
This article mainly shares with you an in-depth understanding of js data types.
In the ECMAScript specification, a total of 7 data types are defined, divided into two categories: basic types and reference types, as shown below:
Basic types: String, Number, Boolean, Symbol, Undefined, Null
Reference type : Object
The basic type is also called a simple type. Because it occupies a fixed space, it is a simple data segment. In order to improve the speed of variable query, it is stored in the stack. , that is, access by value.
Reference types are also called complex types. Since the size of their values will change, they cannot be stored in the stack, otherwise it will reduce the speed of variable query. Therefore, their values are stored in In the heap, the value stored in the variable is a pointer pointing to the memory where the object is stored, that is, access by address. In addition to Object, reference types also include Function, Array, RegExp, Date, etc.
Given that ECMAScript is loosely typed, there needs to be a way to detect the data type of a given variable. JavaScript also provides a variety of methods for this problem, but unfortunately, the results obtained by different methods are uneven. The following introduces four commonly used methods, and briefly analyzes the problems of each method.typeof '';// string 有效 typeof 1;// number 有效 typeof Symbol();// symbol 有效 typeof true;//boolean 有效 typeof undefined;//undefined 有效 typeof null;//object 无效 typeof [] ;//object 无效 typeof new Function();// function 有效 typeof new Date();//object 无效 typeof new RegExp();//object 无效
instanceof detects the prototype , we use a piece of pseudo code to simulate its internal execution process:
instanceof (A,B) = {
var L = A.__proto__;
var R = B.prototype;
if(L === R) {
//A的内部属性__proto__指向B的原型对象
return true;
}
return false;
}[] instanceof Array;//true
{} instanceof Object;//true
new Date() instanceof Date;//true
function Person(){};
new Person() instanceof Person;
[] instanceof Object;//true
new Date() instanceof Object;//true
new Person instanceof Object;//true
从 instanceof 能够判断出 [ ].__proto__ 指向 Array.prototype,而 Array.prototype.__proto__ 又指向了Object.prototype,最终 Object.prototype.__proto__ 指向了null,标志着原型链的结束。因此,[]、Array、Object 就在内部形成了一条原型链:
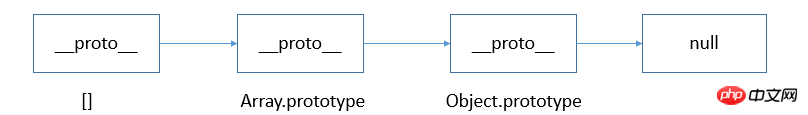
从原型链可以看出,[] 的 __proto__ 直接指向Array.prototype,间接指向 Object.prototype,所以按照 instanceof 的判断规则,[] 就是Object的实例。依次类推,类似的 new Date()、new Person() 也会形成一条对应的原型链 。因此,instanceof 只能用来判断两个对象是否属于实例关系, 而不能判断一个对象实例具体属于哪种类型。
instanceof 操作符的问题在于,它假定只有一个全局执行环境。如果网页中包含多个框架,那实际上就存在两个以上不同的全局执行环境,从而存在两个以上不同版本的构造函数。如果你从一个框架向另一个框架传入一个数组,那么传入的数组与在第二个框架中原生创建的数组分别具有各自不同的构造函数。
var iframe = document.createElement('iframe'); document.body.appendChild(iframe); xArray = window.frames[0].Array; var arr =new xArray(1,2,3);// [1,2,3] arr instanceof Array;// false
针对数组的这个问题,ES5 提供了 Array.isArray() 方法 。该方法用以确认某个对象本身是否为 Array 类型,而不区分该对象在哪个环境中创建。
if (Array.isArray(value)){
//对数组执行某些操作
}Array.isArray() 本质上检测的是对象的 [[Class]] 值,[[Class]] 是对象的一个内部属性,里面包含了对象的类型信息,其格式为 [object Xxx] ,Xxx 就是对应的具体类型 。对于数组而言,[[Class]] 的值就是 [object Array] 。
当一个函数 F被定义时,JS引擎会为F添加 prototype 原型,然后再在 prototype上添加一个 constructor 属性,并让其指向 F 的引用。如下所示:
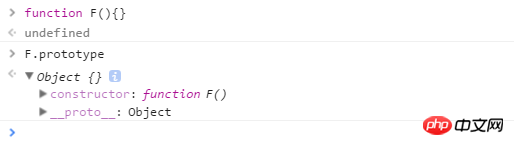
当执行 var f = new F() 时,F 被当成了构造函数,f 是F的实例对象,此时 F 原型上的 constructor 传递到了 f 上,因此 f.constructor == F

可以看出,F 利用原型对象上的 constructor 引用了自身,当 F 作为构造函数来创建对象时,原型上的 constructor 就被遗传到了新创建的对象上, 从原型链角度讲,构造函数 F 就是新对象的类型。这样做的意义是,让新对象在诞生以后,就具有可追溯的数据类型。
同样,JavaScript 中的内置对象在内部构建时也是这样做的:

细节问题:
null 和 undefined 是无效的对象,因此是不会有 constructor 存在的,这两种类型的数据需要通过其他方式来判断。
函数的 constructor 是不稳定的,这个主要体现在自定义对象上,当开发者重写 prototype 后,原有的 constructor 引用会丢失,constructor 会默认为 Object
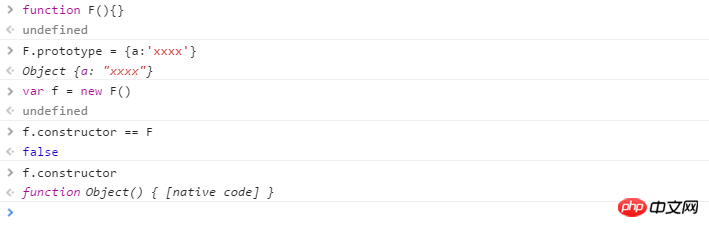
为什么变成了 Object?
因为 prototype 被重新赋值的是一个 { }, { } 是 new Object() 的字面量,因此 new Object() 会将 Object 原型上的 constructor 传递给 { },也就是 Object 本身。
因此,为了规范开发,在重写对象原型时一般都需要重新给 constructor 赋值,以保证对象实例的类型不被篡改。
toString() 是 Object 的原型方法,调用该方法,默认返回当前对象的 [[Class]] 。这是一个内部属性,其格式为 [object Xxx] ,其中 Xxx 就是对象的类型。
对于 Object 对象,直接调用 toString() 就能返回 [object Object] 。而对于其他对象,则需要通过 call / apply 来调用才能返回正确的类型信息。
Object.prototype.toString.call('') ; // [object String] Object.prototype.toString.call(1) ; // [object Number] Object.prototype.toString.call(true) ;// [object Boolean] Object.prototype.toString.call(Symbol());//[object Symbol] Object.prototype.toString.call(undefined) ;// [object Undefined] Object.prototype.toString.call(null) ;// [object Null] Object.prototype.toString.call(new Function()) ;// [object Function] Object.prototype.toString.call(new Date()) ;// [object Date] Object.prototype.toString.call([]) ;// [object Array] Object.prototype.toString.call(new RegExp()) ;// [object RegExp] Object.prototype.toString.call(new Error()) ;// [object Error] Object.prototype.toString.call(document) ;// [object HTMLDocument] Object.prototype.toString.call(window) ;//[object global] window是全局对象 global 的引用
相关推荐:
The above is the detailed content of Deep understanding of js data types. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




