JavaScript Document Object Model-DOM extension
According to W3C's requirements for DOM, the browser can add properties and methods to it on its own to enhance its functionality. Some of the new features are for backward compatibility, while others are added based on developer feedback on common issues.
Presentation mode
Starting from IE6, IE browser distinguishes between standard mode and mixed mode, which requires us to distinguish which mode the browser is in when using it. IE adds an attribute called compatMode to the document object. The only task of this attribute is to identify what mode the browser is in. For example, in the following example, if it is standard mode, the value of document.compatMode is equal to "CSS1Compat"; if it is mixed mode, the value of document.compatMode is equal to "BackCompat".
if(document.compatMode == "CSS1Compat"){
alert("标准模式");
}else{
alert("混杂模式");
}After IE, Firefox, Chrome and Opera browsers have also implemented this attribute. Safari browser implements document.compatMode property starting from version 3.1.
Later, IE8 introduced a new property called documentMode for the document object. Its usage is shown below.
if(document.compatMode > 7){
alert("IE8+ 标准模式");
}This is because IE8 has 3 different rendering modes, and this attribute is introduced precisely to distinguish these modes. If the value of this attribute is 5, it indicates mixed mode (ie IE5 mode), if the value is 7, it indicates IE7 emulation mode, and if it is 8, it indicates IE8 standard mode.
contains() method
When we operate DOM, we often need to determine whether a given node is a descendant node of another node. IE browser first introduced a contains() method, which can obtain this information without traversing the entire DOM tree. The contains() method should be called on the ancestor node as the starting point of the search. The method receives one parameter, which is the descendant node to be detected. If the node passed in is a descendant of the current node, it will return true, otherwise it will return false. For example
alert(document.documentElement.contains(document.body)); //true
The above example tests whether the
element is a descendant of the element. If it is a properly formatted HTML page, then it will return true.IE, Safari3+, Opera8+ and Chrome browsers all support the contains() method.
Firefox browser does not support the contains() method, but Firefox implements an alternative method in DOM3 level: compareDocumentPosition() method. (Opera9.5+ browsers also support this method). This method is used to determine the relationship between two nodes and returns a bitmask (bitmark) representing the relationship. The values for this bitmask are listed in the following table.

If you need to imitate the contains() method, then you should pay attention to mask 16. You can perform a bitwise AND operation on the results of the compareDocumentPosition() method to determine whether the reference node (the current node on which the compareDocumentPosition() method was called) contains the given node (the node passed in as an argument). For example, the following example:
var result = document.documentElement.compareDocumentPosition(document.body);
console.info("result="+result);
console.info("按位与操作后的布尔值结果为:"+!!(result & 16));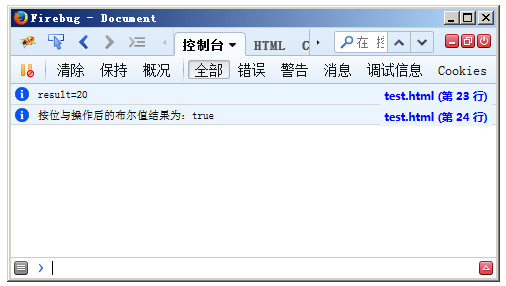
After executing the compareDocumentPosition() method in the above code, the result obtained is 20, which means "backward" 4 and "included" of 16. Then performing a bitwise AND operation on mask 16 returns a non-zero value. The two logical NOT operators are used to convert a numeric value into a Boolean value type.
We can write a general contains() function through browser capability detection.
/*********************************************************/
/* 浏览器通用contains()方法
/* 参数:refNode - 参考节点 */
/* 参数:otherNode - 要检测的节点 */
/* 返回值: refNode包含otherNode是返回true,否则返回false*/
/*********************************************************/
function contains(refNode,otherNode){
if(typeof refNode.contains == "function"){
return refNode.contains(otherNode);
}else if(typeof refNode.compareDocumentPosition == "function"){
return !!(refNode.compareDocumentPosition(otherNode) & 16);
}else{
var node = otherNode.parentNode;
do{
if (node === refNode) {
return true;
}else{
node = node.parentNode;
}
}while(node !== null);
return false;
}
}This general contains() function uses 3 methods to determine whether a node is a descendant node of another node. The first parameter of the function is the reference node, and the second parameter is the node to be detected.
In the function body, first check whether the contains() method exists in refNode, and then check whether there is a compareDocumentPosition() method. The last step of the function is to traverse the DOM tree upwards starting from otherNode, recursively obtain the parentNode and check whether Equal to refNode. At the top of the document tree, the value of parentNode is equal to null, and the loop ends.
The above is the content of JavaScript Document Object Model-DOM extension. For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (www.php.cn)!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript is a programming language widely used in web development, while WebSocket is a network protocol used for real-time communication. Combining the powerful functions of the two, we can create an efficient real-time image processing system. This article will introduce how to implement this system using JavaScript and WebSocket, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to clarify the requirements and goals of the real-time image processing system. Suppose we have a camera device that can collect real-time image data




