Introduction to Vue component communication practices
This article mainly introduces Vue component communication practice records (recommended). The content is quite good. I will share it with you now and give it as a reference.
Component communication
Almost all mvvm frameworks involve the function of component communication (complain about knockout, after all, it is the originator, so let’s not talk about it). And judging from the current front-end form, componentization is the foundation of a project. Therefore, after choosing a suitable framework, as the number of components continues to increase and the complexity of the business increases, communication between components becomes particularly important.
Practical Method
Due to the replacement of a new framework, our project was updated from Avalon to Vue. However, in order to be compatible with previous business codes, the standard practices of vue cannot be used directly. Method, I still took it and encapsulated a vue class. It does not affect the use of the specific business. I will write out the encapsulation process and talk about it later. Let’s summarize the communication practices that have been used recently.
1. The parent component passes data to the child components through props
vmodel contains two child components
<p class="w-base"> <book-component v-bind:bookdata="book"></book-component> </p> <p class="base"> <node-component v-bind:catalog="catalog" ></node-component> </p>
In the above code, we can see that two subcomponents are defined, and data is passed using the specified v-bind instruction, and the subcomponent will receive the passed data.
Vue.component('book-component', {
template: tpl,//可以传进来子组件的模板文件
props: ['book'],
data: function () {
return { myBook: this.bookdata }
}
})It is recommended to define a local variable for initialization after receiving the one-way props data.
2. Other ways to communicate between parent components and child components
vue provides three APIs available to us for instances $children and $refs and $ parent.
$children : Direct child components of the current instance. Note that $children does not guarantee order, nor is it responsive.
$refs : Contains objects of all child components registered with ref in the current instance.
$parent: The parent instance of the current instance.
So, if our component wants to call a subcomponent in terms of communication, the only method that can be used is $refs, because $children is an array, and the order is not guaranteed, and there is no relevant ID to find. That specific subcomponent we need. But if you use $refs to find a specific subcomponent, you must register a ref for that subcomponent.
Template of parent component
<!-- vm.$refs.child will be the child comp instance --> <child-component ref="child"></child-comp>
Parent component
//找到子组件并且调用它的方法 var myChild = this.$refs.child; mymyChild.func();
Subcomponent
//找到父组件并且调用它的方法 var myParent = this.$parent; mymyChild.func();
3. Two communication methods between parallel components
a.Officially provided events bus
var bus = new Vue()
// 触发组件 A 中的事件
bus.$emit('id-selected', 1)
// 在组件 B 创建的钩子中监听事件
bus.$on('id-selected', function (id) {
// ...
})b. Find the sibling component through the parent component
//找到父组件的$refs对象,然后找到组件的兄弟组件
var $refs = this.$parent?this.$parent.$refs:{};
var childComponent = $refs.child; //child为改组件的ref属性值In fact, the above The best practice for both methods is to encapsulate them into the project's base class, so that you don't have to define an empty Vue() instance every time, but instead have this event bus in the base class of each instance. You can also encapsulate the method of finding other sibling components, but the sibling component must register ref
The following method is the method I encapsulated in the project to find the parent component and then find the sibling component.
//平行组件之间的通信
getComponentByRef: function(refId) {
var $refs = this.$parent?this.$parent.$refs:{};
for (var $id in $refs) {
if ($id == refId) {
return $refs[$id];
}
}
return null;
}Use
//在组件中直接使用
this.getComponentByRef("booknode").updateNode(this.node);##4. Complex data communication between components Vuex
When it comes to vuex, many people who are new to vue will actively avoid using it. In fact, it is not as complicated as imagined. The best start is to walk through the small examples given after introducing vuex. But if your project is not complex, you don’t need to consider state management. So when do you need to use state management? Let’s look at such a layout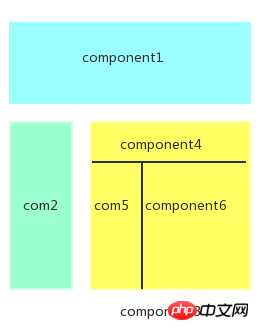
Problem:
- Multiple attempts to rely on the same state
- Multiple levels of nesting Components, data changes and code maintenance are difficult
Vue2.0 Multi-Tab switching component packaging introduction
Vue adds request interceptor and vue -Use of resource interceptor
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to Vue component communication practices. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Vue multi-page development is a way to build applications using the Vue.js framework, where the application is divided into separate pages: Code Maintenance: Splitting the application into multiple pages can make the code easier to manage and maintain. Modularity: Each page can be used as a separate module for easy reuse and replacement. Simple routing: Navigation between pages can be managed through simple routing configuration. SEO Optimization: Each page has its own URL, which helps SEO.
 How to query the version of vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
How to query the version of vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
You can query the Vue version by using Vue Devtools to view the Vue tab in the browser's console. Use npm to run the "npm list -g vue" command. Find the Vue item in the "dependencies" object of the package.json file. For Vue CLI projects, run the "vue --version" command. Check the version information in the <script> tag in the HTML file that refers to the Vue file.
 How to use function intercept vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 06:51 AM
How to use function intercept vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 06:51 AM
Function interception in Vue is a technique used to limit the number of times a function is called within a specified time period and prevent performance problems. The implementation method is: import the lodash library: import { debounce } from 'lodash'; Use the debounce function to create an intercept function: const debouncedFunction = debounce(() => { / Logical / }, 500); Call the intercept function, and the control function is called at most once in 500 milliseconds.




