How Vuex state management should be used
This time I will show you how to use Vuex state management, what are the precautions when using Vuex state management, the following is a practical case, let's take a look.
Vuex is a tool designed for Vue.js State management patterns for application development. It uses centralized storage to manage the state of all components of the application, and uses corresponding rules to ensure that the state changes in a predictable way. Vuex is also integrated into Vue's official Debugging tool devtools extension provides advanced debugging functions such as zero-configuration time-travel debugging, status snapshot import and export, etc.
The above is the introduction of vuex in the official document of vuex. The official document explains the usage of vuex in detail. I won’t go into details about the usage of vuex here. The purpose of writing this blog is just to help some students understand and get started with vuex faster.
1. Install
$ npm install vuex --save
2. Reference store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
import store from './vuex/store' //引用store.js
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止在启动时生成生产提示
//vue实例
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store, //把store挂在到vue的实例下面
template: '<app></app>',
components: { App }
})in main.js main entrance js 3. Reference Vuex
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex) //注册Vuex
// 定义常量 如果访问他的话,就叫访问状态对象
const state = {
count: 1
}
// mutations用来改变store状态, 如果访问他的话,就叫访问触发状态
const mutations = {
//这里面的方法是用 this.$store.commit('jia') 来触发
jia(state){
state.count ++
},
jian(state){
state.count --
},
}
//暴露到外面,让其他地方的引用
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations
})in store.js 4. Use
in vue component Use the $store.commit('jia') area to trigger the addition and subtraction methods below mutations
<template>
<p>
</p>
<h1 id="Hello-Vuex">Hello Vuex</h1>
<h5 id="store-state-count">{{$store.state.count}}</h5>
<p>
<button>+</button>
<button>-</button>
</p>
</template>
<!-- 加上scoped是css只在这个组件里面生效,为了不影响全局样式 -->
<style>
h5{
font-size: 20px;
color: red;
}
</style>5. View the demo

6. state access state object
Use computed calculation
<template>
<p>
</p>
<h1 id="Hello-Vuex">Hello Vuex</h1>
<h5 id="count">{{count}}</h5>
<p>
<button>+</button>
<button>-</button>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
export default{
name:'hello', //写上name的作用是,如果你页面报错了,他会提示你是那个页面报的错,很实用
// 方法一
// computed: {
// count(){
// return this.$store.state.count + 6
// }
// }
// 方法二 需要引入外部 mapState
computed:mapState({
count:state => state.count + 10
})
// ECMA5用法
// computed:mapState({
// count:function(state){
// return state.count
// }
// })
//方法三
// computed: mapState([
// 'count'
// ])
}
</script>7. Mutations trigger state (synchronization state)
<template>
<p>
</p>
<h1 id="Hello-Vuex">Hello Vuex</h1>
<h5 id="count">{{count}}</h5>
<p>
<button>+</button>
<button>-</button>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState,mapMutations} from 'vuex'
export default{
name:'hello', //写上name的作用是,如果你页面报错了,他会提示你是那个页面报的错,很实用
//方法三
computed: mapState([
'count'
]),
methods:{
...mapMutations([
'jia',
'jian'
])
}
}
</script>8. Getters calculate property
Getter cannot use arrow functions, which will change the pointing of this
Add getters
// 计算
const getters = {
count(state){
return state.count + 66
}
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations,
getters
})
//count的参数就是上面定义的state对象
//getters中定义的方法名称和组件中使用的时候一定是一致的,定义的是count方法,使用的时候也用count,保持一致。
组件中使用
<script>
import {mapState,mapMutations,mapGetters} from 'vuex'
export default{
name:'hello',
computed: {
...mapState([
'count'
]),
...mapGetters([
'count'
])
},
methods:{
...mapMutations([
'jia',
'jian'
])
}
}
</script>in store.js 9. actions (asynchronous state)
Add actions
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 定义常量
const state = {
count: 1
}
// mutations用来改变store状态 同步状态
const mutations = {
jia(state){
state.count ++
},
jian(state){
state.count --
},
}
// 计算属性
const getters = {
count(state){
return state.count + 66
}
}
// 异步状态
const actions = {
jiaplus(context){
context.commit('jia') //调用mutations下面的方法
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('jian')
},2000)
alert('我先被执行了,然后两秒后调用jian的方法')
},
jianplus(context){
context.commit('jian')
}
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations,
getters,
actions
})in store.js Use
<template>
<p>
</p>
<h1 id="Hello-Vuex">Hello Vuex</h1>
<h5 id="count">{{count}}</h5>
<p>
<button>+</button>
<button>-</button>
</p>
<p>
<button>+plus</button>
<button>-plus</button>
</p>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState,mapMutations,mapGetters,mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default{
name:'hello',
computed: {
...mapState([
'count'
]),
...mapGetters([
'count'
])
},
methods:{
// 这里是数组的方式触发方法
...mapMutations([
'jia',
'jian'
]),
// 换一中方式触发方法 用对象的方式
...mapActions({
jiaplus: 'jiaplus',
jianplus: 'jianplus'
})
}
}
</script>
<style>
h5{
font-size: 20px;
color: red;
}
</style>in components 10. modules module
Suitable for very large projects with many statuses, easy to manage
Modify store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const state = {
count: 1
}
const mutations = {
jia(state){
state.count ++
},
jian(state){
state.count --
},
}
const getters = {
count(state){
return state.count + 66
}
}
const actions = {
jiaplus(context){
context.commit('jia') //调用mutations下面的方法
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('jian')
},2000)
alert('我先被执行了,然后两秒后调用jian的方法')
},
jianplus(context){
context.commit('jian')
}
}
//module使用模块组的方式 moduleA
const moduleA = {
state,
mutations,
getters,
actions
}
// 模块B moduleB
const moduleB = {
state: {
count:108
}
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB,
}
})I believe you have mastered the method after reading the case in this article. For more exciting information, please pay attention to other related articles on the php Chinese website!
Recommended reading:
The above is the detailed content of How Vuex state management should be used. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1653
1653
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1305
1305
 25
25
 1251
1251
 29
29
 1224
1224
 24
24
 How to use magnet links
Feb 18, 2024 am 10:02 AM
How to use magnet links
Feb 18, 2024 am 10:02 AM
Magnet link is a link method for downloading resources, which is more convenient and efficient than traditional download methods. Magnet links allow you to download resources in a peer-to-peer manner without relying on an intermediary server. This article will introduce how to use magnet links and what to pay attention to. 1. What is a magnet link? A magnet link is a download method based on the P2P (Peer-to-Peer) protocol. Through magnet links, users can directly connect to the publisher of the resource to complete resource sharing and downloading. Compared with traditional downloading methods, magnetic
 How to use mdf and mds files
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
How to use mdf and mds files
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
How to use mdf files and mds files With the continuous advancement of computer technology, we can store and share data in a variety of ways. In the field of digital media, we often encounter some special file formats. In this article, we will discuss a common file format - mdf and mds files, and introduce how to use them. First, we need to understand the meaning of mdf files and mds files. mdf is the extension of the CD/DVD image file, and the mds file is the metadata file of the mdf file.
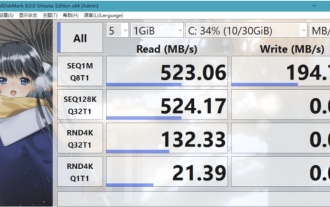 What software is crystaldiskmark? -How to use crystaldiskmark?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
What software is crystaldiskmark? -How to use crystaldiskmark?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
CrystalDiskMark is a small HDD benchmark tool for hard drives that quickly measures sequential and random read/write speeds. Next, let the editor introduce CrystalDiskMark to you and how to use crystaldiskmark~ 1. Introduction to CrystalDiskMark CrystalDiskMark is a widely used disk performance testing tool used to evaluate the read and write speed and performance of mechanical hard drives and solid-state drives (SSD). Random I/O performance. It is a free Windows application and provides a user-friendly interface and various test modes to evaluate different aspects of hard drive performance and is widely used in hardware reviews
 How to download foobar2000? -How to use foobar2000
Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
How to download foobar2000? -How to use foobar2000
Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
foobar2000 is a software that can listen to music resources at any time. It brings you all kinds of music with lossless sound quality. The enhanced version of the music player allows you to get a more comprehensive and comfortable music experience. Its design concept is to play the advanced audio on the computer The device is transplanted to mobile phones to provide a more convenient and efficient music playback experience. The interface design is simple, clear and easy to use. It adopts a minimalist design style without too many decorations and cumbersome operations to get started quickly. It also supports a variety of skins and Theme, personalize settings according to your own preferences, and create an exclusive music player that supports the playback of multiple audio formats. It also supports the audio gain function to adjust the volume according to your own hearing conditions to avoid hearing damage caused by excessive volume. Next, let me help you
 Simple guide to pip mirror source: easily master how to use it
Jan 16, 2024 am 10:18 AM
Simple guide to pip mirror source: easily master how to use it
Jan 16, 2024 am 10:18 AM
Get started easily: How to use pip mirror source With the popularity of Python around the world, pip has become a standard tool for Python package management. However, a common problem that many developers face when using pip to install packages is slowness. This is because by default, pip downloads packages from Python official sources or other external sources, and these sources may be located on overseas servers, resulting in slow download speeds. In order to improve download speed, we can use pip mirror source. What is a pip mirror source? To put it simply, just
 BTCC tutorial: How to bind and use MetaMask wallet on BTCC exchange?
Apr 26, 2024 am 09:40 AM
BTCC tutorial: How to bind and use MetaMask wallet on BTCC exchange?
Apr 26, 2024 am 09:40 AM
MetaMask (also called Little Fox Wallet in Chinese) is a free and well-received encryption wallet software. Currently, BTCC supports binding to the MetaMask wallet. After binding, you can use the MetaMask wallet to quickly log in, store value, buy coins, etc., and you can also get 20 USDT trial bonus for the first time binding. In the BTCCMetaMask wallet tutorial, we will introduce in detail how to register and use MetaMask, and how to bind and use the Little Fox wallet in BTCC. What is MetaMask wallet? With over 30 million users, MetaMask Little Fox Wallet is one of the most popular cryptocurrency wallets today. It is free to use and can be installed on the network as an extension
 How to use NetEase Mailbox Master
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
How to use NetEase Mailbox Master
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
NetEase Mailbox, as an email address widely used by Chinese netizens, has always won the trust of users with its stable and efficient services. NetEase Mailbox Master is an email software specially created for mobile phone users. It greatly simplifies the process of sending and receiving emails and makes our email processing more convenient. So how to use NetEase Mailbox Master, and what specific functions it has. Below, the editor of this site will give you a detailed introduction, hoping to help you! First, you can search and download the NetEase Mailbox Master app in the mobile app store. Search for "NetEase Mailbox Master" in App Store or Baidu Mobile Assistant, and then follow the prompts to install it. After the download and installation is completed, we open the NetEase email account and log in. The login interface is as shown below
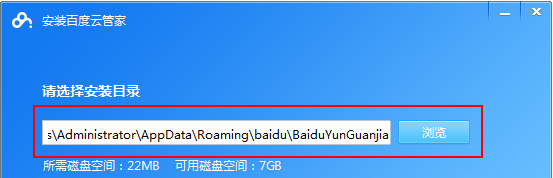 How to use Baidu Netdisk app
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
How to use Baidu Netdisk app
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
Cloud storage has become an indispensable part of our daily life and work nowadays. As one of the leading cloud storage services in China, Baidu Netdisk has won the favor of a large number of users with its powerful storage functions, efficient transmission speed and convenient operation experience. And whether you want to back up important files, share information, watch videos online, or listen to music, Baidu Cloud Disk can meet your needs. However, many users may not understand the specific use method of Baidu Netdisk app, so this tutorial will introduce in detail how to use Baidu Netdisk app. Users who are still confused can follow this article to learn more. ! How to use Baidu Cloud Network Disk: 1. Installation First, when downloading and installing Baidu Cloud software, please select the custom installation option.




