 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Detailed explanation of React Native's prop-types for attribute confirmation
Detailed explanation of React Native's prop-types for attribute confirmation
Detailed explanation of React Native's prop-types for attribute confirmation
This article mainly introduces the detailed explanation of property confirmation using prop-types in React Native. The editor thinks it is quite good, so I will share it with you now and give it as a reference. Let’s follow the editor to take a look, I hope it can help everyone.
The role of attribute confirmation
Components created using React Native can be reused, so the components we develop may be used by other colleagues in the project team . But others may not be familiar with this component and often forget to use certain attributes, or the data types passed by some attributes are incorrect.
So when we develop a React Native custom component, we can declare which properties the component requires through property confirmation. In this way, if the corresponding attributes are not provided when calling this custom component, a warning message will pop up on the mobile phone and debugging tools to inform the developer what attributes the component requires.
React Native has been upgraded to 0.51.0. The version upgrade is very fast, but there are also some problems with old projects. The most common problem is that attributes cannot be found. For example:
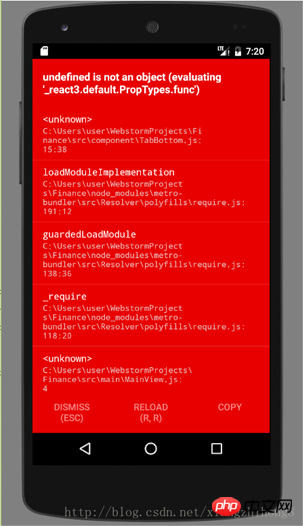
The main reason is that with the upgrade of React Native, the system has abandoned a lot of things. In the past, we could directly use React.PropTypes to confirm properties, but this automatically React v15.5 has been removed and replaced with the prop-types library
Attribute confirmation
The role of attribute confirmation
Components created using React Native can be reused, so the components we develop may be used by other colleagues in the project team. But others may not be familiar with this component and often forget to use certain attributes, or the data types passed by some attributes are wrong. Therefore, when we develop a React Native custom component, we can use property confirmation to declare which properties the component requires.
Note: In order to ensure that React Native code runs efficiently, attribute confirmation is only valid in the development environment and will not be checked when the officially released App is run.
prop-types library usage
is similar to other third-party libraries. To install prop-types, first enter the project root directory and execute the following code to install prop-types. Library:
npm install --save prop-types
Then introduce it where you need to use the PropTypes attribute:
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
Example
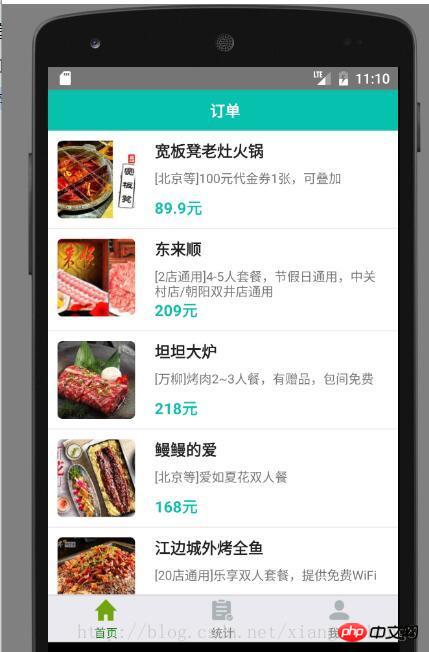
For example, we write an example of a navigation bar, the effect is as follows:
import React, {
Component
} from 'react'
import {
StyleSheet,
View,
Animated,
Image,
TouchableOpacity,
TouchableNativeFeedback,
Platform
} from 'react-native'
import px2dp from '../utils/Utils'
import Icon from 'react-native-vector-icons/Ionicons'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
export default class NavBar extends Component{
static propTypes = {
title: PropTypes.string,
leftIcon: PropTypes.string,
rightIcon: PropTypes.string,
leftPress: PropTypes.func,
rightPress: PropTypes.func,
style: PropTypes.object
}
static topbarHeight = (Platform.OS === 'ios' ? 64 : 44)
renderBtn(pos){
let render = (obj) => {
const { name, onPress } = obj
if(Platform.OS === 'android'){
return (
)
}else{
return (
)
}
}
if(pos == "left"){
if(this.props.leftIcon){
return render({
name: this.props.leftIcon,
onPress: this.props.leftPress
})
}else{
// return ()
return ()
}
}else if(pos == "right"){
if(this.props.rightIcon){
return render({
name: this.props.rightIcon,
onPress: this.props.rightPress
})
}else{
return ()
}
}
}
render(){
return(
{this.renderBtn("left")}
{this.props.title}
{this.renderBtn("right")}
)
}
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
topbar: {
height: NavBar.topbarHeight,
backgroundColor: "#06C1AE",
flexDirection: 'row',
justifyContent: 'space-between',
alignItems: 'center',
paddingTop: (Platform.OS === 'ios') ? 20 : 0,
paddingHorizontal: px2dp(10)
},
btn: {
width: 22,
height: 22,
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center'
},
title:{
color: "#fff",
fontWeight: "bold",
fontSize: px2dp(16),
marginLeft: px2dp(5),
}
}); Syntax
1, requires the attribute to be the specified JavaScript basic type. For example:
Properties: PropTypes.array,
Properties: PropTypes.bool,
Properties: PropTypes.func,
Properties: PropTypes.number,
Properties: PropTypes.object,
Attribute: PropTypes.string,
2, requires the attribute to be a renderable node. For example:
Attribute: PropTypes.node,
3, requires the attribute to be a certain React element. For example:
Attribute: PropTypes.element,
4, requires the attribute to be an instance of a specified class. For example:
Attribute: PropTypes.instanceOf(NameOfAClass),
5, requires the attribute value to be certain values. For example:
Attribute: PropTypes.oneOf(['value1', 'value2']),
6, the required attribute can be any one of the specified types. For example:
Attribute: PropTypes.oneOfType([
PropTypes.bool,
PropTypes.number,
PropTypes.instanceOf(NameOfAClass),
])
7, requires the attribute to be an array of the specified type. For example:
Property: PropTypes.arrayOf(PropTypes.number),
8, the required property is an object with specific member variables. For example:
Attributes: PropTypes.objectOf(PropTypes.number),
9, the required attribute is an object with a specified composition method. For example:
Attribute: PropTypes.shape({
color: PropTypes.string,
fontSize: PropTypes.number,
}),
10, Properties can be of any type. For example:
Properties: PropTypes.any
Declare a property as required
Use the keyword isRequired to declare that it is required.
Properties: PropTypes.array.isRequired,
Properties: PropTypes.any.isRequired,
Properties: PropTypes.instanceOf(NameOfAClass).isRequired,
Related recommendations :
Detailed explanation of the communication instance between react native and webview
Detailed explanation of the React Native open source time and date selector component
Introduction to the ref attribute in the View component in react native
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of React Native's prop-types for attribute confirmation. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Guide to React front-end and back-end separation: How to achieve decoupling and independent deployment of front-end and back-end
Sep 28, 2023 am 10:48 AM
Guide to React front-end and back-end separation: How to achieve decoupling and independent deployment of front-end and back-end
Sep 28, 2023 am 10:48 AM
React front-end and back-end separation guide: How to achieve front-end and back-end decoupling and independent deployment, specific code examples are required In today's web development environment, front-end and back-end separation has become a trend. By separating front-end and back-end code, development work can be made more flexible, efficient, and facilitate team collaboration. This article will introduce how to use React to achieve front-end and back-end separation, thereby achieving the goals of decoupling and independent deployment. First, we need to understand what front-end and back-end separation is. In the traditional web development model, the front-end and back-end are coupled
 How to build a reliable messaging app with React and RabbitMQ
Sep 28, 2023 pm 08:24 PM
How to build a reliable messaging app with React and RabbitMQ
Sep 28, 2023 pm 08:24 PM
How to build a reliable messaging application with React and RabbitMQ Introduction: Modern applications need to support reliable messaging to achieve features such as real-time updates and data synchronization. React is a popular JavaScript library for building user interfaces, while RabbitMQ is a reliable messaging middleware. This article will introduce how to combine React and RabbitMQ to build a reliable messaging application, and provide specific code examples. RabbitMQ overview:
 React Router User Guide: How to implement front-end routing control
Sep 29, 2023 pm 05:45 PM
React Router User Guide: How to implement front-end routing control
Sep 29, 2023 pm 05:45 PM
ReactRouter User Guide: How to Implement Front-End Routing Control With the popularity of single-page applications, front-end routing has become an important part that cannot be ignored. As the most popular routing library in the React ecosystem, ReactRouter provides rich functions and easy-to-use APIs, making the implementation of front-end routing very simple and flexible. This article will introduce how to use ReactRouter and provide some specific code examples. To install ReactRouter first, we need
 PHP, Vue and React: How to choose the most suitable front-end framework?
Mar 15, 2024 pm 05:48 PM
PHP, Vue and React: How to choose the most suitable front-end framework?
Mar 15, 2024 pm 05:48 PM
PHP, Vue and React: How to choose the most suitable front-end framework? With the continuous development of Internet technology, front-end frameworks play a vital role in Web development. PHP, Vue and React are three representative front-end frameworks, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. When choosing which front-end framework to use, developers need to make an informed decision based on project needs, team skills, and personal preferences. This article will compare the characteristics and uses of the three front-end frameworks PHP, Vue and React.
 Integration of Java framework and front-end React framework
Jun 01, 2024 pm 03:16 PM
Integration of Java framework and front-end React framework
Jun 01, 2024 pm 03:16 PM
Integration of Java framework and React framework: Steps: Set up the back-end Java framework. Create project structure. Configure build tools. Create React applications. Write REST API endpoints. Configure the communication mechanism. Practical case (SpringBoot+React): Java code: Define RESTfulAPI controller. React code: Get and display the data returned by the API.
 How to use React to develop a responsive backend management system
Sep 28, 2023 pm 04:55 PM
How to use React to develop a responsive backend management system
Sep 28, 2023 pm 04:55 PM
How to use React to develop a responsive backend management system. With the rapid development of the Internet, more and more companies and organizations need an efficient, flexible, and easy-to-manage backend management system to handle daily operations. As one of the most popular JavaScript libraries currently, React provides a concise, efficient and maintainable way to build user interfaces. This article will introduce how to use React to develop a responsive backend management system and give specific code examples. Create a React project first
 Vue.js vs. React: Project-Specific Considerations
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Vue.js vs. React: Project-Specific Considerations
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Vue.js is suitable for small and medium-sized projects and fast iterations, while React is suitable for large and complex applications. 1) Vue.js is easy to use and is suitable for situations where the team is insufficient or the project scale is small. 2) React has a richer ecosystem and is suitable for projects with high performance and complex functional needs.
 What closures does react have?
Oct 27, 2023 pm 03:11 PM
What closures does react have?
Oct 27, 2023 pm 03:11 PM
React has closures such as event handling functions, useEffect and useCallback, higher-order components, etc. Detailed introduction: 1. Event handling function closure: In React, when we define an event handling function in a component, the function will form a closure and can access the status and properties within the component scope. In this way, the state and properties of the component can be used in the event processing function to implement interactive logic; 2. Closures in useEffect and useCallback, etc.





