Vuex is a state management pattern developed specifically for Vue.js applications. It uses centralized storage to manage the state of all components of the application, and uses corresponding rules to ensure that the state changes in a predictable way. Vuex is also integrated into Vue's official debugging tool devtools extension, which provides advanced debugging functions such as zero-configuration time-travel debugging, state snapshot import and export, etc. This article mainly introduces a brief discussion of Vuex state management (Family Bucket). The editor thinks it is quite good, so I will share it with you now and give it as a reference. Let’s follow the editor to take a look, I hope it can help everyone.
The above is the introduction of vuex in the official document of vuex. The official document explains the usage of vuex in detail. I won’t go into details about the usage of vuex here. The purpose of writing this blog is just to help some students understand and get started with vuex faster.
1. Install
$ npm install vuex --save
Copy after login
2. Reference store.js in main.js main entrance js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
import store from './vuex/store' //引用store.js
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止在启动时生成生产提示
//vue实例
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store, //把store挂在到vue的实例下面
template: '<App/>',
components: { App }
})Copy after login
3. Reference Vuex
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex) //注册Vuex
// 定义常量 如果访问他的话,就叫访问状态对象
const state = {
count: 1
}
// mutations用来改变store状态, 如果访问他的话,就叫访问触发状态
const mutations = {
//这里面的方法是用 this.$store.commit('jia') 来触发
jia(state){
state.count ++
},
jian(state){
state.count --
},
}
//暴露到外面,让其他地方的引用
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations
})Copy after login
in store.js
4. Use in the vue component
Use the $store.commit('jia') area to trigger the addition and subtraction methods under mutations
<template>
<p class="hello">
<h1>Hello Vuex</h1>
<h5>{{$store.state.count}}</h5>
<p>
<button @click="$store.commit('jia')">+</button>
<button @click="$store.commit('jian')">-</button>
</p>
</p>
</template>
<!-- 加上scoped是css只在这个组件里面生效,为了不影响全局样式 -->
<style scoped>
h5{
font-size: 20px;
color: red;
}
</style>Copy after login
5. View the demo
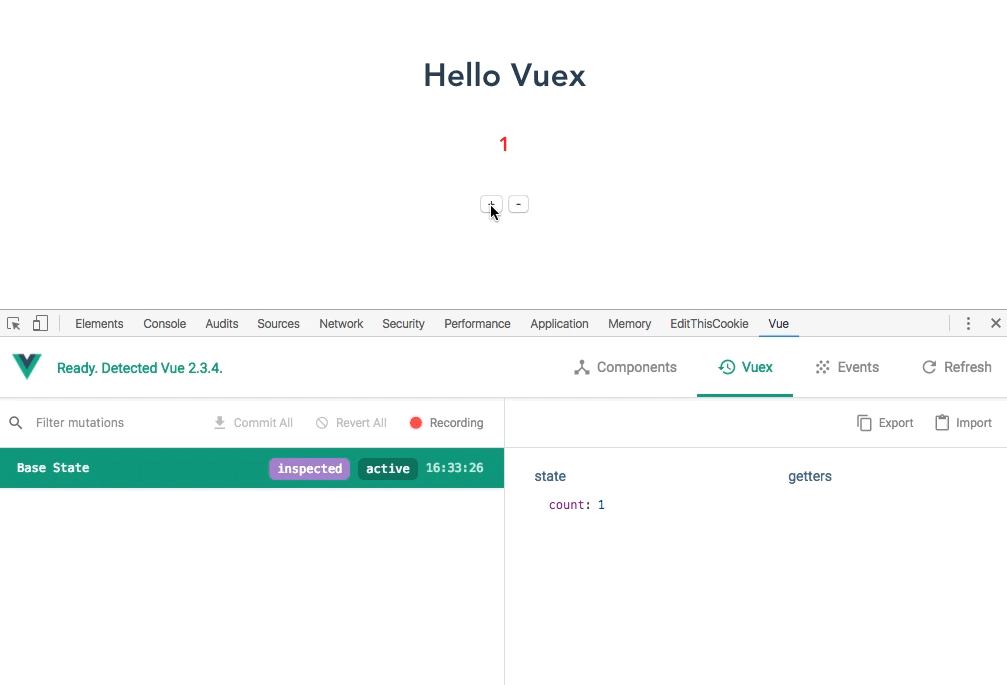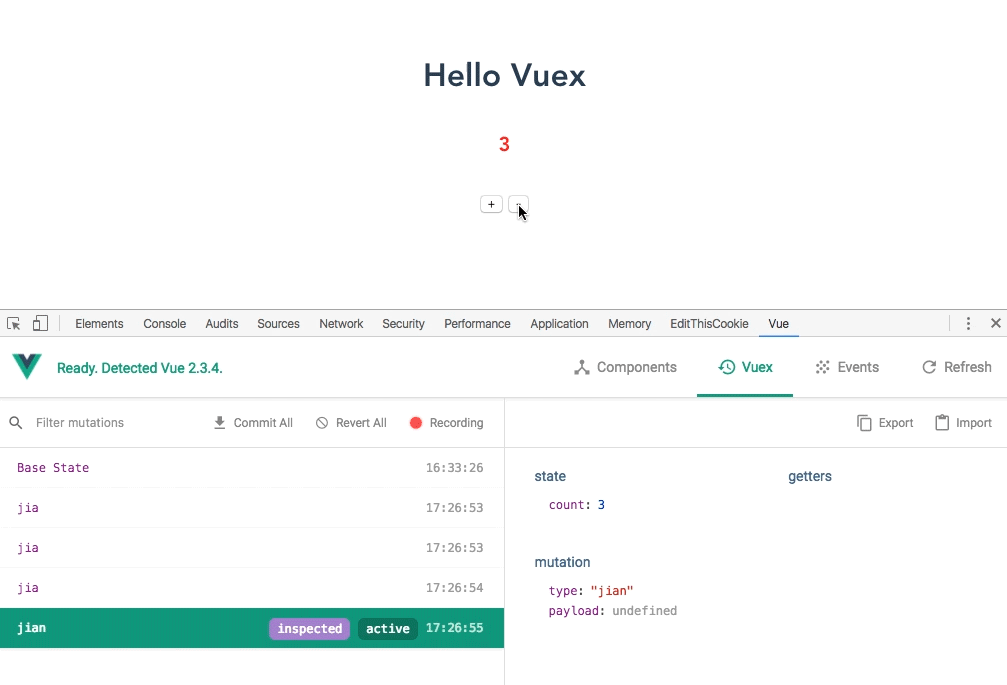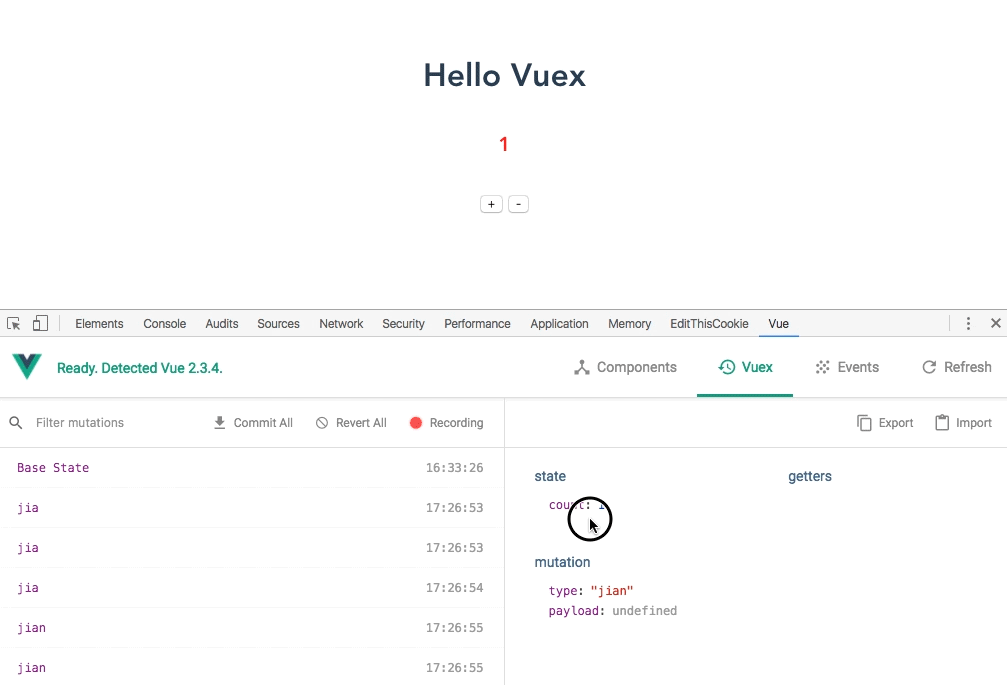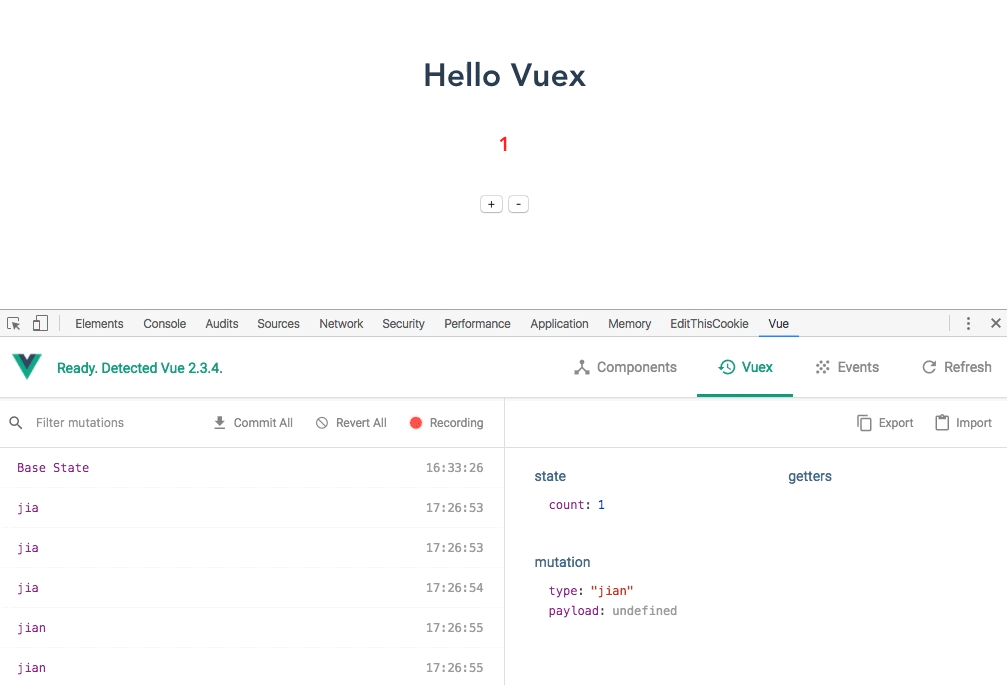
6. State access state object
Use computed calculation
<template>
<p class="hello">
<h1>Hello Vuex</h1>
<h5>{{count}}</h5>
<p>
<button @click="$store.commit('jia')">+</button>
<button @click="$store.commit('jian')">-</button>
</p>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
export default{
name:'hello', //写上name的作用是,如果你页面报错了,他会提示你是那个页面报的错,很实用
// 方法一
// computed: {
// count(){
// return this.$store.state.count + 6
// }
// }
// 方法二 需要引入外部 mapState
computed:mapState({
count:state => state.count + 10
})
// ECMA5用法
// computed:mapState({
// count:function(state){
// return state.count
// }
// })
//方法三
// computed: mapState([
// 'count'
// ])
}
</script>Copy after login
7. Mutations trigger state (synchronization state)
<template>
<p class="hello">
<h1>Hello Vuex</h1>
<h5>{{count}}</h5>
<p>
<button @click="jia">+</button>
<button @click="jian">-</button>
</p>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState,mapMutations} from 'vuex'
export default{
name:'hello', //写上name的作用是,如果你页面报错了,他会提示你是那个页面报的错,很实用
//方法三
computed: mapState([
'count'
]),
methods:{
...mapMutations([
'jia',
'jian'
])
}
}
</script>Copy after login
8. Getters computed properties
Getters cannot use arrow functions, which will change the point of this
Add getters in store.js
// 计算
const getters = {
count(state){
return state.count + 66
}
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations,
getters
})
//count的参数就是上面定义的state对象
//getters中定义的方法名称和组件中使用的时候一定是一致的,定义的是count方法,使用的时候也用count,保持一致。
组件中使用
<script>
import {mapState,mapMutations,mapGetters} from 'vuex'
export default{
name:'hello',
computed: {
...mapState([
'count'
]),
...mapGetters([
'count'
])
},
methods:{
...mapMutations([
'jia',
'jian'
])
}
}
</script>Copy after login
9. actions (asynchronous state)
Add actions in store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 定义常量
const state = {
count: 1
}
// mutations用来改变store状态 同步状态
const mutations = {
jia(state){
state.count ++
},
jian(state){
state.count --
},
}
// 计算属性
const getters = {
count(state){
return state.count + 66
}
}
// 异步状态
const actions = {
jiaplus(context){
context.commit('jia') //调用mutations下面的方法
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('jian')
},2000)
alert('我先被执行了,然后两秒后调用jian的方法')
},
jianplus(context){
context.commit('jian')
}
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations,
getters,
actions
})Copy after login
Use in components
<template>
<p class="hello">
<h1>Hello Vuex</h1>
<h5>{{count}}</h5>
<p>
<button @click="jia">+</button>
<button @click="jian">-</button>
</p>
<p>
<button @click="jiaplus">+plus</button>
<button @click="jianplus">-plus</button>
</p>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState,mapMutations,mapGetters,mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default{
name:'hello',
computed: {
...mapState([
'count'
]),
...mapGetters([
'count'
])
},
methods:{
// 这里是数组的方式触发方法
...mapMutations([
'jia',
'jian'
]),
// 换一中方式触发方法 用对象的方式
...mapActions({
jiaplus: 'jiaplus',
jianplus: 'jianplus'
})
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
h5{
font-size: 20px;
color: red;
}
</style>Copy after login
10. modules module
Applicable to Use it when a very large project has a lot of status and is easy to manage
Modify store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const state = {
count: 1
}
const mutations = {
jia(state){
state.count ++
},
jian(state){
state.count --
},
}
const getters = {
count(state){
return state.count + 66
}
}
const actions = {
jiaplus(context){
context.commit('jia') //调用mutations下面的方法
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('jian')
},2000)
alert('我先被执行了,然后两秒后调用jian的方法')
},
jianplus(context){
context.commit('jian')
}
}
//module使用模块组的方式 moduleA
const moduleA = {
state,
mutations,
getters,
actions
}
// 模块B moduleB
const moduleB = {
state: {
count:108
}
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB,
}
})Copy after login

Related recommendations:
Example sharing Vue Family Bucket practical project summary
Using React Family Bucket to build a backend management system example detailed explanation
Vue2.0 Web application developed by FamilyBucket (refer to Wuji APP)
The above is the detailed content of About Vuex's family bucket status management. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!































![[Web front-end] Node.js quick start](https://img.php.cn/upload/course/000/000/067/662b5d34ba7c0227.png)



