Detailed examples of how to use Generator in JavaScript
This article mainly shares with you how to use Generator in JavaScript. Generator is a very powerful syntax, but its use is not widely used (see the survey on twitter below!). Why is this so? Compared with async/await, its use is more complex and debugging is not easy (most cases are back to the past). Even though we can obtain a similar experience in a very simple way, people generally prefer async/await .
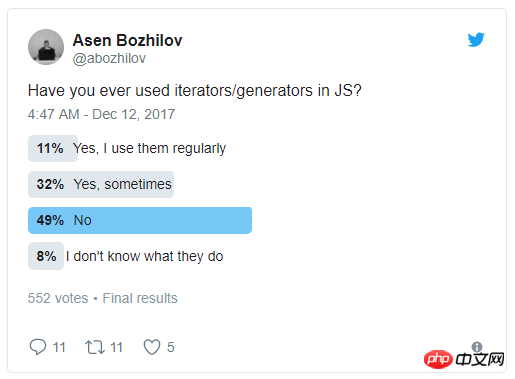
However, Generator allows us to iterate through our own code via the yield keyword! This is a super powerful syntax and we can actually manipulate the execution! Starting with the less obvious cancellation operation, let's start with the synchronization operation.
I created a code repository for the functions mentioned in the article - github.com/Bloomca/obs...
Batch processing (or plan)
Executing the Generator function will Returns a traverser object, which means that we can traverse synchronously through it. Why do we want to do this? The reason may be to implement batch processing. Imagine we need to download 1000 items and display them row by row in a table (don't ask me why, assuming we don't use a framework). While there's nothing wrong with showing them off right away, sometimes that might not be the best solution — maybe your MacBook Pro can handle it with ease, but the average person's computer can't (let alone a phone). So, this means we need to delay execution somehow.
Please note that this example is about performance optimization. There is no need to do this before you encounter this problem - premature optimization is the root of all evil!
// 最初的同步实现版本
function renderItems(items) {
for (item of items) {
renderItem(item);
}
}
// 函数将由我们的执行器遍历执行
// 实际上,我们可以用相同的同步方式来执行它!
function* renderItems(items) {
// 我使用 for..of 遍历方法来避免新函数的产生
for (item of items) {
yield renderItem(item);
}
}There is no difference, right? ? Well, the difference here is that now we can run this function differently without changing the source code. Actually, as I mentioned before, there is no need to wait, we can do it synchronously. So, let’s tweak our code. How about adding a delay of 4 ms (one heartbeat in the JavaScript VM) after each yield? We have 1000 items and rendering will take 4 seconds - not bad, assuming I want to render in 2 seconds, the easy way to think of it is to render 2 at a time. Suddenly the solution using Promises becomes more complicated - we have to pass another parameter: the number of items to render each time. Through our executor, we still need to pass this parameter, but the benefit is that it has absolutely no effect on our renderItems method.
function runWithBatch(chunk, fn, ...args) {
const gen = fn(...args);
let num = 0;
return new Promise((resolve, promiseReject) => {
callNextStep();
function callNextStep(res) {
let result;
try {
result = gen.next(res);
} catch (e) {
return reject(e);
}
next(result);
}
function next({ done, value }) {
if (done) {
return resolve(value);
}
// every chunk we sleep for a tick
if (num++ % chunk === 0) {
return sleep(4).then(proceed);
} else {
return proceed();
}
function proceed() {
return callNextStep(value);
}
}
});
}
// 第一个参数 —— 每批处理多少个项目
const items = [...];
batchRunner(2, function*() {
for (item of items) {
yield renderItem(item);
}
});As you can see, we can easily change the number of items per batch, regardless of the executor, and go back to normal synchronous execution - all without affecting our renderItems method.
Cancel
Let’s consider the traditional function - Cancel. I have talked about it in detail in my article Promises cancellation in general (Translation: How to cancel your Promise? ). So I'll use some of this code:
function runWithCancel(fn, ...args) {
const gen = fn(...args);
let cancelled, cancel;
const promise = new Promise((resolve, promiseReject) => {
// define cancel function to return it from our fn
// 定义 cancel 方法,并返回它
cancel = () => {
cancelled = true;
reject({ reason: 'cancelled' });
};
onFulfilled();
function onFulfilled(res) {
if (!cancelled) {
let result;
try {
result = gen.next(res);
} catch (e) {
return reject(e);
}
next(result);
return null;
}
}
function onRejected(err) {
var result;
try {
result = gen.throw(err);
} catch (e) {
return reject(e);
}
next(result);
}
function next({ done, value }) {
if (done) {
return resolve(value);
}
// 假设我们总是接收 Promise,所以不需要检查类型
return value.then(onFulfilled, onRejected);
}
});
return { promise, cancel };
}The best part here is that we can cancel all requests that haven't had a chance to execute yet (we can also pass an object parameter like AbortController to our executor, so it can even Cancel the current request!), and we have not modified a single line of code in our business logic.
Pause/Resume
Another special need may be the pause/resume functionality. Why do you want this feature? Imagine we're rendering 1000 rows of data, and it's very slow, and we want to give the user the ability to pause/resume rendering so they can stop all the background work and read what has been downloaded. let's start!
// 实现渲染的方法还是一样的
function* renderItems() {
for (item of items) {
yield renderItem(item);
}
}
function runWithPause(genFn, ...args) {
let pausePromiseResolve = null;
let pausePromise;
const gen = genFn(...args);
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
onFulfilledWithPromise();
function onFulfilledWithPromise(res) {
if (pausePromise) {
pausePromise.then(() => onFulfilled(res));
} else {
onFulfilled(res);
}
}
function onFulfilled(res) {
let result;
try {
result = gen.next(res);
} catch (e) {
return reject(e);
}
next(result);
return null;
}
function onRejected(err) {
var result;
try {
result = gen.throw(err);
} catch (e) {
return reject(e);
}
next(result);
}
function next({ done, value }) {
if (done) {
return resolve(value);
}
// 假设我们总是接收 Promise,所以不需要检查类型
return value.then(onFulfilledWithPromise, onRejected);
}
});
return {
pause: () => {
pausePromise = new Promise(resolve => {
pausePromiseResolve = resolve;
});
},
resume: () => {
pausePromiseResolve();
pausePromise = null;
},
promise
};
}Calling this executor can return us an object with pause/resume functions, all of which can be easily obtained, or use our previous business code! So, if you have a lot of "heavy" request chains that take a long time, and you want to provide pause/resume functionality to your users, feel free to implement this executor in your code.
Error handling
We have a mysterious onRejected call, which is the topic of our discussion in this part. If we use normal async/await or Promise chaining, we will handle errors through try/catch statements, which is difficult to handle without adding a lot of logic code. Normally, if we need to handle an error in some way (like retrying), we just do it inside a Promise, which will call back on itself, possibly back to the same point again. And, this is not yet a universal solution - sadly, not even Generator can help us here. We discovered a limitation of Generator - although we can control the flow of execution, we cannot move the body of the Generator function; so we cannot step back and re-execute our command. A possible solution is to use the command pattern, which tells us the data structure of the yield result - should be all the information we need to execute this command so that we can execute it again. Therefore, our method needs to be changed to:
function* renderItems() {
for (item of items) {
// 我们需要将所有东西传递出去:
// 方法, 内容, 参数
yield [renderItem, null, item];
}
}正如你所看到的,这使得我们不清楚发生了什么 —— 所以,也许最好是写一些 wrapWithRetry 方法,它会检查 catch 代码块中的错误类型并再次尝试。但是我们仍然可以做一些不影响我们功能的事情。例如,我们可以增加一个关于忽略错误的策略 —— 在 async/await 中我们不得不使用 try/catch 包装每个调用,或者添加空的 .catch(() => {}) 部分。有了 Generator,我们可以写一个执行器,忽略所有的错误。
function runWithIgnore(fn, ...args) {
const gen = fn(...args);
return new Promise((resolve, promiseReject) => {
onFulfilled();
function onFulfilled(res) {
proceed({ data: res });
}
// 这些是 yield 返回的错误
// 我们想忽略它们
// 所以我们像往常一样做,但不去传递出错误
function onRejected(error) {
proceed({ error });
}
function proceed(data) {
let result;
try {
result = gen.next(data);
} catch (e) {
// 这些错误是同步错误(比如 TypeError 等)
return reject(e);
}
// 为了区分错误和正常的结果
// 我们用它来执行
next(result);
}
function next({ done, value }) {
if (done) {
return resolve(value);
}
// 假设我们总是接收 Promise,所以不需要检查类型
return value.then(onFulfilled, onRejected);
}
});
}关于 async/await
Async/await 是现在的首选语法(甚至 co 也谈到了它 ),这也是未来。但是,Generator 也在 ECMAScript 标准内,这意味着为了使用它们,除了写几个工具函数,你不需要任何东西。我试图向你们展示一些不那么简单的例子,这些实例的价值取决于你的看法。请记住,没有那么多人熟悉 Generator,并且如果在整个代码库中只有一个地方使用它们,那么使用 Promise 可能会更容易一些 —— 但是另一方面,通过 Generator 某些问题可以被优雅和简洁的处理。
相关推荐:
Promise,Generator(生成器),async(异步)函数的用法
The above is the detailed content of Detailed examples of how to use Generator in JavaScript. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 Recommended: Excellent JS open source face detection and recognition project
Apr 03, 2024 am 11:55 AM
Recommended: Excellent JS open source face detection and recognition project
Apr 03, 2024 am 11:55 AM
Face detection and recognition technology is already a relatively mature and widely used technology. Currently, the most widely used Internet application language is JS. Implementing face detection and recognition on the Web front-end has advantages and disadvantages compared to back-end face recognition. Advantages include reducing network interaction and real-time recognition, which greatly shortens user waiting time and improves user experience; disadvantages include: being limited by model size, the accuracy is also limited. How to use js to implement face detection on the web? In order to implement face recognition on the Web, you need to be familiar with related programming languages and technologies, such as JavaScript, HTML, CSS, WebRTC, etc. At the same time, you also need to master relevant computer vision and artificial intelligence technologies. It is worth noting that due to the design of the Web side
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 Essential tools for stock analysis: Learn the steps to draw candle charts with PHP and JS
Dec 17, 2023 pm 06:55 PM
Essential tools for stock analysis: Learn the steps to draw candle charts with PHP and JS
Dec 17, 2023 pm 06:55 PM
Essential tools for stock analysis: Learn the steps to draw candle charts in PHP and JS. Specific code examples are required. With the rapid development of the Internet and technology, stock trading has become one of the important ways for many investors. Stock analysis is an important part of investor decision-making, and candle charts are widely used in technical analysis. Learning how to draw candle charts using PHP and JS will provide investors with more intuitive information to help them make better decisions. A candlestick chart is a technical chart that displays stock prices in the form of candlesticks. It shows the stock price
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 PHP and JS Development Tips: Master the Method of Drawing Stock Candle Charts
Dec 18, 2023 pm 03:39 PM
PHP and JS Development Tips: Master the Method of Drawing Stock Candle Charts
Dec 18, 2023 pm 03:39 PM
With the rapid development of Internet finance, stock investment has become the choice of more and more people. In stock trading, candle charts are a commonly used technical analysis method. It can show the changing trend of stock prices and help investors make more accurate decisions. This article will introduce the development skills of PHP and JS, lead readers to understand how to draw stock candle charts, and provide specific code examples. 1. Understanding Stock Candle Charts Before introducing how to draw stock candle charts, we first need to understand what a candle chart is. Candlestick charts were developed by the Japanese
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We






