
a.String String:
Features: Content wrapped in double quotes or single quotes. Such as: "123"; "Zhang San";
Note: single and double quotation marks are nested. Double quotation marks are used as characters, ' ''" '; single quotation marks are used as characters, " '' ";
b.Number Number:
Features: Direct numbers such as: 1; 3.14; -1; 0; NaN;
Normal numbers: positive numbers, negative numbers, 0 Abnormal numbers: NaN
c.Boolean Boolean:
Characteristics: There are only two values, true and false, such as: true; false;
d.Undefined Undefined:
Characteristics: There is only one value, undefined. When a variable is not assigned a value, the default value is undefined. Such as: var a;
e.Null empty object:
Features: The type is called Null, but the actual type is object. It has something to do with the garbage collection mechanism. For example: var a = null;
is also the object type Object type , such as: Object, Array, Function, Data, etc. The special Array and Function
javascript reference data types are objects stored in heap memory.
The difference from other languages is that you cannot directly access the location in the heap memory space and operate the heap memory space. Only the reference address of the object in the stack memory can be manipulated.
So, the reference type data stored in the stack memory is actually the reference address of the object in the heap memory. Through this reference address, you can quickly find the object saved in the heap memory.
var obj1 = new Object();
var obj2 = obj1;
obj2.name = "I have a name";
console.log(obj1.name); // I have a name The
indicates that these two reference data types point to the same heap memory object. obj1 is assigned to onj2. In fact, the reference address of this heap memory object in the stack memory is copied to obj2,
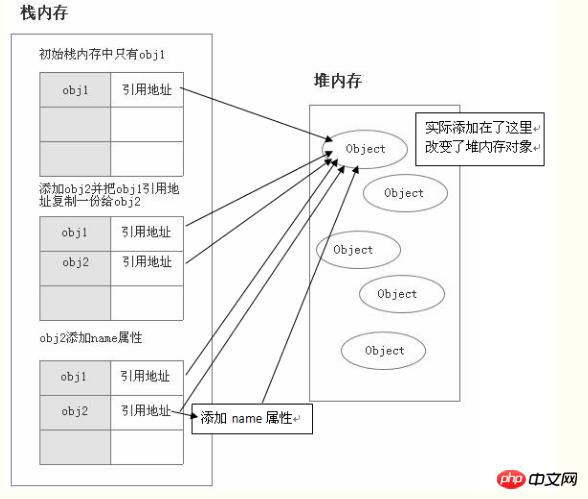
Understand the two basic structures of memory: memory can be divided into stack area and heap area
Features of the stack area: It stores data and variable names of basic data types;
Features of the heap area: It stores data of reference type data types.
Difference:
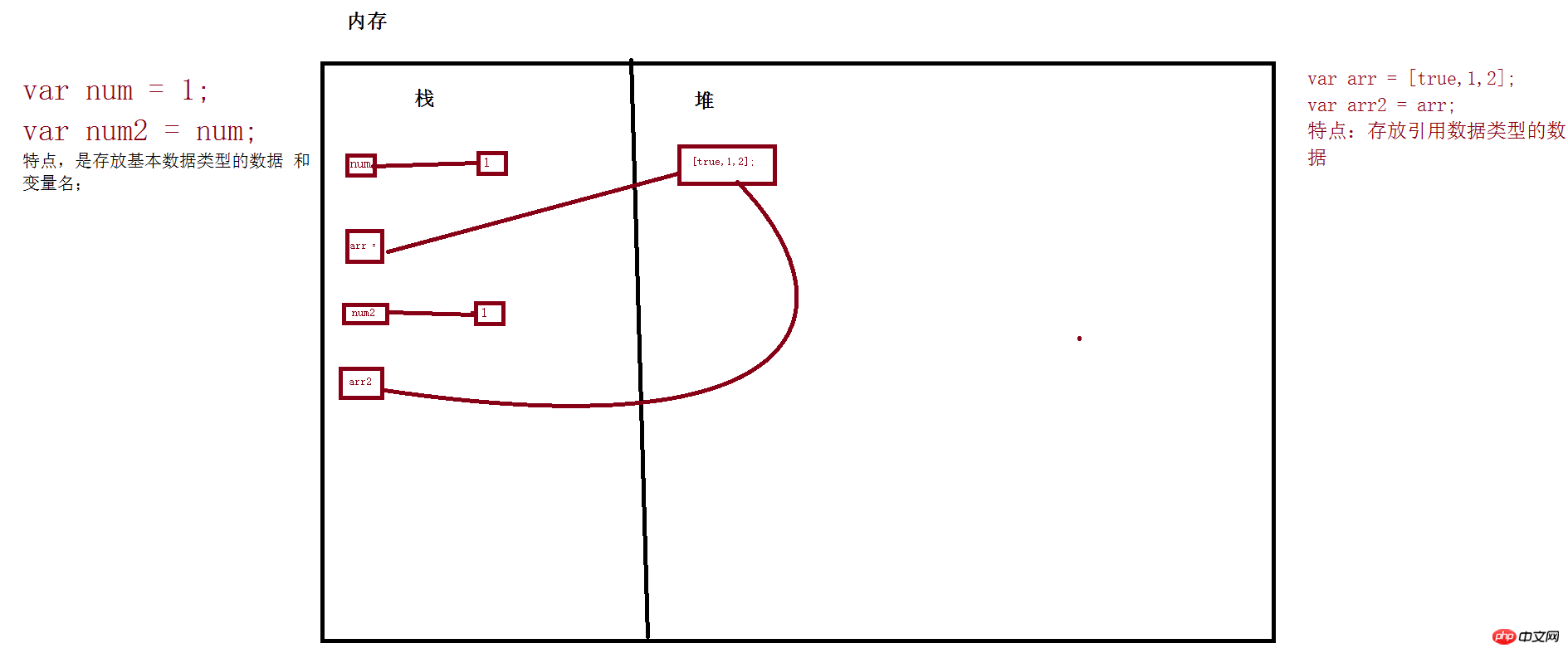
When the basic data type data is copied, the copied data will clone a new data in the stack area of the memory, and the new data will be copied. The new address of the data is associated with the new variable.
When data of a reference data type is copied, the copied data will not be re-cloned in the heap area, but only the address of the original data will be cloned to the new variable.
①The identifier typeof
## can be distinguished: numerical value, string, Boolean value, undefined, function cannot be distinguished: null and object, general object and array
eg:var a;
console.log(typeof a);Enter the type of a
Or console.log(typeof a==="undefined"); if it is true, a is undefined
②instanceof
is specially used to determine the type of object data: object, array and function
③===
You can judge: undefined and null
Note that quotation marks cannot be added here: console.log(a===undefined), such as adding (console. log(a===“undefined”) will report an error)
<span style="font-size: 14px;">//1.基本类型<br/>var a;//定义变量没有赋值<br/>console.log(a,typeof a==="undefined",a===undefined);<br/>a=null;<br/>console.log(a,typeof a==="object",a===null);//null true true<br/><br/>//2.对象类型<br/>/*<br/>obj是对象<br/>a1是数组同时也是对象类型 console.log是函数Function<br/>*/<br/>const obj={<br/>a1:[1,'abc',true,console.log]<br/>}<br/><br/>console.log(obj instanceof Object);//true<br/>console.log(obj.a1 instanceof Object,obj.a1 instanceof Array);//true true<br/>console.log(obj.a1[3] instanceof Function,typeof obj.a1[3]==='function');//true true<br/>obj.a1[3]('123456');//console.log中log本身是一个属性值,是一个函数 所以可以输出值</span>Note: The difference between pseudo array and true array
Same gender: both It is an object object type
Different:
Pseudo array: length attribute, with numeric subscript attribute ([1]...[10 ])
Can pseudo arrays use the method of calling arrays (such as: foreach attribute)
undefined代表没有赋值
null代表赋值,只是值为null
<span style="font-size: 14px;">// 1.undefined的情况<br/> //①定义变量没有赋值<br/> var a;<br/> console.log(a);//undefined<br/> //②对象中不存在的属性<br/> a={};<br/> console.log(a.a);//undefined<br/> //③函数没有指定返回值<br/> function fn(){<br/> //return<br/> }<br/> console.log(fn())//undefined<br/><br/> //以下是null<br/> a=null;<br/> console.log(a);//null<br/> a={<br/> a:null<br/> }<br/> console.log(a.a);//null</span>a.初始时,准备保存对象的变量
b.结束时,让变量向的对象成为垃圾对象
<span style="font-size: 14px;">//a.初始时,准备保存对象的变量<br/> var a=null;<br/> //a=null后,后面做一些事情后产生数据<br/> a={n:2,m:'abc'}<br/> //b.结束时,让变量向的对象成为垃圾对象<br/> a=null;//此时a的值不在是{n:2,m:'abc'},而是一个空,当然也可以用a=1,<br/> //不过虽然覆盖{n:2,m:'abc'},但是却产生了数据1,所以这样就是不对,a=null,就不会产生数据了</span> js的变量本身是没有类型,变量的类型实际上是变量内存中的数据的类型
->变量类型:基本类型和引用类型
a.基本类型:保存基本类型数据的变量
b.引用类型:保存对象地址值的变量
->数据对象:
基本类型和对象类型(不严格来说对象类型就是引用类型)
b={}//b是引用变量,内存中保存是对象内存的地址值
console.log({} instanceof Object,b instanceof Object)//true trueJs中的数据类型一共有六种,即number,string,boolean,underfine,null,object。
注意:需要知道某些变量的数据类型,并将其转换为我们所需要的数据类型。通常,我们判断变量的数据类型会用到标识符typeof,如:
<span style="font-size: 14px;">var mood = "happy";<br/>alert(typeof mood);</span>
通过标识符typeof,我们可以很快获取数据的类型;
①其他数据转换成数字:parseInt() 转换成整数,parseFloat()转换成浮点数
<span style="font-size: 14px;">var test = parseInt(“blue”); //returns NaN<br/>var test = parseInt(“1234blue”); //returns 1234<br/>var test = parseInt(“22.5”); //returns 22<br/>var test = parseFloat(“1234blue”); //returns 1234<br/>var test = parseFloat(“22.5”); //returns 22.5<br/></span>
注意:当其他数据不能正常转换为数字数值时,结果就是NaN;
②其他数据转换成字符串:String(其他数据);
<span style="font-size: 14px;">var married = false;<br/> alert(married.toString());</span>
③其他数组转Boolean:
Boolean(其他数据);
注意:null、undefined、0、NaN、””转换为boolean结果为false,其他的数据转换的结果为true。
自动类型转换一般是根运行环境和操作符联系在一起的,是一种隐式转换,看似难以捉摸,其实是有一定规律性的,大体可以划分为:转换为字符串类型、转换为布尔类型、转换为数字类型。今天我们就介绍一下这几种转换机制
i. 字符串类型转为数字: 空字符串被转为0,非空字符串中,符合数字规则的会被转换为对应的数字,否则视为NaN
ii. 布尔类型转为数字: true被转为1,false被转为0
iii. null被转为0,undefined被转为NaN
iv. 对象类型转为数字: valueOf()方法先试图被调用,如果调用返回的结果为基础类型,则再将其转为数字,如果返回结果不是基础类型,则会再试图调用toString()方法,最后试图将返回结果转为数字,如果这个返回结果是基础类型,则会得到一个数字或NaN,如果不是基础类型,则会抛出一个异常
<span style="font-size: 14px;">var foo = +''; // 0<br/>var foo = +'3'; // 3<br/>var foo = +'3px'; // NaN<br/>var foo = +false; // 0<br/>var foo = +true; // 1<br/>var foo = +null; // 0<br/>var foo = +undefined; // NaN</span>
对于不符合数字规则的字符串,和直接调用Number()函数效果相同,但和parseInt()有些出入:
<span style="font-size: 14px;">var foo = Number('3px'); // NaN<br/>var foo = parseInt('3px'); // 3<br/></span>
注意:任何数据和NaN(除了和字符串做相加操作外)做运算,结果始终都是NaN
<span style="font-size: 14px;">var foo = null + undefined; // NaN<br/>var foo = null + NaN; // NaN</span>
其他数据和字符串数据做相加操作时,其他数据会自动的转换为字符串类型。就相当于悄悄的用了String()工具。
<span style="font-size: 14px;">// 基础类型<br/>var foo = 3 + ''; // "3"<br/>var foo = true + ''; // "true"<br/>var foo = undefined + ''; // "undefined"<br/>var foo = null + ''; // "null"<br/><br/>// 复合类型<br/>var foo = [1, 2, 3] + ''; // "1,2,3"<br/>var foo = {} + ''; // "[object Object]"</span> a. 数字转为布尔类型(from number)
当数字在逻辑环境中执行时,会自动转为布尔类型。0(0,-0)和NaN会自动转为false,其余数字(1,2,3,-2,-3...)都被认为是true
b. 字符串转为布尔类型(from string)
和数字类似,当字符串在逻辑环境中执行时,也会被转为布尔类型。空字符串会被转为false,其它字符串都会转为true
c. undefined和null转为布尔类型(from undefined and null)
当undefined和null在逻辑环境中执行时,都被认为是false
d. 对象转为布尔类型(from object)
相关推荐:
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of JavaScript data types. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




