
This article is the editor’s daily collection of some classic js examples. I would like to share them on the Script Home platform for your reference!
Add events across browsers
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
Cross-browser removal event
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
Cross-browser blocking default behavior
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
|
Get target object across browsers
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
Get scroll bar position across browsers
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
|
Get the visual window size across browsers
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
|
js object impersonation
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
|
js asynchronous loading and synchronous loading
Asynchronous loading is also called non-blocking mode loading. While the browser is downloading js, it will also perform subsequent page processing.
In the script tag, use js to create a script element and insert it into the document. This is to load the js file asynchronously:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
Synchronized loading
Normally, synchronous loading is used by default. Such as:
1 |
|
Synchronous mode, also known as blocking mode, will prevent the browser from subsequent processing. Stops subsequent file parsing and execution, such as image rendering. The reason why the browser adopts the synchronous mode is because the loaded js file has default behaviors such as operating the dom, redirecting, and outputting the document, so synchronization is the safest.
Usually the js to be loaded is placed before the end tag of the body, so that the js can be loaded at the end of the page and minimizes blocking the rendering of the page. This will allow the page to be displayed first.
The synchronous loading process is a waterfall model, and the asynchronous loading process is a concurrent model.
js gets screen coordinates
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
|
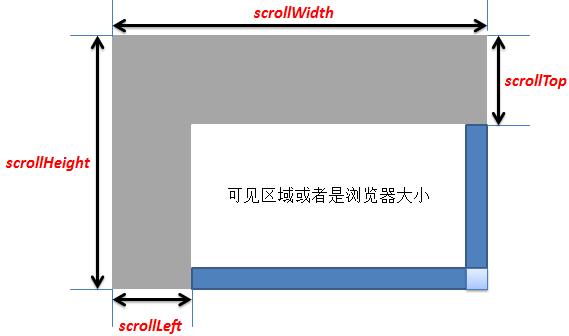
Note:
1. The documentElement property returns the root node of the document.
2.scrollTop() is the distance the scroll bar moves downward
3.document.documentElement.scrollTop refers to the vertical coordinate of the scroll bar
4.document.documentElement.clientHeight refers to the height of the visible area of the browser
-------------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
When the DTD has been declared:
1 |
|
如果在页面中添加这行标记的话
IE
document.body.clientWidth ==> BODY对象宽度
document.body.clientHeight ==> BODY对象高度
document.documentElement.clientWidth ==> 可见区域宽度
document.documentElement.clientHeight ==> 可见区域高度
Firefox
document.documentElement.scrollHeight ==> 浏览器所有内容高度
document.body.scrollHeight ==> 浏览器所有内容高度
document.documentElement.scrollTop ==> 浏览器滚动部分高度
document.body.scrollTop ==>始终为0
document.documentElement.clientHeight ==>浏览器可视部分高度
document.body.clientHeight ==> 浏览器所有内容高度
Chrome
document.documentElement.scrollHeight ==> 浏览器所有内容高度
document.body.scrollHeight ==> 浏览器所有内容高度
document.documentElement.scrollTop==> 始终为0
document.body.scrollTop==>浏览器滚动部分高度
document.documentElement.clientHeight ==> 浏览器可视部分高度
document.body.clientHeight ==> 浏览器所有内容高度
浏览器所有内容高度即浏览器整个框架的高度,包括滚动条卷去部分+可视部分+底部隐藏部分的高度总和
浏览器滚动部分高度即滚动条卷去部分高度即可视顶端距离整个对象顶端的高度。
综上
1、document.documentElement.scrollTop和document.body.scrollTop始终有一个为0,所以可以用这两个的和来求scrollTop
2、scrollHeight、clientHeight 在DTD已声明的情况下用documentElement,未声明的情况下用body
clientHeight
在IE和FF下,该属性没什么差别,都是指浏览器的可视区域,即除去浏览器的那些工具栏状态栏剩下的页面展示空间的高度。
PageX和clientX
PageX:鼠标在页面上的位置,从页面左上角开始,即是以页面为参考点,不随滑动条移动而变化
clientX:鼠标在页面上可视区域的位置,从浏览器可视区域左上角开始,即是以浏览器滑动条此刻的滑动到的位置为参考点,随滑动条移动 而变化.
可是悲剧的是,PageX只有FF特有,IE则没有这个,所以在IE下使用这个:
PageY=clientY+scrollTop-clientTop;(只讨论Y轴,X轴同理,下同)
scrollTop代表的是被浏览器滑动条滚过的长度
offsetX:IE特有,鼠标相比较于触发事件的元素的位置,以元素盒子模型的内容区域的左上角为参考点,如果有boder`,可能出现负值
只有clientX和screenX 皆大欢喜是W3C标准.其他的,都纠结了.
最给力的是,chrome和safari一条龙通杀!完全支持所有属性
js拖拽效果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
|
offsetTop 返回的是数字,而 style.top 返回的是字符串,除了数字外还带有单位:px。
js获取图片原始大小尺寸
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
js循环遍历数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
|
遍历二维数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
|
阻止表单重复提交
有两种方法可以解决:一是提交之后,立刻禁用点击按钮;第二种就是提交之后取消后续的表单提交操作。
document.getElementById("btn").disabled = true;//第一次提交后,将按钮禁用
这种方式只能用于通过提交按钮防止重复提交,还可以使用如下方式:
1 2 3 |
|
字符串部分
在字符串中查找子字符串
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
Number和Math部分
数字可以是一个直接量,也可以是一个对象,但是Math对象不同,他没有构造函数,并且其所有的属性和方法都是直接通过这个对象来访问的
把十进制转化为一个十六进制值
1 2 |
|
js中,十进制数字以0x开头,八进制数字总是以0开头
随进产生颜色
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
目前,所有浏览器都支持RGB表示法和十六进制表示法,除了IE7,它只支持十六进制表示法
在角度和弧度之间转换
var rad = degrees*(Math.PI/180);
var degrees = rad*(180/Math.PI);
数组部分
创建多维数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
|
排序数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
Array对象的sort方法会按照字母顺序来排序数组元素。对于数字,是按照字符编码的顺序进行排序
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
Date日期时间部分
js计算时间差
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
|
正则部分
js实现千分位分隔
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
|
js判断传入参数是否为质数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
|
js判断字符串出现最多的字符,并统计次数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
|
以上内容是小编日常收集整理的JavaScript 经典实例,非常具有参考价值,感兴趣的朋友收藏起来吧。
 How to learn go language from 0 basics
How to learn go language from 0 basics
 What currency is BTC?
What currency is BTC?
 Characteristics of relational databases
Characteristics of relational databases
 What is machine language
What is machine language
 c/s architecture and b/s architecture
c/s architecture and b/s architecture
 Reasons why ping fails
Reasons why ping fails
 What is a servo motor
What is a servo motor
 The difference between win10 home version and professional version
The difference between win10 home version and professional version
 How do mysql and redis ensure double-write consistency?
How do mysql and redis ensure double-write consistency?




