted into different numerical formats during output depending on the base.
When you don’t know whether the value to be converted is null or undefined, you can also use the conversion function String(). This function can convert any type of value into a string. The String() function follows the following conversion rules:
● If the value has a toString() method, call the method (without parameters) and return the corresponding result
● If the value is null, return "null"
● If the value is undefined, return "undefined"
var value1 = 10;
var value2 = true;
var value3 = null;
var value4;
alert(String(value1)); //"10"
alert(String( value2)); //"true"
alert(String(value3)); //"null"
alert(String(value4)); //"undefined"
Object type
An object is actually a collection of data and functions. Objects can be created by executing the new operator followed by the name of the type of object to be created. You can create a custom object by creating an instance of the Object type and adding properties and/or methods to it.
var o = new Object();
Each instance of Object has the following properties and methods:
● constructor - holds the function used to create the current object
● hasOwnProperty(propertyName) - used to check whether a given property is present exists in the current object instance (rather than in the instance's prototype). Among them, the property name (propertyName) as a parameter must be specified in the form of a string (for example: o.hasOwnProperty("name"))
● isPrototypeOf(object) - used to check whether the incoming object is another object Prototype of
● propertyIsEnumerable(propertyName) - Used to check whether a given property can be enumerated using a for-in statement
● toString() - Returns the string representation of the object
● valueOf( )—Returns a string, numeric, or Boolean representation of the object. Usually the same as the return value of the toString() method.