JavaScript event model (graphic tutorial)
This article mainly introduces the event model in JavaScript, which includes the DOM0-level event model and the DOM2-level event model (event capture and event bubbling and DOM2-level registration events and deactivation events). Friends who need it can refer to it. There are two event models in
javascript: DOM0 and DOM2. As for these two time models, I have never been very clear about them. Now I finally understand a little more by looking up information online.
1. DOM0-level event model
The DOM0-level event model is an early event model and is supported by all browsers. Its implementation is also relatively simple. The code is as follows:
<p id = 'click'>click me</p>
<script>
document.getElementById('click').onclick = function(event){
alert(event.target);
}
</script>This event model is to register the event name directly on the dom object. This code is on the p tag. An onclick event is registered, and the clicked target is output inside this event function. Dismissing the event is even simpler, just copy null to the event function, as follows:
document.getElementById('click'_).onclick = null;
From this we can We know that in dom0, a dom object can only register one function of the same type, because if multiple functions of the same type are registered, overwriting will occur and the previously registered functions will be invalid.
var click = document.getElementById('click');
click.onclick = function(){
alert('you click the first function');
};
click.onclick = function(){
alert('you click the second function')
}In this code, we registered two onclick functions for the dom object, but the result was that only the second one was executed. A registered function, the previously registered function is overwritten.
2. DOM2-level event model
1. Event capture and event bubbling (capture, bubble)
First of all, IE8 and below do not support this event model. The mechanism of event capture and event bubbling is as follows:
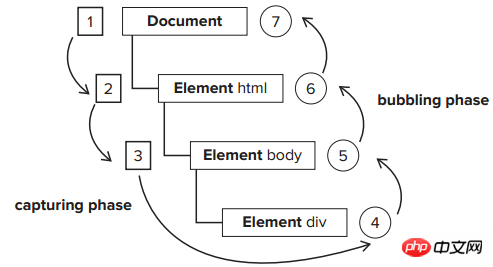
As shown in the figure above, 123 represents event capture and 4567 represents event bubbling. First we use the following code:
<p id = 'outer' style = 'margin: 100px 0 0 100px; width: 200px;height: 200px; background: red;'> <p id="inner" style = 'margin-left:20px; width: 50px;height:50px; background: green;'></p> </p>
## Suppose we click on p with the ID of inner, then the event at this time The process is to first execute the capture phase: document-html-body-p(outer). Then execute the bubbling phase: p(inner)-p(outer)-body-html-document.
2. DOM2-level registration events and deactivation events
Use addEventListener and removeEventListener in DOM2 level to register and deactivate events (IE8 and Not supported in previous versions). The advantage of this function compared to the previous method is that a DOM object can register multiple events of the same type, and event overwriting will not occur, and each event function will be executed in sequence. addEventListener('event name','event callback','capture/bubble'). The example is as follows:<p id = 'outer' style = 'margin: 100px 0 0 100px; width: 200px;height: 200px; background: red;'>
<p id="inner" style = 'margin-left:20px; width: 50px;height:50px; background: green;'></p>
</p>
<script>
var click = document.getElementById('inner');
click.addEventListener('click',function(){
alert('click one');
},false);
click.addEventListener('click',function(){
alert('click two');
},false);
</script> Next we demonstrate how to use the event stream generation mechanism.
<p id = 'outer' style = 'margin: 100px 0 0 100px; width: 200px;height: 200px; background: red;'>
<p id="inner" style = 'margin-left:20px; width: 50px;height:50px; background: green;'></p>
</p>
<script>
var click = document.getElementById('inner');
var clickouter = document.getElementById('outer');
click.addEventListener('click',function(){
alert('inner show');
},true);
clickouter.addEventListener('click',function(){
alert('outer show');
},true);
</script>alickouter.addEventListener('click',function(){
alert('outer show');
},false);<script>
var click = document.getElementById('inner');
var clickouter = document.getElementById('outer');
click.addEventListener('click',function(){
alert('capture show');
},true);
click.addEventListener('click',function(){
alert('bubble show');
},false);
</script>比如在自制下拉框的时候,我们点击浏览器的其他位置,我们需要下拉框的options隐藏,这时我们就要用到stopPropagation了。如下:
<script>
var click = document.getElementById('inner');
var clickouter = document.getElementById('outer');
click.addEventListener('click',function(event){
alert('inner show');
event.stopPropagation();
},false);
clickouter.addEventListener('click',function(){
alert('outer show');
},false);
</script> 正常的情况下,我们在不添加stopPropagation函数时,首先应该执行inner,然后执行outer,但是当我们在inner的事件函数中添加了stopPropagation函数之后,执行完inner的事件函数之后,就不会在执行outer的事件函数了,也可以理解为事件冒泡到inner之后就消失了,因此也就不会在执行接下来的事件函数了。
由于事件捕获阶段没有可以阻止事件的函数,所以一般都是设置为事件冒泡。
好了以上就是全部内容啦 ,希望对大家的学习有所帮助~~
上面是我整理给大家的,希望今后会对大家有帮助。
相关文章:
The above is the detailed content of JavaScript event model (graphic tutorial). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1672
1672
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1332
1332
 25
25
 1277
1277
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 Recommended: Excellent JS open source face detection and recognition project
Apr 03, 2024 am 11:55 AM
Recommended: Excellent JS open source face detection and recognition project
Apr 03, 2024 am 11:55 AM
Face detection and recognition technology is already a relatively mature and widely used technology. Currently, the most widely used Internet application language is JS. Implementing face detection and recognition on the Web front-end has advantages and disadvantages compared to back-end face recognition. Advantages include reducing network interaction and real-time recognition, which greatly shortens user waiting time and improves user experience; disadvantages include: being limited by model size, the accuracy is also limited. How to use js to implement face detection on the web? In order to implement face recognition on the Web, you need to be familiar with related programming languages and technologies, such as JavaScript, HTML, CSS, WebRTC, etc. At the same time, you also need to master relevant computer vision and artificial intelligence technologies. It is worth noting that due to the design of the Web side
 PHP and JS Development Tips: Master the Method of Drawing Stock Candle Charts
Dec 18, 2023 pm 03:39 PM
PHP and JS Development Tips: Master the Method of Drawing Stock Candle Charts
Dec 18, 2023 pm 03:39 PM
With the rapid development of Internet finance, stock investment has become the choice of more and more people. In stock trading, candle charts are a commonly used technical analysis method. It can show the changing trend of stock prices and help investors make more accurate decisions. This article will introduce the development skills of PHP and JS, lead readers to understand how to draw stock candle charts, and provide specific code examples. 1. Understanding Stock Candle Charts Before introducing how to draw stock candle charts, we first need to understand what a candle chart is. Candlestick charts were developed by the Japanese
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 The relationship between js and vue
Mar 11, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
The relationship between js and vue
Mar 11, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
The relationship between js and vue: 1. JS as the cornerstone of Web development; 2. The rise of Vue.js as a front-end framework; 3. The complementary relationship between JS and Vue; 4. The practical application of JS and Vue.
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service
 How to implement change event binding of select elements in jQuery
Feb 23, 2024 pm 01:12 PM
How to implement change event binding of select elements in jQuery
Feb 23, 2024 pm 01:12 PM
jQuery is a popular JavaScript library that can be used to simplify DOM manipulation, event handling, animation effects, etc. In web development, we often encounter situations where we need to change event binding on select elements. This article will introduce how to use jQuery to bind select element change events, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to create a dropdown menu with options using labels:
 How to build event-based applications using PHP
May 04, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
How to build event-based applications using PHP
May 04, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
Methods for building event-based applications in PHP include using the EventSourceAPI to create an event source and using the EventSource object to listen for events on the client side. Send events using Server Sent Events (SSE) and listen for events on the client side using an XMLHttpRequest object. A practical example is to use EventSource to update inventory counts in real time in an e-commerce website. This is achieved on the server side by randomly changing the inventory and sending updates, and the client listens for inventory updates through EventSource and displays them in real time.
 A Deep Dive into Close Button Events in jQuery
Feb 24, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
A Deep Dive into Close Button Events in jQuery
Feb 24, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
In-depth understanding of the close button event in jQuery During the front-end development process, we often encounter situations where we need to implement the close button function, such as closing pop-up windows, closing prompt boxes, etc. When using jQuery, a popular JavaScript library, it becomes extremely simple and convenient to implement the close button event. This article will delve into how to use jQuery to implement close button events, and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand and master this technology. First, we need to understand how to define




