How to use Vue nextTick
This time I will show you how to use Vue nextTick and what are the precautions for using Vue nextTick. The following is a practical case, let's take a look.
export default {
data () {
return {
msg: 0
}
},
mounted () {
this.msg = 1
this.msg = 2
this.msg = 3
},
watch: {
msg () {
console.log(this.msg)
}
}
}queueWatcher
We define watch to listen to msg, which will actually be called by Vue like vm.$watch(keyOrFn, handler, options). $watch is a function bound to vm when we initialize it, used to create Watcher objects. Then let's take a look at how the handler is handled in Watcher:this.deep = this.user = this.lazy = this.sync = false
...
update () {
if (this.lazy) {
this.dirty = true
} else if (this.sync) {
this.run()
} else {
queueWatcher(this)
}
}
...const queue: Array<Watcher> = []
let has: { [key: number]: ?true } = {}
let waiting = false
let flushing = false
...
export function queueWatcher (watcher: Watcher) {
const id = watcher.id
if (has[id] == null) {
has[id] = true
if (!flushing) {
queue.push(watcher)
} else {
// if already flushing, splice the watcher based on its id
// if already past its id, it will be run next immediately.
let i = queue.length - 1
while (i > index && queue[i].id > watcher.id) {
i--
}
queue.splice(i + 1, 0, watcher)
}
// queue the flush
if (!waiting) {
waiting = true
nextTick(flushSchedulerQueue)
}
}
}ViewUpdate:
function flushSchedulerQueue () {
flushing = true
let watcher, id
...
for (index = 0; index < queue.length; index++) {
watcher = queue[index]
id = watcher.id
has[id] = null
watcher.run()
...
}
}export const nextTick = (function () {
const callbacks = []
let pending = false
let timerFunc
function nextTickHandler () {
pending = false
const copies = callbacks.slice(0)
callbacks.length = 0
for (let i = 0; i < copies.length; i++) {
copies[i]()
}
}
// An asynchronous deferring mechanism.
// In pre 2.4, we used to use microtasks (Promise/MutationObserver)
// but microtasks actually has too high a priority and fires in between
// supposedly sequential events (e.g. #4521, #6690) or even between
// bubbling of the same event (#6566). Technically setImmediate should be
// the ideal choice, but it's not available everywhere; and the only polyfill
// that consistently queues the callback after all DOM events triggered in the
// same loop is by using MessageChannel.
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (typeof setImmediate !== 'undefined' && isNative(setImmediate)) {
timerFunc = () => {
setImmediate(nextTickHandler)
}
} else if (typeof MessageChannel !== 'undefined' && (
isNative(MessageChannel) ||
// PhantomJS
MessageChannel.toString() === '[object MessageChannelConstructor]'
)) {
const channel = new MessageChannel()
const port = channel.port2
channel.port1.onmessage = nextTickHandler
timerFunc = () => {
port.postMessage(1)
}
} else
/* istanbul ignore next */
if (typeof Promise !== 'undefined' && isNative(Promise)) {
// use microtask in non-DOM environments, e.g. Weex
const p = Promise.resolve()
timerFunc = () => {
p.then(nextTickHandler)
}
} else {
// fallback to setTimeout
timerFunc = () => {
setTimeout(nextTickHandler, 0)
}
}
return function queueNextTick (cb?: Function, ctx?: Object) {
let _resolve
callbacks.push(() => {
if (cb) {
try {
cb.call(ctx)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, ctx, 'nextTick')
}
} else if (_resolve) {
_resolve(ctx)
}
})
if (!pending) {
pending = true
timerFunc()
}
// $flow-disable-line
if (!cb && typeof Promise !== 'undefined') {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
_resolve = resolve
})
}
}
})()if (typeof setImmediate !== 'undefined' && isNative(setImmediate)) {
timerFunc = () => {
setImmediate(nextTickHandler)
}
} else if (typeof MessageChannel !== 'undefined' && (
isNative(MessageChannel) ||
// PhantomJS
MessageChannel.toString() === '[object MessageChannelConstructor]'
)) {
const channel = new MessageChannel()
const port = channel.port2
channel.port1.onmessage = nextTickHandler
timerFunc = () => {
port.postMessage(1)
}
} else
/* istanbul ignore next */
if (typeof Promise !== 'undefined' && isNative(Promise)) {
// use microtask in non-DOM environments, e.g. Weex
const p = Promise.resolve()
timerFunc = () => {
p.then(nextTickHandler)
}
} else {
// fallback to setTimeout
timerFunc = () => {
setTimeout(nextTickHandler, 0)
}
}setImmediate, MessageChannel VS setTimeout
We define setImmediate and MessageChannel first. Why should we use them first to create macroTask instead of setTimeout? HTML5 stipulates that the minimum time delay of setTimeout is 4ms, which means that under ideal circumstances, the fastest asynchronous callback can trigger is 4ms. Vue uses so many functions to simulate asynchronous tasks, with only one purpose, which is to make the callback asynchronous and called as early as possible. The delays of MessageChannel and setImmediate are obviously smaller than setTimeout.Solution to the problem
With these foundations in mind, let’s look at the problems mentioned above again. Because Vue's event mechanism schedules execution through the event queue, it will wait for the main process to be idle before scheduling, so go back and wait for all processes to complete before updating again. This kind of performance advantage is obvious, for example: Now there is a situation where the value of test will beInteresting question
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#example',
data: {
msg: 'begin',
},
mounted () {
this.msg = 'end'
console.log('1')
setTimeout(() => { // macroTask
console.log('3')
}, 0)
Promise.resolve().then(function () { //microTask
console.log('promise!')
})
this.$nextTick(function () {
console.log('2')
})
}
})- Because this.msg = 'end' is triggered first, the watcher's update is triggered, thereby pushing the update operation callback into the vue event queue.
- this.$nextTick also enters a new callback function for event queue push. They all come through setImmediate --> MessageChannel --> Promise --> setTimeout Define timeFunc. Promise.resolve().then is a microTask, so it will print the promise first.
When MessageChannel and setImmediate are supported, their execution order takes precedence over setTimeout (in IE11/Edge, setImmediate delay can be within 1ms, while setTimeout has a minimum delay of 4ms, so setImmediate executes the callback function earlier than setTimeout(0). Secondly, because in the event queue, the callback array is received first), so 2 will be printed, and then 3
but In the case where MessageChannel and setImmediate are not supported, timeFunc will be defined through Promise, and the old version of Vue before 2.4 will execute promise first. This situation will cause the order to become: 1, 2, promise, 3. Because this.msg must first trigger the dom update function, the dom update function will first be collected by the callback into the asynchronous time queue, and then Promise.resolve().then(function () { console.log('promise!')} will be defined. ) such a microTask, and then defining $nextTick will be collected by the callback. We know that the queue satisfies the first-in-first-out principle, so the objects collected by the callback are executed first.
I believe you have mastered the method after reading the case in this article. For more exciting information, please pay attention to other related articles on the php Chinese website!
Recommended reading:
How to operate JS to realize transparency gradient animation
##How to operate JS to realize simple folding and unfolding animation
The above is the detailed content of How to use Vue nextTick. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use magnet links
Feb 18, 2024 am 10:02 AM
How to use magnet links
Feb 18, 2024 am 10:02 AM
Magnet link is a link method for downloading resources, which is more convenient and efficient than traditional download methods. Magnet links allow you to download resources in a peer-to-peer manner without relying on an intermediary server. This article will introduce how to use magnet links and what to pay attention to. 1. What is a magnet link? A magnet link is a download method based on the P2P (Peer-to-Peer) protocol. Through magnet links, users can directly connect to the publisher of the resource to complete resource sharing and downloading. Compared with traditional downloading methods, magnetic
 How to use mdf and mds files
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
How to use mdf and mds files
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
How to use mdf files and mds files With the continuous advancement of computer technology, we can store and share data in a variety of ways. In the field of digital media, we often encounter some special file formats. In this article, we will discuss a common file format - mdf and mds files, and introduce how to use them. First, we need to understand the meaning of mdf files and mds files. mdf is the extension of the CD/DVD image file, and the mds file is the metadata file of the mdf file.
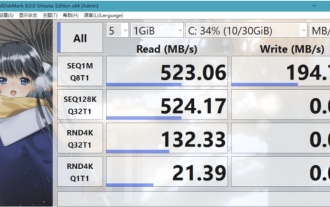 What software is crystaldiskmark? -How to use crystaldiskmark?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
What software is crystaldiskmark? -How to use crystaldiskmark?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
CrystalDiskMark is a small HDD benchmark tool for hard drives that quickly measures sequential and random read/write speeds. Next, let the editor introduce CrystalDiskMark to you and how to use crystaldiskmark~ 1. Introduction to CrystalDiskMark CrystalDiskMark is a widely used disk performance testing tool used to evaluate the read and write speed and performance of mechanical hard drives and solid-state drives (SSD). Random I/O performance. It is a free Windows application and provides a user-friendly interface and various test modes to evaluate different aspects of hard drive performance and is widely used in hardware reviews
 How to download foobar2000? -How to use foobar2000
Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
How to download foobar2000? -How to use foobar2000
Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
foobar2000 is a software that can listen to music resources at any time. It brings you all kinds of music with lossless sound quality. The enhanced version of the music player allows you to get a more comprehensive and comfortable music experience. Its design concept is to play the advanced audio on the computer The device is transplanted to mobile phones to provide a more convenient and efficient music playback experience. The interface design is simple, clear and easy to use. It adopts a minimalist design style without too many decorations and cumbersome operations to get started quickly. It also supports a variety of skins and Theme, personalize settings according to your own preferences, and create an exclusive music player that supports the playback of multiple audio formats. It also supports the audio gain function to adjust the volume according to your own hearing conditions to avoid hearing damage caused by excessive volume. Next, let me help you
 Simple guide to pip mirror source: easily master how to use it
Jan 16, 2024 am 10:18 AM
Simple guide to pip mirror source: easily master how to use it
Jan 16, 2024 am 10:18 AM
Get started easily: How to use pip mirror source With the popularity of Python around the world, pip has become a standard tool for Python package management. However, a common problem that many developers face when using pip to install packages is slowness. This is because by default, pip downloads packages from Python official sources or other external sources, and these sources may be located on overseas servers, resulting in slow download speeds. In order to improve download speed, we can use pip mirror source. What is a pip mirror source? To put it simply, just
 BTCC tutorial: How to bind and use MetaMask wallet on BTCC exchange?
Apr 26, 2024 am 09:40 AM
BTCC tutorial: How to bind and use MetaMask wallet on BTCC exchange?
Apr 26, 2024 am 09:40 AM
MetaMask (also called Little Fox Wallet in Chinese) is a free and well-received encryption wallet software. Currently, BTCC supports binding to the MetaMask wallet. After binding, you can use the MetaMask wallet to quickly log in, store value, buy coins, etc., and you can also get 20 USDT trial bonus for the first time binding. In the BTCCMetaMask wallet tutorial, we will introduce in detail how to register and use MetaMask, and how to bind and use the Little Fox wallet in BTCC. What is MetaMask wallet? With over 30 million users, MetaMask Little Fox Wallet is one of the most popular cryptocurrency wallets today. It is free to use and can be installed on the network as an extension
 How to use NetEase Mailbox Master
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
How to use NetEase Mailbox Master
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
NetEase Mailbox, as an email address widely used by Chinese netizens, has always won the trust of users with its stable and efficient services. NetEase Mailbox Master is an email software specially created for mobile phone users. It greatly simplifies the process of sending and receiving emails and makes our email processing more convenient. So how to use NetEase Mailbox Master, and what specific functions it has. Below, the editor of this site will give you a detailed introduction, hoping to help you! First, you can search and download the NetEase Mailbox Master app in the mobile app store. Search for "NetEase Mailbox Master" in App Store or Baidu Mobile Assistant, and then follow the prompts to install it. After the download and installation is completed, we open the NetEase email account and log in. The login interface is as shown below
 How to use Baidu Netdisk app
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
How to use Baidu Netdisk app
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
Cloud storage has become an indispensable part of our daily life and work nowadays. As one of the leading cloud storage services in China, Baidu Netdisk has won the favor of a large number of users with its powerful storage functions, efficient transmission speed and convenient operation experience. And whether you want to back up important files, share information, watch videos online, or listen to music, Baidu Cloud Disk can meet your needs. However, many users may not understand the specific use method of Baidu Netdisk app, so this tutorial will introduce in detail how to use Baidu Netdisk app. Users who are still confused can follow this article to learn more. ! How to use Baidu Cloud Network Disk: 1. Installation First, when downloading and installing Baidu Cloud software, please select the custom installation option.






