
This time I will bring you the use of webpack automatic refresh and parsing. What are the precautions for using webpack automatic refresh and parsing? The following is a practical case, let's take a look.
The front end needs to frequently modify js and styles, and needs to be constantly adjusted according to the browser's page effect; and often our development directory and the local release directory are not the same, and we need to publish them after modification; another point That is, not all effects can be seen directly by double-clicking the page. We often need to use nginx to build a site locally to observe (it is ok on our own computer before putting it into the test environment). So if you have to manually refresh the browser and manually (or click) publish, and start the site, it is indeed a lot of physical work. And these three points webpack can help us do it. webpack-dev-serverWebpack implements automatic refresh through webpack-dev-server (WDS). WDS is a development server (an express) running in memory. After starting, it will detect whether the file has changed and automatically compile again. 1. Installationnpm install webpack-dev-server --save-dev
"scripts": { "start": "webpack-dev-server --env development", "build": "webpack --env production"
}
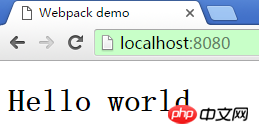
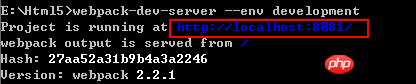
webpack-dev-server --env development
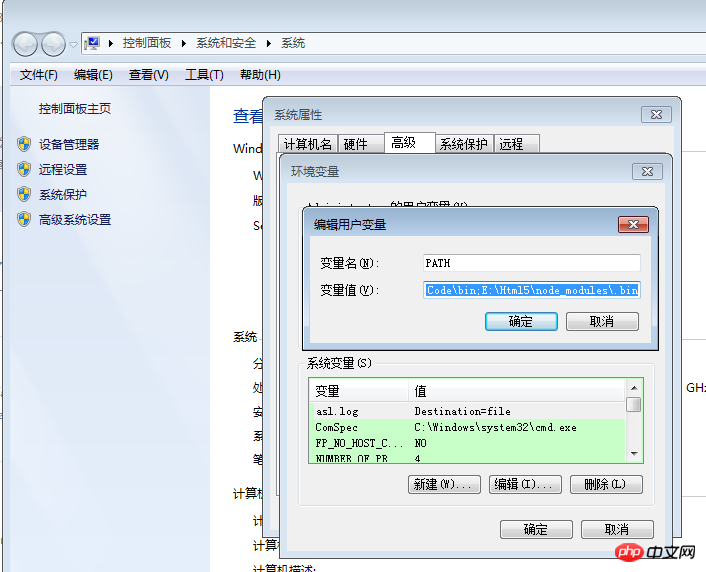
C:\Users\Administrator.9BBOFZPACSCXLG2\AppData\Roaming\npm;C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft VS Code\bin;E:\Html5\node_modules\.bin
server{
listen 8080;
location / {
root E:/Html5/build;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
devServer:{ //...
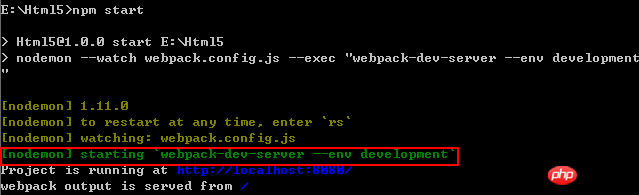
port: 9000}npm install nodemon --save-dev
"scripts": { "start": "nodemon --watch webpack.config.js --exec \"webpack-dev-server --env development\"", "build": "webpack --env production"
},
https://github.com/webpack/webpack-dev-server/tree/master/examples/proxy-advanced
module.exports = {
context: dirname,
entry: "./app.js",
devServer: { proxy: { "/api": {
target: "http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/",
changeOrigin: true,
pathRewrite: { "^/api": ""
},
bypass: function(req) { if(req.url === "/api/nope") { return "/bypass.html";
}
}
}
}
}
}but,这种刷新是怎么实现的呢?因为页面上没有嵌入什么别的js,去翻原码 web-dev-server/server.js中有这么一段:
Server.prototype._watch = function(path) { const watcher = chokidar.watch(path).on("change", function() { this.sockWrite(this.sockets, "content-changed");
}.bind(this)) this.contentBaseWatchers.push(watcher);
}用chokidar来监视文件变化,server的内部维护的有一个socket集合:
Server.prototype.sockWrite = function(sockets, type, data) {
sockets.forEach(function(sock) {
sock.write(JSON.stringify({
type: type,
data: data
}));
});
}sock是一个sockjs对象。https://github.com/sockjs/sockjs-client,从http://localhost:8080/webpack-dev-server/页面来看,sockjs是用来通信记录日志的。
var onSocketMsg = {
hot: function() {
hot = true;
log("info", "[WDS] Hot Module Replacement enabled.");
},
invalid: function() {
log("info", "[WDS] App updated. Recompiling...");
sendMsg("Invalid");
},
hash: function(hash) {
currentHash = hash;
},
...
}我们在看app.js,其中有一个OnSocketMsg 对象。
var onSocketMsg = {
hot: function() {
hot = true;
log("info", "[WDS] Hot Module Replacement enabled.");
},
invalid: function() {
log("info", "[WDS] App updated. Recompiling...");
sendMsg("Invalid");
},
hash: function(hash) {
currentHash = hash;
}, "still-ok": function() {
log("info", "[WDS] Nothing changed.") if(useWarningOverlay || useErrorOverlay) overlay.clear();
sendMsg("StillOk");
}, "log-level": function(level) {
logLevel = level;
}, "overlay": function(overlay) { if(typeof document !== "undefined") { if(typeof(overlay) === "boolean") {
useWarningOverlay = overlay;
useErrorOverlay = overlay;
} else if(overlay) {
useWarningOverlay = overlay.warnings;
useErrorOverlay = overlay.errors;
}
}
},
ok: function() {
sendMsg("Ok"); if(useWarningOverlay || useErrorOverlay) overlay.clear(); if(initial) return initial = false;
reloadApp();
}, "content-changed": function() {
log("info", "[WDS] Content base changed. Reloading...")
self.location.reload();
},
warnings: function(warnings) {
log("info", "[WDS] Warnings while compiling."); var strippedWarnings = warnings.map(function(warning) { return stripAnsi(warning);
});
sendMsg("Warnings", strippedWarnings); for(var i = 0; i < strippedWarnings.length; i++)
console.warn(strippedWarnings[i]); if(useWarningOverlay) overlay.showMessage(warnings); if(initial) return initial = false;
reloadApp();
},
errors: function(errors) {
log("info", "[WDS] Errors while compiling. Reload prevented."); var strippedErrors = errors.map(function(error) { return stripAnsi(error);
});
sendMsg("Errors", strippedErrors); for(var i = 0; i < strippedErrors.length; i++)
console.error(strippedErrors[i]); if(useErrorOverlay) overlay.showMessage(errors);
},
close: function() {
log("error", "[WDS] Disconnected!");
sendMsg("Close");
}
};View Code
ok的时候触发一个reloadApp
function reloadApp() { if(hot) {
log("info", "[WDS] App hot update..."); var hotEmitter = webpack_require("./node_modules/webpack/hot/emitter.js");
hotEmitter.emit("webpackHotUpdate", currentHash); if(typeof self !== "undefined") { // broadcast update to window
self.postMessage("webpackHotUpdate" + currentHash, "*");
}
} else {
log("info", "[WDS] App updated. Reloading..."); self.location.reload();
}
}也就是说WDS先检测文件是否变化,然后通过sockjs通知到客户端,这样就实现了刷新。之前WebSocket的第三方只用过socket.io,看起来sockjs也蛮好用的。不必外带一个js,在主js里面就可以写了。
相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
The above is the detailed content of The use of webpack automatic refresh and parsing. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




