
The content this article brings to you is about what is the JavaScript prototype? The detailed explanation of JavaScript prototype has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Prototype is still relatively important. I would like to elaborate on it separately. Speaking of prototype, what is a prototype?
When the constructor is created, there is a prototype attribute. This attribute is a pointer. The system will create and associate an object by default. This object is the prototype. The prototype object is an empty object by default. , and the purpose of this object is to contain properties and methods that can be shared by all instances of a specific type.
To put it bluntly, you can call the prototype attribute on the constructor to point to the prototype, thereby creating the prototype object of that object instance.
What are the benefits of using prototypes?
The advantage of using a prototype is that all object instances can share the properties and methods it contains.
Are you dizzy? Isn’t it super messy? Constructor, prototype, and instance, don’t worry, I’ll point it out for you in one sentence
All our constructors must eventually evolve into instances to make sense, because the methods defined in the constructor cannot be used by all Instances are shared, so you can only find the upper level of the constructor, which is the prototype. The properties and methods defined on the prototype can be shared by all instances. This is the nature of the prototype object
Look You will know from the picture, the relationship between the three of them is a love triangle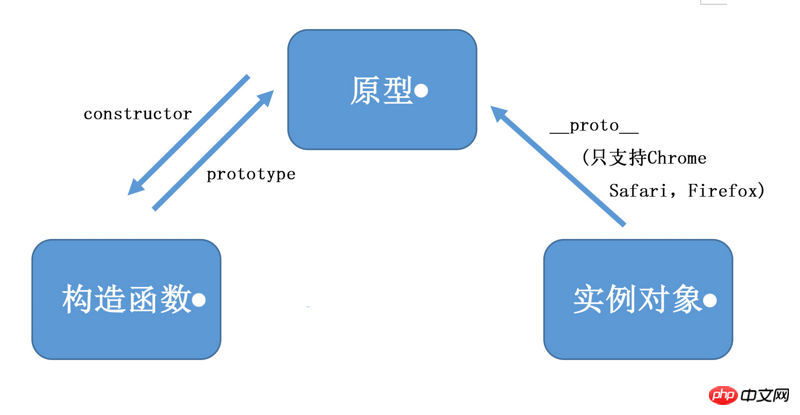
It is very easy to understand
Constructor.prototype = prototype
Prototype .constructor = constructor
Instance object .constructor = constructor (this is because the instance object cannot find the constructor attribute on itself, so it will find it in the prototype through __proto__, and point to the constructor through the prototype bridge)
Instance object.__proto__ = prototype
The prototype cannot be displayed by printing, it can only be expressed through Constructor.prototype
The following are two other ways to obtain the prototype Method
isPrototypeOf() method: Used to determine whether the pointer of this instance points to this prototype.
Object.getPrototypeOf() method: Get the prototype of the instance. The browsers supported by this method are IE9, Firefox 3.5, Safari 5, Opera 12 and Chrome, so it is recommended to obtain the object through this method. prototype.
假定有个Person构造函数和person对象 Person.prototype.isPrototypeof(person) // 返回true说明前者是person1的原型 Object.getPrototypeOf(person) === Person.prototype // 获取person的原型
The basic principle of multiple object instances sharing the properties and methods saved by the prototype
Every time the code reads a property of an object, a search will be performed. The target is the attribute with the given name. Start with the object instance itself. If an attribute with the given name is found in the instance, the value of the attribute is returned; if not found, the prototype object pointed to by the pointer is searched and the attribute with the given name is found in the prototype object. If this property is found in the prototype object, the property value is returned.
We can access the value in the prototype, but we cannot overwrite the value in the prototype. If we add an attribute to the instance, and the attribute name has the same name as the prototype, this attribute will be blocked ( Override) that property in the prototype.
function Person() {}
Person.prototype.name = "George"
Person.prototype.sayName = function() {
console.log(this.name)
}
let person1 = new Person();
let person2 = new Person();
person1.name = "命名最头痛";
// 在这一环节,person1.name会从他实例中找,若实例没找到,则继续搜索它的原型对象
console.log(person1.name); // 命名最头痛
console.log(person2.name); // GeorgeAdding a property to an instance object will only prevent us from accessing that property in the prototype, but will not modify that property. Even if this property is set to null, this property will only be set on the instance without restoring its connection to the prototype .
If you want to completely delete instance properties, you can use the delete operator, which allows us to re-access the properties in the prototype.
依旧用上面那个例子 delete操作符可用于删除对象的属性,无论是实例上的属性,还是在原型上的属性都可以删 delete person1.name // 删除这个实例的属性 delete Person.prototype.name // 删除原型上的属性 delete Person.prototype.constructor // 删除constructor属性,这样就没办法指回函数了
hasOwnProperty() method can be used to detect whether a property exists in the instance or in the prototype. This method only returns true if the given property exists in the object instance. It can also be understood that the hasOwnProperty method is used to detect whether this property is a property of the object itself.
obj.hasOwnProperty('property name')
Demo:
function Person(){
this.name = '命名最头痛'
}
var person = new Person()
Person.prototype.age = '18'
console.log(person.hasOwnProperty('name')) // true
console.log(Person.prototype.hasOwnProperty('age')) // trueThe in operator has two uses
①Put it in for Used in -in loop, for-in can return all enumerable (enumerable) properties that can be accessed through objects (enumerable properties can be seen at a glance)
The above is the detailed content of What is a javascript prototype? Detailed explanation of javascript prototype. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!