Detailed explanation of the use of jQuery without new construction
This time I will bring you a detailed explanation of the use of jQuery without new construction. What are the precautions for using jQuery without new construction? The following is a practical case, let's take a look.
jQuery's new-free construction
The core of the jQuery framework is to match elements from HTML documents and perform operations on them. Recall using jQuery When using jQuery, the method of instantiating a jQuery object is:// 无 new 构造
$('#test').text('Test');
// 当然也可以使用 new
var test = new $('#test');
test.text('Test'); $('') Structure, this is also a very convenient place for jQuery.
new jQuery(), so how is it implemented internally in jQuery? Take a look:
(function(window, undefined) {
var
// ...
jQuery = function(selector, context) {
// The jQuery object is actually just the init constructor 'enhanced'
return new jQuery.fn.init(selector, context, rootjQuery);
},
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype = {
init: function(selector, context, rootjQuery) {
// ...
}
}
jQuery.fn.init.prototype = jQuery.fn;
})(window);Function expressionand function declaration
In ECMAScript, the two most common ways to create functions are function expressions and function declarations , the difference between the two is a bit confusing, because the ECMA specification only clarifies one point: the function declaration must have an identifier (Identifier) (which is what everyone often calls the function name), while the function expression can Omit this identifier:
//函数声明:
function 函数名称 (参数:可选){ 函数体 }
//函数表达式:
function 函数名称(可选)(参数:可选){ 函数体 }name is not declared, it must be an expression. But if the function name is declared, how to judge whether it is a function declaration or What about function expressions? ECMAScript is distinguished by context. If
function foo(){} is used as part of an assignment expression, then it is a function expression, If
is contained within a function body, or is at the top of the program, it is a function declaration. <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false"> function foo(){} // 声明,因为它是程序的一部分
var bar = function foo(){}; // 表达式,因为它是赋值表达式的一部分
new function bar(){}; // 表达式,因为它是new表达式
(function(){
function bar(){} // 声明,因为它是函数体的一部分
})();</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div>There is also a less common function expression, which is
enclosed in parentheses. The reason why it is an expression is because the parentheses () are A grouping operator, which can only contain expressions Let’s look at the jQuery source code again:
(function(window, undefined) {
/...
})(window)The above code structure can be divided into two parts
: (function(){window , undefined}) and (window) ,
So adding (window) after this expression means executing this anonymous function and passing in the parameter window.
prototype prototype
Let’s understand what a prototype is?
In JavaScript,
The prototype is also an object. The property inheritance of the object can be realized through the prototype. JavaScript objects all contain a " [[Prototype]]"Internal attribute, this attribute corresponds to the prototype of the object. The two attributes "prototype" and "proto" may sometimes be confused. "Person.prototype" and "Person.proto" are completely different.
Here is a brief introduction to "prototype" and "proto":
1. For all objects, there is a proto attribute, which corresponds to the prototype of the object
2. For function objects, in addition to the proto attribute, there is also a prototype attribute.
When a function is used as a constructor to create an instance, the prototype attribute value of the function will be used as The prototype is assigned to all object instances (that is, setting the proto attribute of the instance)function Person(name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.getInfo = function(){
console.log(this.name + " is " + this.age + " years old");
};
//调用
var will = new Person("Will", 28);
will.getInfo();//"Will is 28 years old"
Definition of closure:
When an
inner functionis referenced by a variable outside of its outer function, a closure is formed.
The role of closure:Before understanding the role of closure, we first understand the GC mechanism in javascript:
In javascript ,
If an object is no longer referenced, then the object will be recycled by GC, otherwise the object will always be saved in memory.在上述例子中,B定义在A中,因此B依赖于A,而外部变量 c 又引用了B, 所以A间接的被 c 引用, 也就是说,A不会被GC回收,会一直保存在内存中。为了证明我们的推理,看如下例子: count是A中的一个变量,它的值在B中被改变,函数B每执行一次,count的值就在原来的基础上累加1。因此,A中的count一直保存在内存中。 这就是闭包的作用,有时候我们需要一个模块中定义这样一个变量:希望这个变量一直保存在内存中但又不会“污染”全局的变量,这个时候,我们就可以用闭包来定义这个模块 在看jQuery源码: 我们知道了 什么是闭包:当一个内部函数被其外部函数之外的变量引用时,就形成了一个闭包。 jQuery.fn的init 函数被jQuery 的构造函数调用了,这里形成了一个闭包。 问题关键来了。 如何实现无new构建 JavaScript是函数式语言,函数可以实现类,类就是面向对象编程中最基本的概念 这是常规的使用方法,显而易见jQuery不是这样玩的 要实现这样,那么jQuery就要看成一个类,那么$()应该是返回类的实例才对 按照jQuery的抒写方式 要实现这样,那么jQuery就要看成一个类,那么$()应该是返回类的实例才对 所以把代码改一下: 通过 那么如何返回一个正确的实例? 在javascript中实例this只跟原型有关系 那么可以把jQuery类当作一个工厂方法来创建实例,把这个方法放到aQuery.prototye原型中 当执行 很明显 问题来了init的this指向的是 因为this只是指向 这样看似没有问题,其实问题很大的 为什么是new jQuery.fn.init? 看如下代码: 当我调用 传入"a"的时候,修改age=18,及aQuery("a").age 的值为18 但是当我 传入"b"的时候 并没又修改 age的值,我也希望得到默认age的值20,但是aQuery("b").age 的值为18. 因为在 调用aQuery("a").age 的时候age被修改了。 这样的情况下就出错了,所以需要设计出独立的作用域才行。 jQuery框架分隔作用域的处理 很明显通过实例 我们修改一下代码: 又出现一个新的问题, 怎么访问jQuery类原型上的属性与方法? 做到既能隔离作用域还能使用jQuery原型对象的作用域呢,还能在返回实例中访问jQuery的原型对象? 实现的关键点 我们再改一下: 最后在看一下jQuery源码: 是不是明白了? 哈哈哈~~~ 在简单说两句: 大部分人初看 1)首先要明确,使用 2)将 3)也就是实例化方法存在这么一个关系链 1.jQuery.fn.init.prototype = jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype ; 2.new jQuery.fn.init() 相当于 new jQuery() ; 3.jQuery() 返回的是 new jQuery.fn.init(),而 var obj = new jQuery(),所以这 2 者是相当的,所以我们可以无 new 实例化 jQuery 对象。 相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章! 推荐阅读:function A(){
var count = 0;
function B(){
count ++;
console.log(count);
}
return B;
}
var c = A();
c();// 1
c();// 2
c();// 3(function(window, undefined) {
var
// ...
jQuery = function(selector, context) {
// The jQuery object is actually just the init constructor 'enhanced'
return new jQuery.fn.init(selector, context, rootjQuery);
},
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype = {
init: function(selector, context, rootjQuery) {
// ...
}
}
jQuery.fn.init.prototype = jQuery.fn;
})(window);
构造函数及调用代码:// ...
jQuery = function(selector, context) {
// The jQuery object is actually just the init constructor 'enhanced'
return new jQuery.fn.init(selector, context, rootjQuery);
},var aQuery = function(selector, context) {
//构造函数
}
aQuery.prototype = {
//原型
name:function(){},
age:function(){}
}
var a = new aQuery();
a.name();$().ready()
$().noConflict()
var aQuery = function(selector, context) {
return new aQuery();
}
aQuery.prototype = {
name:function(){},
age:function(){}
}new aQuery(),虽然返回的是一个实例,但是也能看出很明显的问题,死循环了!var aQuery = function(selector, context) {
return aQuery.prototype.init(selector);
}
aQuery.prototype = {
init:function(selector){
return this;
}
name:function(){},
age:function(){}
}aQuery() 返回的实例: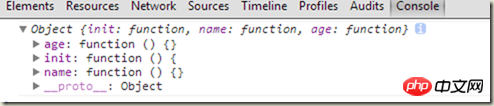
aQuery()返回的是aQuery类的实例,那么在init中的this其实也是指向的aQuery类的实例aQuery类,如果把init函数也当作一个构造器,那么内部的this要如何处理?var aQuery = function(selector, context) {
return aQuery.prototype.init(selector);
}
aQuery.prototype = {
init: function(selector) {
this.age = 18
return this;
},
name: function() {},
age: 20
}
aQuery().age //18aQuery类的,所以aQuery的age属性是可以被修改的。var aQuery = function(selector, context) {
return aQuery.prototype.init(selector);
}
aQuery.prototype = {
init: function(selector) {
if(selector=="a")
this.age = 18
return this;
},
name: function() {},
age: 20
}
aQuery("a").age //18
aQuery("b").age //18jQuery = function( selector, context ) {
// The jQuery object is actually just the init constructor 'enhanced'
return new jQuery.fn.init( selector, context, rootjQuery );
},init函数,每次都构建新的init实例对象,来分隔this,避免交互混淆var aQuery = function(selector, context) {
return new aQuery.prototype.init(selector);
}
aQuery.prototype = {
init: function(selector) {
if(selector=="a")
this.age = 18
return this;
},
name: function() {},
age: 20
}
aQuery("a").age //18
aQuery("b").age //undefined
aQuery("a").name() //Uncaught TypeError: Object [object Object] has no method 'name'age :undefined,name() :抛出错误,无法找到这个方法,所以很明显new的init跟jquery类的this分离了// Give the init function the jQuery prototype for later instantiation
jQuery.fn.init.prototype = jQuery.fn;
var aQuery = function(selector, context) {
return new aQuery.prototype.init(selector);
}
aQuery.prototype = {
init: function(selector) {
if(selector=="a")
this.age = 18
return this;
},
name: function() {
return age;
},
age: 20
}
aQuery.prototype.init.prototype = aQuery.prototype;
aQuery("a").age //18
aQuery("b").age //20
aQuery("a").name() //20(function(window, undefined) {
var
// ...
jQuery = function(selector, context) {
// The jQuery object is actually just the init constructor 'enhanced'
return new jQuery.fn.init(selector, context, rootjQuery);
},
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype = {
init: function(selector, context, rootjQuery) {
// ...
}
}
jQuery.fn.init.prototype = jQuery.fn;
})(window); jQuery.fn.init.prototype = jQuery.fn 这一句都会被卡主,很是不解。但是这句真的算是 jQuery 的绝妙之处。理解这几句很重要,分点解析一下: $('xxx') 这种实例化方式,其内部调用的是 return new jQuery.fn.init(selector, context, rootjQuery) 这一句话,也就是构造实例是交给了 jQuery.fn.init() 方法取完成。jQuery.fn.init 的 prototype 属性设置为 jQuery.fn,那么使用 new jQuery.fn.init() 生成的对象的原型对象就是 jQuery.fn ,所以挂载到 jQuery.fn 上面的函数就相当于挂载到 jQuery.fn.init() 生成的 jQuery 对象上,所有使用 new jQuery.fn.init() 生成的对象也能够访问到 jQuery.fn 上的所有原型方法。
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the use of jQuery without new construction. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Windows operating system is one of the most popular operating systems in the world, and its new version Win11 has attracted much attention. In the Win11 system, obtaining administrator rights is an important operation. Administrator rights allow users to perform more operations and settings on the system. This article will introduce in detail how to obtain administrator permissions in Win11 system and how to effectively manage permissions. In the Win11 system, administrator rights are divided into two types: local administrator and domain administrator. A local administrator has full administrative rights to the local computer
 Detailed explanation of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Detailed explanation of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Detailed explanation of division operation in OracleSQL In OracleSQL, division operation is a common and important mathematical operation, used to calculate the result of dividing two numbers. Division is often used in database queries, so understanding the division operation and its usage in OracleSQL is one of the essential skills for database developers. This article will discuss the relevant knowledge of division operations in OracleSQL in detail and provide specific code examples for readers' reference. 1. Division operation in OracleSQL
 Detailed explanation of the role and usage of PHP modulo operator
Mar 19, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
Detailed explanation of the role and usage of PHP modulo operator
Mar 19, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
The modulo operator (%) in PHP is used to obtain the remainder of the division of two numbers. In this article, we will discuss the role and usage of the modulo operator in detail, and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand. 1. The role of the modulo operator In mathematics, when we divide an integer by another integer, we get a quotient and a remainder. For example, when we divide 10 by 3, the quotient is 3 and the remainder is 1. The modulo operator is used to obtain this remainder. 2. Usage of the modulo operator In PHP, use the % symbol to represent the modulus
 How to use PUT request method in jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
How to use PUT request method in jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
How to use PUT request method in jQuery? In jQuery, the method of sending a PUT request is similar to sending other types of requests, but you need to pay attention to some details and parameter settings. PUT requests are typically used to update resources, such as updating data in a database or updating files on the server. The following is a specific code example using the PUT request method in jQuery. First, make sure you include the jQuery library file, then you can send a PUT request via: $.ajax({u
 jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page
Feb 28, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page
Feb 28, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Title: jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page In web development, we often need to modify and operate elements on the page. When using jQuery, sometimes you need to modify the text content of all a tags in the page at once, which can save time and energy. The following will introduce how to use jQuery to quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page, and give specific code examples. First, we need to introduce the jQuery library file and ensure that the following code is introduced into the page: <
 Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags
Feb 28, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags
Feb 28, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
Title: Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags. jQuery is a popular JavaScript library that is widely used to handle DOM operations. In web development, we often encounter the need to modify the text content of the link tag (a tag) on the page. This article will explain how to use jQuery to achieve this goal, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to introduce the jQuery library into the page. Add the following code in the HTML file:
 How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute?
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:03 AM
How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute?
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:03 AM
How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute? When using jQuery to operate DOM elements, you often encounter situations where you need to determine whether an element has a specific attribute. In this case, we can easily implement this function with the help of the methods provided by jQuery. The following will introduce two commonly used methods to determine whether a jQuery element has specific attributes, and attach specific code examples. Method 1: Use the attr() method and typeof operator // to determine whether the element has a specific attribute
 Build browser-based applications with Golang
Apr 08, 2024 am 09:24 AM
Build browser-based applications with Golang
Apr 08, 2024 am 09:24 AM
Build browser-based applications with Golang Golang combines with JavaScript to build dynamic front-end experiences. Install Golang: Visit https://golang.org/doc/install. Set up a Golang project: Create a file called main.go. Using GorillaWebToolkit: Add GorillaWebToolkit code to handle HTTP requests. Create HTML template: Create index.html in the templates subdirectory, which is the main template.




