Animation effects of native js carousel renderings (with code)
The content of this article is about the animation effect of the native js carousel renderings (with code). It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Native JS-Carousel
Today I will write a carousel JS effect written in native JS.
Implementation principle:
1. Create an array and write the corresponding z-index, opacity, top, width for each picture;
2. The operation to realize rotation is to construct The first set of values in the array is placed in the last set, and it will be executed once when the button is clicked.
Display renderings: 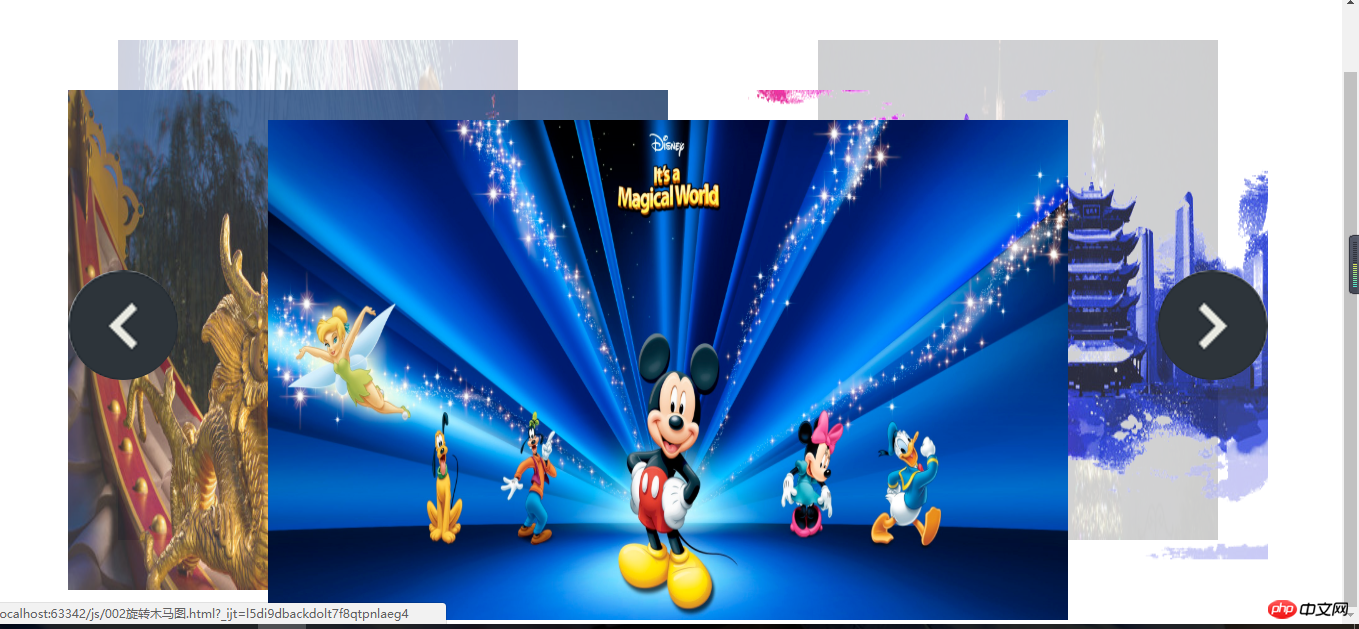
html layout:
<p class="wrap" id="wrap">
<p class="slide" id="slide">
<ul>
<li><a href=""><img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="images/logo.png" class="lazy" style="max-width:90%" style="max-width:90%" alt=""></a></li>
<li><a href=""><img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="images/slide.jpg" class="lazy" style="max-width:90%" style="max-width:90%" alt=""></a></li>
<li><a href=""><img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="images/slide2.jpg" class="lazy" style="max-width:90%" style="max-width:90%" alt=""></a></li>
<li><a href=""><img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="images/i1.jpg" class="lazy" style="max-width:90%" style="max-width:90%" alt=""></a></li>
<li><a href=""><img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="images/sto.jpg" class="lazy" style="max-width:90%" style="max-width:90%" alt=""></a></li>
</ul>
<p class="arrow" id="arrow">
<a href="javascript:;" id="arrLeft" class="prev"></a>
<a href="javascript:;" id="arrRight" class="next"></a>
</p>
</p></p>css style:
* { margin: 0; padding: 0; }
ul { list-style: none; }
.wrap { width: 1200px; margin: 100px auto; }
.slide { height: 500px; position: relative; width: 1200px; }
.slide ul li { position: absolute; top: 0; left: 0; z-index: 1; }
.slide li img { width: 100%; }
.arrow { position: absolute; width: 100%; top: 50%; opacity: 0; z-index: 3; }
.prev, .next { position: absolute; height: 110px; width: 110px; border-radius: 50%; top: 50%; //margin-top: -56px; overflow: hidden; text-decoration: none; }
.prev{ left: 0; background: url("images/slider-icons.png") no-repeat left top; }
.next{ right: 0; background: url("images/slider-icons.png") no-repeat right top; }JS part:
Next, we first store the style of the corresponding image in an array.
//写每张图片对应的样式
var config = [
{ "width": 400, "top": 20, "left": 50, "opacity": 0.2, "zIndex": 2
}, //0
{ "width": 600, "top": 70, "left": 0, "opacity": 0.8, "zIndex": 3
}, //1
{ "width": 800, "top": 100, "left": 200, "opacity": 1, "zIndex": 4
}, //2
{ "width": 600, "top": 70, "left": 600, "opacity": 0.8, "zIndex": 3
}, //3
{ "width": 400, "top": 20, "left": 750, "opacity": 0.2, "zIndex": 2
} //4
];When the page is loaded, the pictures are scattered, that is, the array just created is called, and they are assigned to each picture one by one.
var list=my$("slide").getElementsByTagName("li"); //拿到所有li
function assign() { //分配函数
for (var i=0;i<list.length;i++){
animate(list[i],config[i],function () {
flag=true;
});
}
}
assign();There will be left and right arrows when the mouse enters and leaves. Show and hide, the principle of clicking the button rotation is to change the first of the array to the last or the last group to the first. The flag is to control when the button is clicked to ensure that a set of animations is completed before the next rotation animation can continue.
//鼠标进入,左右焦点的p显示
my$("wrap").onmouseover=function () {
animate(my$("arrow"),{"opacity":1});
}; //鼠标离开,左右焦点的p隐藏
my$("wrap").onmouseout=function () {
animate(my$("arrow"),{"opacity":0});
}; //点击右边按钮事件
my$("arrRight").onclick=function () {
if (flag){
flag=false;
config.push(config.shift()); //把第一组值放到最后一组
assign();
}
}; //点击左边按钮事件
my$("arrLeft").onclick=function () {
if (flag){
flag=false;
config.unshift(config.pop()); //把最后一组值放到第一组
assign();
}
};
};Complete JS code:
<script>
//变速动画函数
function animate(element, json, fn) {
clearInterval(element.timeId); //清理定时器
element.timeId = setInterval(function () {
var flag = true; //假设默认为当前值已经等于目标值
for (var arrt in json) { if (arrt == "opacity") { //如果属性值为opacity
var current = getStyle(element, arrt) * 100; //current和target先扩大100倍
target = json[arrt] * 100; var step = (target - current) / 10;
step = step > 0 ? Math.ceil(step) : Math.floor(step);
current += step;
element.style[arrt] = current / 100; //运算完后缩小100倍
} else if (arrt == "zIndex") { //如果属性值为zindex
element.style[arrt] = json[arrt];
} else { //普通属性
var current = parseInt(getStyle(element, arrt));
target = json[arrt]; var step = (target - current) / 10;
step = step > 0 ? Math.ceil(step) : Math.floor(step); //step大于零向上取整,小于零向下取整
current += step;
element.style[arrt] = current + "px";
} if (current != target) {
flag = false;
}
} if (flag) { //只有所有属性的当前值已经等于目标值,才清理定时器
clearInterval(element.timeId); if (fn) { //回调函数
fn();
}
}
console.log("当前位置:" + current + "目标位置:" + target + " 移动步数:" + step); //测试函数
}, 20);
} function getStyle(element, arrt) {
return window.getComputedStyle ? window.getComputedStyle(element, null)[arrt] : element.currentStyle[arrt];
} function my$(id) {
return document.getElementById(id);
} //写每张图片对应的样式
var config = [
{ "width": 400, "top": 20, "left": 50, "opacity": 0.2, "zIndex": 2
}, //0
{ "width": 600, "top": 70, "left": 0, "opacity": 0.8, "zIndex": 3
}, //1
{ "width": 800, "top": 100, "left": 200, "opacity": 1, "zIndex": 4
}, //2
{ "width": 600, "top": 70, "left": 600, "opacity": 0.8, "zIndex": 3
}, //3
{ "width": 400, "top": 20, "left": 750, "opacity": 0.2, "zIndex": 2
} //4
]; var flag=true; //假设动画全部执行完毕-----锁
//页面加载的事件
window.onload=function () {
//1---散开图片
var list=my$("slide").getElementsByTagName("li"); //拿到所有li
function assign() { //分配函数
for (var i=0;i<list.length;i++){
animate(list[i],config[i],function () {
flag=true;
});
}
}
assign(); //鼠标进入,左右焦点的p显示
my$("wrap").onmouseover=function () {
animate(my$("arrow"),{"opacity":1});
}; //鼠标离开,左右焦点的p隐藏
my$("wrap").onmouseout=function () {
animate(my$("arrow"),{"opacity":0});
}; //点击右边按钮事件
my$("arrRight").onclick=function () {
if (flag){
flag=false;
config.push(config.shift()); //把第一组值放到最后一组
assign();
}
}; //点击左边按钮事件
my$("arrLeft").onclick=function () {
if (flag){
flag=false;
config.unshift(config.pop()); //把最后一组值放到第一组
assign();
}
};
};</script>Related recommendations:
javascript image compression code
javascript realizes code sharing of province and city linkageThe above is the detailed content of Animation effects of native js carousel renderings (with code). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1317
1317
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1246
1246
 24
24
 The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The latest trends in JavaScript include the rise of TypeScript, the popularity of modern frameworks and libraries, and the application of WebAssembly. Future prospects cover more powerful type systems, the development of server-side JavaScript, the expansion of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and the potential of IoT and edge computing.
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing Implementations
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing Implementations
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Different JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web Language
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web Language
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript is the core language of modern web development and is widely used for its diversity and flexibility. 1) Front-end development: build dynamic web pages and single-page applications through DOM operations and modern frameworks (such as React, Vue.js, Angular). 2) Server-side development: Node.js uses a non-blocking I/O model to handle high concurrency and real-time applications. 3) Mobile and desktop application development: cross-platform development is realized through ReactNative and Electron to improve development efficiency.
 How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
This article demonstrates frontend integration with a backend secured by Permit, building a functional EdTech SaaS application using Next.js. The frontend fetches user permissions to control UI visibility and ensures API requests adhere to role-base
 Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
I built a functional multi-tenant SaaS application (an EdTech app) with your everyday tech tool and you can do the same. First, what’s a multi-tenant SaaS application? Multi-tenant SaaS applications let you serve multiple customers from a sing
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
The shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.
 JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use Cases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use Cases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of JavaScript in web development include client interaction, form verification and asynchronous communication. 1) Dynamic content update and user interaction through DOM operations; 2) Client verification is carried out before the user submits data to improve the user experience; 3) Refreshless communication with the server is achieved through AJAX technology.




