
This time I will bring you jQuery to implement the recursive infinite layer function. What are the precautions for jQuery to implement the recursive infinite layer function? The following is a practical case, let's take a look.
Nagging
Two days ago, a friend told me that he wanted a ztree search function, and I slapped him in the face: This kind of Are there too many methods that countless predecessors have failed to do? I went to find it myself, I was very busy~ Then I squatted silently and wrote the zTree search method. why? Because I said, "It's impossible to find it. Many people must have done it countless times. If you can't find it, I'll write it to you and ask you to have lunch." However, I searched for a long time and couldn't find it ( Tears, my plan, my lunch~). Most of them use getNodesByParamFuzzy() or highlighting in the API. However, friends said that the requirements are not met: 1. If the matching fails, the parent node is also hidden; 2. The matching rules can be customized, that is, it can match names and attributes... (Anyway, what I want is not spicy, Xiaosheng With a smile on my face, but in my heart...then I will write it for you~), enter the text below:
Mind Map

The general search function only matches keywords within the "established range (convenient name)". The "established range" means that we already know the search range: for example, a text library, a drop-down box , in other words, the size of our matching object set has been determined. However, this is not feasible on ztree. Why? When I thought about the implementation logic of the ztree search function, I asked: So, is the level of this tree fixed? Or are you not sure how many layers there are? The old man looked at me and smiled knowingly: You write in infinite layers~ Xiaosheng’s calf twitched. . Because the level of the tree is uncertain, the search range is uncertain. For example: the target node is matched successfully. If this node is a child node, then its parent node should also be displayed, and then the parent node of its parent node should also be Displayed, and then the parent node of its parent node's parent node... Orz... It seems that it will never end... There is no other way but to: recurse to find all the parent nodes and child nodes of the target node.
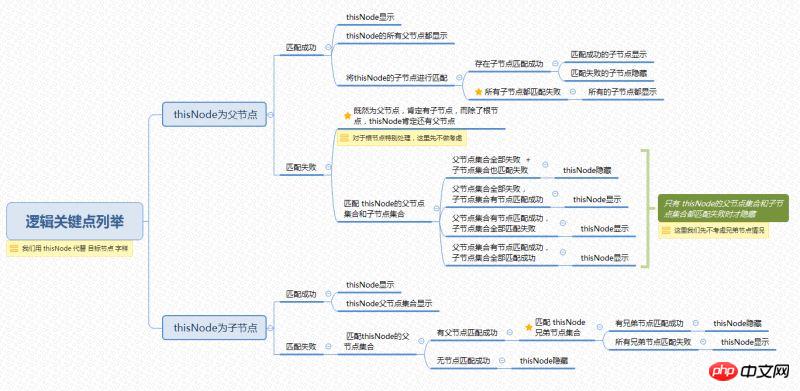
Key points of logic
In the above mind map, I roughly listed the logic, under what circumstances the target node is displayed, and what This is a key point that we must be clear about. Let’s take a closer look at the existence of the target node: The development of the search function has been clearly understood in the mind. The only thing left is the implementation method. However, this is not a problem at all~ (Xiaosheng secretly thinks that what is really worrying is that the process of the function is not clear. As for the implementation method, you all know it. Right? 0.0..)
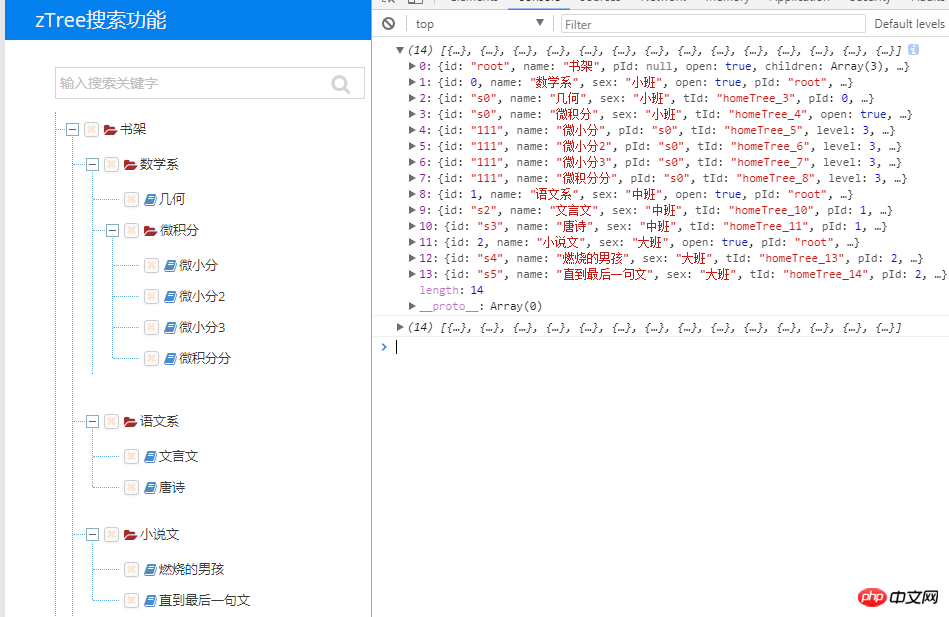
 ##About tree nodes
##About tree nodes
var treeObj=$.fn.zTree.getZTreeObj("homeTree"); // 设置根节点
var node = treeObj.getNodes(); // 获取根节点
var nodes = treeObj.transformToArray(node); // 获取所有节点
console.log(nodes);Look at the picture again: we can see various attributes of any node, including the child node set we want, the parent node attribute isParent, the node id tId, the parent node id parentTid...
 Everything is ready, get started
Everything is ready, get started
Let’s take a look at the relevant methods. Many small details need to be discovered during the actual coding process. For the convenience of display, they are listed here. method.
Declare the backup array: 
// 地区搜索 var parentArray = []; var childArray = [];
// 递归获取目标节点所有父节点
function getParentsNode(treeNode){
var thisParentNode = treeNode.getParentNode(); //得到该节点的父节点
if( thisParentNode != null ){ // 父节点存在
parentArray.push(thisParentNode); // 储存至数组
getParentsNode(thisParentNode); // 重调
}else{
return false;
}
} // 递归获取目标节点所有子节点
function getChildrenNode(treeNode){
var thisIsParent = treeNode.isParent; // 获取目标节点 isParent 属性,判断是否为父节点
if( thisIsParent == true ){
var thisChildrenNode = treeNode.children; // 得到该节点的子节点集合
for(var i=0;i<thisChildrenNode.length;i++){
childArray.push(thisChildrenNode[i]); // 将该子节点加入数组中
getChildrenNode(thisChildrenNode[i]); // 重调
}
}else{
return false;
}
} //匹配节点
function matchNode(treeNode,num){
var inputArea = $("input[name='searchArea']");
var name = treeNode.name;
var entityCode = treeNode.entity_code|| '';
var val = inputArea.val(); // 获取检索值
var numName = name.indexOf(val);
var numCode = entityCode.indexOf(val);
var num = -1;
if( numName != -1 || numCode !=-1 ){
num = 1;
}
if( numName == -1 && numCode == -1 ){
num = -1;
}
return num;
}节点匹配成功方法:
// 节点匹配成功
function checkTrueArray(arr,treeNode){
var thisTid = treeNode.tId;
var thisLi = $("#"+thisTid);
for(var n=0;n<arr.length;n++){
var thisNodeId = arr[n].tId;
var thisNodeLi = $("#"+thisNodeId);
thisLi.show();
thisNodeLi.show();
}
}节点匹配失败方法:
// 节点匹配失败
function checkFalseArray(arr,treeNode){
var result = [];
var result2 = [];
var thisTid = treeNode.tId;
var thisLi = $("#"+thisTid);
var val = inputArea.val(); // 获取检索值
var thisParent = treeNode.getParentNode(); // 获取目标节点父节点
if( thisParent != null ){ // 有父节点
var thisBrotherArr = treeNode.getParentNode().children; // 得到包含自身的兄弟数组
for(var m=0;m<arr.length;m++){ // 匹配父节点
var num = matchNode(arr[m]);
if( num != -1 ){
result.push(arr[m]);
}
}
var resultLength = result.length;
for( var m=0;m<thisBrotherArr.length;m++ ){ // 匹配兄弟节点
var num = matchNode(thisBrotherArr[m]);
if( num != -1 ){
result2.push(thisBrotherArr[m]);
}
}
var resultLength2 = result2.length;
// 对于自身匹配失败的节点,要显示必须满足有父节点匹配成功,且兄弟级节点都匹配失败
if( (resultLength == 0 && resultLength2 == 0) || resultLength2 != 0 ){
thisLi.hide();
}
if( resultLength !=0 && resultLength2 == 0 ){
thisLi.show();
}
}else{
thisLi.hide();
}
}目标节点匹配失败 目标节点即有父节点又有子节点:
// 目标节点匹配失败 目标节点即有父节点又有子节点
function checkAllArray(arr,arr2,treeNode){
var result = [];
var result2 = [];
var thisTid = treeNode.tId;
var thisLi = $("#"+thisTid);
var val = inputArea.val(); // 获取检索值
for(var m=0;m<arr.length;m++){ // 匹配子节点或父节点
var num = matchNode(arr[m]);
if( num != -1 ){
result.push(arr[m]); // 匹配成功储存至数组
}
}
var resultLength = result.length; // 获取匹配成功后返回的数组长度
for(var m=0;m<arr2.length;m++){ // 匹配子节点或父节点
var num = matchNode(arr2[m]);
if( num != -1 ){
result2.push(arr2[m]); // 匹配成功储存至数组
}
}
var resultLength2 = result2.length; // 获取匹配成功后返回的数组长度
if( resultLength == 0 && resultLength2 == 0 ){ // 子节点和父节点都匹配失败
thisLi.hide();
}else{
thisLi.show(); // 有一种匹配成功或都匹配成功
}
}定义搜索方法:
function searchArea(treeId, treeNode){ // 定义搜索方法
var inputArea = $("input[name='searchArea']");
var val = inputArea.val(); // 获取检索值
var treeObj=$.fn.zTree.getZTreeObj("homeTree"); // 设置根节点
var node = treeObj.getNodes(); // 获取根节点
var nodes = treeObj.transformToArray(node); // 获取所有节点
console.log(nodes);
for(var i=0;iCopy after login 调用搜索方法:
// 调用搜索方法
$(".searchAreaBtn").click(function(treeId, treeNode){
searchArea(treeId, treeNode);
});
var inputArea = $("input[name='searchArea']");
inputArea.keyup(function(treeId, treeNode,e){
var e = event || window.event;
var val = inputArea.val();
if( e.keyCode == 13 || val == "" ){
searchArea(treeId, treeNode);
}
});看效果(电脑ps出问题了,用美图秀秀拼的图~囧...):
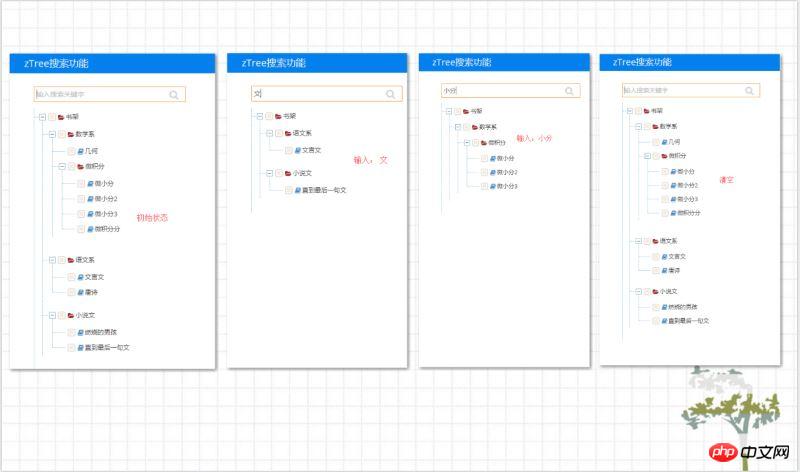
结语
理论上来说应该是能支持无限层的,最多试了四层,没有问题,没有做更多测试,有兴趣的看官可以试试,需要demo的可以留言,互相学习,一起进步,么么哒~
相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
The above is the detailed content of jQuery implements recursive infinite layer function. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




