Use JS to create a stopwatch accurate to 10ms (code attached)
The content of this article is about using JS to realize the production of a stopwatch that can be accurate to 10ms (with code). It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you. help.
I have just come into contact with js during this period and want to use the knowledge I have learned to make a simple stopwatch.
The ideas for making a stopwatch are as follows:
1. First determine the function and interface.
My purpose is to make the simplest stopwatch, so I only need the start, end and clear functions. The interface is as shown below:
Not started running: 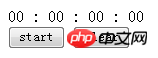
Running: 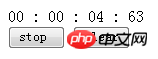
2. Conceive the implementation method.
First of all, the core method is definitely the setInterval() method, which is used to display the time periodically. Because I want to be accurate to 10ms, I set the time interval to 10.
Furthermore, how to increase the time?
A . What I started to think of was setting variables milliSeconds, seconds, minutes, and hours. milliSeconds increments by 1 every 10ms, when When milliSeconds >= 100, use milliSeconds modulo 100, and at the same time, seconds is increased by 1. In the same way, when seconds reaches 60 minutes is incremented by 1, and hours is incremented by 1 when minutes reaches 60.
However, in order to ensure the uniformity of the format (I want to display 02:01:24:06 instead of 2:1:24:6), I changed the four variables into 8 variables. , the same thoughts as above. (For the code, see “Stopwatch with Delay” at the end of this page).
However, there is a delay problem during operation, and the delay will accumulate. It can still run relatively accurately when the time is short. As time goes by, the time on the stopwatch will deviate greatly from the standard time.
B . In order to reduce the delay, I designed another method (actually this method has a higher delay than the previous one). At this time, only one time variable is used to record the trigger start The number of milliseconds that have passed since the button was pressed (time is in 10ms, a/b/c/d below represents milliseconds (10ms), seconds, minutes, and hours). In order to pursue the unity of format, I added if statement, when a/b/c/d is less than 10, add 0 placeholder in front.
var a=time%100; var b=time%6000/100; var c=time%360000/6000; var d=time%8640000/36000;
Compare plan A with plan B. Since A uses a nested form to calculate time, when the time is short, plan A requires fewer judgments and is more efficient; while for plan B, each cycle must go through four calculations. Therefore, in When the time is short, the efficiency is even lower than A.
#C . In order to synchronize with the real time without any error, I thought of another way. In the JS Date object, there is a method called getTime(), which is used to return the number of milliseconds since January 1, 1970. When start is clicked, getTime() is triggered, and this time is used as the basis. getTime() is executed every ten milliseconds, and the latter is subtracted from the former to obtain the relative time. In this way, the problem of synchronization with real time is perfectly solved.
Attached are three pieces of code:
Code 1
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>有延迟的秒表</title>
<style type="text/css"></style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<span id="span10">0</span><span id="span11">0</span> :
<span id="span20">0</span><span id="span21">0</span> :
<span id="span30">0</span><span id="span31">0</span> :
<span id="span40">0</span><span id="span41">0</span>
</div>
<input id="input1" type="button" value="start" onclick="whenClick();">
<input id="input2" type="button" value="clear" onclick="clear1();">
<script type="text/javascript">
var milliSeconds1 = document.getElementById("span41");
var milliSeconds0 = document.getElementById("span40");
var seconds1 = document.getElementById("span31");
var seconds0 = document.getElementById("span30");
var minutes1 = document.getElementById("span21");
var minutes0 = document.getElementById("span20");
var hours1 = document.getElementById("span11");
var hours0 = document.getElementById("span10");
var flag;
function whenClick(){// 开始/暂停
var inputValue = document.getElementById("input1");
if(inputValue.value=="start"||inputValue.value=="continue"){
inputValue.value=" stop";
start1();
}
else {
inputValue.value="continue";
stop1();
}
}
function clear1(){// 清零
stop1();
milliSeconds1.innerHTML = milliSeconds0.innerHTML =
seconds1.innerHTML = seconds0.innerHTML = minutes1.innerHTML =
minutes0.innerHTML = hours1.innerHTML = hours0.innerHTML = 0;
document.getElementById("input1").value = "start";
}
function start1(){// 开始/继续
flag = setInterval("timeIncrement();",10);
}
function timeIncrement(){
milliSeconds1.innerHTML++;
if(milliSeconds1.innerHTML>=10){
milliSeconds1.innerHTML%=10;
milliSeconds0.innerHTML++;
if(milliSeconds0.innerHTML>=10){
milliSeconds0.innerHTML%=10;
seconds1.innerHTML++;
if(seconds1.innerHTML>=10){
seconds1.innerHTML%=10;
seconds0.innerHTML++;
if(seconds0.innerHTML>=6){
seconds0.innerHTML%=6
minutes1.innerHTML++;
if(minutes1.innerHTML>=10){
minutes1.innerHTML%=10;
minutes0.innerHTML++;
if(minutes0.innerHTML>=6){
minute0.innerHTML%=6;
hours1.innerHTML++;
if(hours1.innerHTML>=10){
hours1.innerHTML%=10;
hours0.innerHTML++;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
function stop1(){// 暂停/停止
clearInterval(flag);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Code 2
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>仍然有延迟的秒表</title>
<style type="text/css"></style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<span id="span1">00</span> :
<span id="span2">00</span> :
<span id="span3">00</span> :
<span id="span4">00</span>
</div>
<input id="input1" type="button" value="start" onclick="whenClick();">
<input id="input2" type="button" value="clear" onclick="clear1();">
<script type="text/javascript">
var milliSeconds1 = document.getElementById("span4");
var seconds1 = document.getElementById("span3");
var minutes1 = document.getElementById("span2");
var hours1 = document.getElementById("span1");
var time = 0;
var flag;
function whenClick(){// 开始/暂停
var inputValue = document.getElementById("input1");
if(inputValue.value=="start"||inputValue.value=="continue"){
inputValue.value=" stop";
start1();
}
else {
inputValue.value="continue";
stop1();
}
}
function clear1(){// 清零
stop1();
milliSeconds1.innerHTML = seconds1.innerHTML =minutes1.innerHTML = hours1.innerHTML = "00";
time=0;
document.getElementById("input1").value = "start";
}
function start1(){// 开始/继续
flag = setInterval("timeIncrement();",10);
}
function timeIncrement(){
time++;
var a=time%100;
var b=time%6000/100;
var c=time%360000/6000;
var d=time%8640000/360000;
milliSeconds1.innerHTML=(a<10)?('0'+a):a;
seconds1.innerHTML=(b<10)?('0'+Math.floor(b)):(Math.floor(b));
minutes1.innerHTML=(c<10)?('0'+Math.floor(c)):(Math.floor(c));
hours1.innerHTML=(d<10)?('0'+Math.floor(d)):(Math.floor(d));
}
function stop1(){// 暂停/停止
clearInterval(flag);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Code 3 (code synchronized with time)
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>秒表</title>
<style type="text/css"></style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<span id="span1">00</span> :
<span id="span2">00</span> :
<span id="span3">00</span> :
<span id="span4">00</span>
</div>
<input id="input1" type="button" value="start" onclick="whenClick();">
<input id="input2" type="button" value="clear" onclick="clear1();">
<script type="text/javascript">
var milliSeconds1 = document.getElementById("span4");
var seconds1 = document.getElementById("span3");
var minutes1 = document.getElementById("span2");
var hours1 = document.getElementById("span1");
var time=0;
var pre_time=0;
var intervals=0;
var pre_intervals=0;
var flag;
function whenClick(){// 开始/暂停
var inputValue = document.getElementById("input1");
if(inputValue.value=="start"||inputValue.value=="continue"){
var date= new Date();
time = date.getTime();
pre_time=time;
inputValue.value="stop ";
start1();
}
else {
inputValue.value="continue";
stop1();
}
}
function clear1(){// 清零
stop1();
milliSeconds1.innerHTML = seconds1.innerHTML =minutes1.innerHTML = hours1.innerHTML = "00";
time=0;
pre_time=0;
intervals=0;
pre_intervals=0;
document.getElementById("input1").value = "start";
}
function start1(){// 开始/继续
flag = setInterval("timeIncrement();",10);
}
function timeIncrement(){
date = new Date();
intervals=date.getTime()-time+pre_intervals;
var a=intervals%1000/10;
var b=intervals%60000/1000;
var c=intervals%3600000/60000;
var d=intervals/3600000;
milliSeconds1.innerHTML=(a<10)?('0'+Math.floor(a)):(Math.floor(a));
seconds1.innerHTML=(b<10)?('0'+Math.floor(b)):(Math.floor(b));
minutes1.innerHTML=(c<10)?('0'+Math.floor(c)):(Math.floor(c));
hours1.innerHTML=(d<10)?('0'+Math.floor(d)):(Math.floor(d));
}
function stop1(){// 暂停/停止
date = new Date();
pre_intervals += date.getTime()-pre_time;
clearInterval(flag);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Recommended related articles:
The above is the detailed content of Use JS to create a stopwatch accurate to 10ms (code attached). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1655
1655
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1306
1306
 25
25
 1252
1252
 29
29
 1225
1225
 24
24
 What should I do if I encounter garbled code printing for front-end thermal paper receipts?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
What should I do if I encounter garbled code printing for front-end thermal paper receipts?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
Frequently Asked Questions and Solutions for Front-end Thermal Paper Ticket Printing In Front-end Development, Ticket Printing is a common requirement. However, many developers are implementing...
 Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript is the cornerstone of modern web development, and its main functions include event-driven programming, dynamic content generation and asynchronous programming. 1) Event-driven programming allows web pages to change dynamically according to user operations. 2) Dynamic content generation allows page content to be adjusted according to conditions. 3) Asynchronous programming ensures that the user interface is not blocked. JavaScript is widely used in web interaction, single-page application and server-side development, greatly improving the flexibility of user experience and cross-platform development.
 Who gets paid more Python or JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Who gets paid more Python or JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
There is no absolute salary for Python and JavaScript developers, depending on skills and industry needs. 1. Python may be paid more in data science and machine learning. 2. JavaScript has great demand in front-end and full-stack development, and its salary is also considerable. 3. Influencing factors include experience, geographical location, company size and specific skills.
 How to achieve parallax scrolling and element animation effects, like Shiseido's official website?
or:
How can we achieve the animation effect accompanied by page scrolling like Shiseido's official website?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
How to achieve parallax scrolling and element animation effects, like Shiseido's official website?
or:
How can we achieve the animation effect accompanied by page scrolling like Shiseido's official website?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
Discussion on the realization of parallax scrolling and element animation effects in this article will explore how to achieve similar to Shiseido official website (https://www.shiseido.co.jp/sb/wonderland/)...
 The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The latest trends in JavaScript include the rise of TypeScript, the popularity of modern frameworks and libraries, and the application of WebAssembly. Future prospects cover more powerful type systems, the development of server-side JavaScript, the expansion of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and the potential of IoT and edge computing.
 How to merge array elements with the same ID into one object using JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
How to merge array elements with the same ID into one object using JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
How to merge array elements with the same ID into one object in JavaScript? When processing data, we often encounter the need to have the same ID...
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing Implementations
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing Implementations
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Different JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 How to implement panel drag and drop adjustment function similar to VSCode in front-end development?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
How to implement panel drag and drop adjustment function similar to VSCode in front-end development?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
Explore the implementation of panel drag and drop adjustment function similar to VSCode in the front-end. In front-end development, how to implement VSCode similar to VSCode...




