
This time I will show you how to implement page code splitting and on-demand loading in react. What are the precautions for react to implement page code splitting and on-demand loading. Here are practical cases. Let’s take a look. .
Although I have been doing react-related optimizations, such as on-demand loading, dll separation, and server-side rendering, I have never started with routingCode splitting. I didn't do it yesterday when I was developing locally. The test was successful. I did it again today and it has been deployed to the online environment. I will record this today.
Modify configuration
Development environment: webpack@v3, react-router@v4
Installation dependencies:
$ yarn add babel-plugin-syntax-dynamic-import -dev
Modify. babelrc file: Add "syntax-dynamic-import" in plugins
Transform the project code
Installation dependencies:
$ yarn add react-loadable
According to react-loadable documentation Tip, we need to provide a Loading component when loading a new page, and distinguish between loading and timeout status Tip:
import React from 'react';
import { Icon } from 'antd';
const Loading = ({ pastDelay, timedOut, error }) => {
if (pastDelay) {
return <p><Icon type="loading" /></p>;
} else if (timedOut) {
return <p>Taking a long time...</p>;
} else if (error) {
return <p>Error!</p>;
}
return null;
};Change the page component import method:
import React from 'react';
import Loadable from 'react-loadable';
import { Route, Switch } from 'react-router-dom';
const Home = Loadable({
loader: () => import('../Home'),
loading: Loading,
timeout: 10000
});
const EditArticle = Loadable({
loader: () => import('../EditArticle'),
loading: Loading,
timeout: 10000
});
...
<Switch>
<Route exact path="/home" component={Home} />
<Route path="/editarticle" component={EditArticle} />
</Switch>Then the packaging result will be Separate the code of each page:
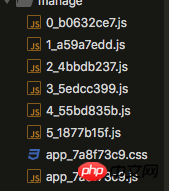
In the page, we only need to load the entry file app.js, and other scripts will be loaded when accessing the corresponding page. Load via this file.
Verification results
After uploading static resources to cdn, load app.css and app.js in the page, and access after running Each page will load the corresponding script in turn. The result is as shown in the figure:
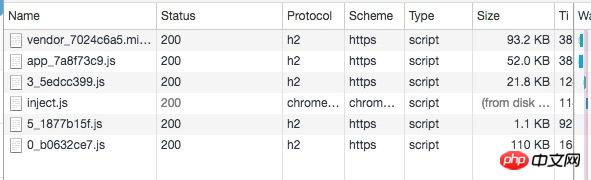
#It can be seen that the page script loaded when accessing the first page is only 21.8 after gzip compression. KB! ! ! Of course, this is also related to the complexity of the page, but compared with loading all scripts, it has been greatly reduced. This optimization is particularly obvious to users with highly targeted access.
Another benefit of doing this is that when we only change the business code of some pages in the project, the code of other pages remains unchanged, so at this time other pages use client cache. Another level of optimization has been done.
Tips
I believe you have mastered the method after reading the case in this article. For more exciting information, please pay attention to other related articles on the php Chinese website!
Recommended reading:
React realizes data synchronization of mobile phone numbers
How to use node server for cross-domain development in local development
The above is the detailed content of How react implements page code splitting and on-demand loading. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




