Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Introduction to binary trees (binary heaps) in JavaScript (code examples)
Introduction to binary trees (binary heaps) in JavaScript (code examples)
Introduction to binary trees (binary heaps) in JavaScript (code examples)
This article brings you an introduction (code example) about binary trees (binary heaps) in JavaScript. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Binary Tree
Binary Tree (Binary Tree) is a tree structure. Its characteristic is that each node has at most two branch nodes. A binary tree usually consists of It consists of root node, branch node and leaf node. Each branch node is often called a subtree.
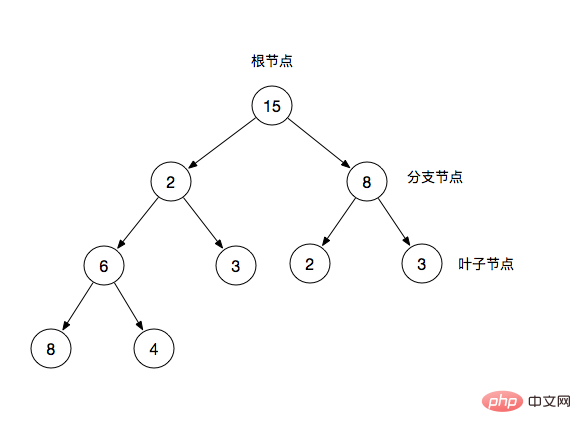
Root node: the top node of the binary tree
Branch node: In addition to the root node and has leaf nodes
Leaf node: except itself, has no other child nodes
Common terms
In a binary tree, we often use parent nodes and child nodes to describe it. For example, 2 in the figure is the parent node of 6 and 3, and conversely 6 and 3 are the child nodes of 2
Three properties of binary trees
- ##On the i-th level of the binary tree, there are at most 2^i-1 nodes
- When i=1, there is only one root node, 2^(i-1) = 2^0 = 1
- When i=2, 2^k-1 = 2^2 - 1 = 3 nodes
- The number of nodes of a tree is at least 1, while the number of nodes of a binary tree can be 0
- There is no limit to the maximum degree (number of nodes) of a node in a tree, while the maximum degree of a node in a binary tree is 2
- There is no left or right distinction between the nodes of a tree, while the nodes of a binary tree There are left and right sides
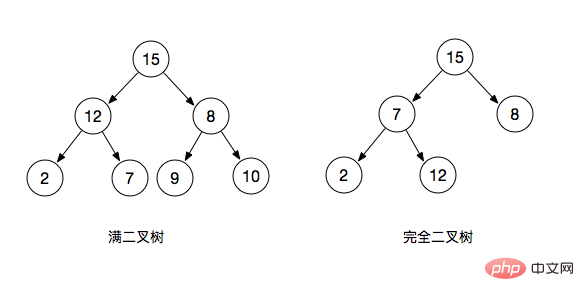
- Full binary tree: A binary tree with depth k and 2^k - 1 nodes is called a full binary tree
- Complete binary tree: A complete binary tree refers to the left side of the last layer It is full, the right side may be full or not full, and the remaining levels are full. The binary tree is called a complete binary tree (a full binary tree is also a complete binary tree)
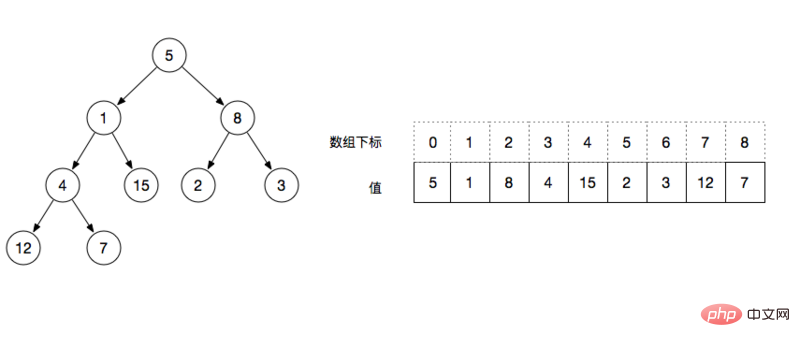
- left = index * 2 1, for example: the subscript of the root node is 0, then the value of the left node is the subscript array[0*2 1]=1
- right = index * 2 2, for example: the subscript of the root node is 0, then the value of the right node is the subscript array[0*2 2]=2
- Ordinal>= floor(N/2) are all leaf nodes, for example: floor(9/2) = 4, then the values starting from subscript 4 are all leaf nodes
- The key value of the parent node of the binary heap is always greater than or equal to (less than or equal to) the key value of any child node
- When the key value of the parent node is greater than or equal to ( Less than or equal to) the key value of each of its child nodes, it is called
max heap (minimum heap)

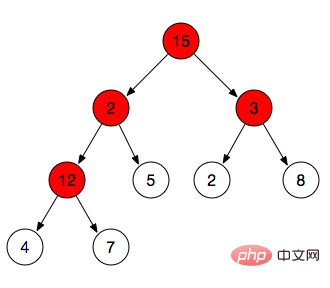
- Left picture: The parent node is always greater than or equal to its child node , so it satisfies the properties of a binary heap,
- Right picture: Branch node 7, as the parent node of 2 and 12, does not satisfy its properties (greater than or equal to the child node).
- insert: insert node
- delete: delete node
- max-hepify: Adjust branch node heap properties
- rebuildHeap: Rebuild the entire binary heap
- sort: Sort
- Initialize an array structure
Save the array length
class Heap{
constructor(arr){
this.data = [...arr];
this.size = this.data.length;
}
}max-heapify maximum heap operation
max-heapify is to convert each item that does not satisfy the maximum heap properties An operation for adjusting branch nodes.
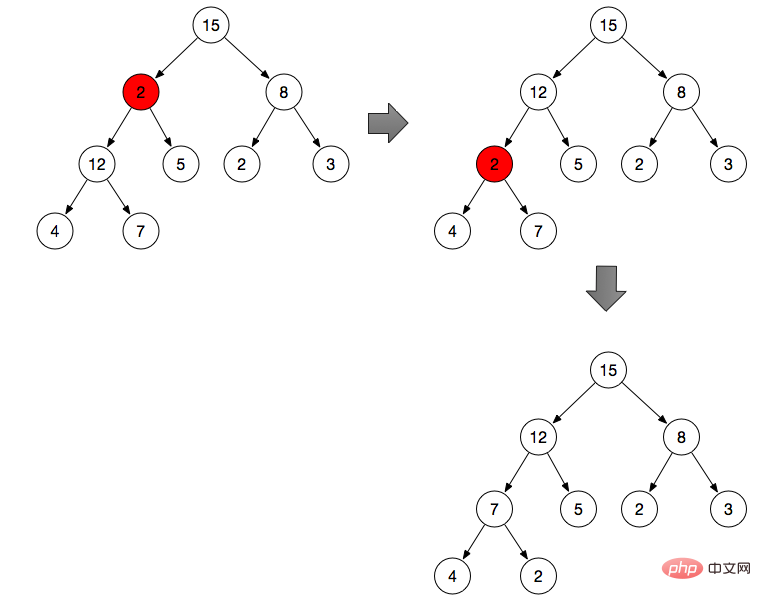
As shown above:
Adjust branch node 2 (branch node 2 does not meet the properties of the maximum heap )
By default, the branch node is the maximum value
Compare 2 with the left and right branches, from 2, 12, Find the maximum value in 5, and then exchange the position with 2
According to the binary heap properties above, get the left node and right node of branch node 2 respectively
Compare three nodes and get the subscript max of the maximum value
If the node itself is the maximum value, stop the operation
Exchange the max node with the parent node
Repeat the operation of step 2, find the maximum value from 2, 4, and 7 and exchange it with 2
Recursion
maxHeapify(i) {
let max = i;
if(i >= this.size){
return;
}
// 当前序号的左节点
const l = i * 2 + 1;
// 当前需要的右节点
const r = i * 2 + 2;
// 求当前节点与其左右节点三者中的最大值
if(l this.data[max]){
max = l;
}
if(r this.data[max]){
max = r;
}
// 最终max节点是其本身,则已经满足最大堆性质,停止操作
if(max === i) {
return;
}
// 父节点与最大值节点做交换
const t = this.data[i];
this.data[i] = this.data[max];
this.data[max] = t;
// 递归向下继续执行
return this.maxHeapify(max);
}Reconstructing the heap
We can see that the newly initialized heap Represented by an array, at this time it may not satisfy the properties of a maximum heap or a minimum heap. At this time, we may need to build the entire heap into what we want.
We did the max-heapify operation above, and max-heapify only adjusts a certain branch node. To build the entire heap into a maximum heap, you need to perform a max-heapify operation on all branch nodes. As shown in the figure below, we need to perform max-hepify operations on the four branch nodes 12, 3, 2, and 15 in sequence
- Find all branch nodes: The properties of the heap mentioned above mentioned that the serial number of the leaf node>=Math.floor(n/2), so it is smaller than the serial number of Math.floor(n/2) These are all nodes we need to adjust.
- For example, the array shown in the middle is [15,2,3,12,5,2,8,4,7] => Math.floor(9/2 )=4 => Those with index less than 4 are 15, 2, 3, and 12 (nodes that need to be adjusted), while 5, 2, 8, 4, and 7 are leaf nodes.
- Perform maxHeapify operation on all found nodes
rebuildHeap(){
// 叶子节点
const L = Math.floor(this.size / 2);
for(let i = L - 1; i>=0; i--){
this,maxHeapify(i);
}
}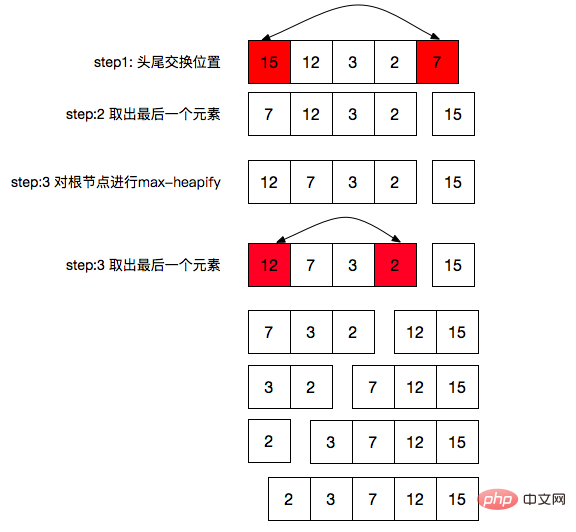
- Exchange the first and last positions
- Change the last The element is taken out from the heap, which is equivalent to the size-1 of the heap
- Then perform a max-heapify operation on the root node of the heap
- Repeat In the above three steps, we know that size=0 (we have already done this boundary condition in the max-heapify function)
sort() {
for(let i = this.size - 1; i > 0; i--){
swap(this.data, 0, i);
this.size--;
this.maxHeapify(0);
}
}- Insert to the end
- Heap length 1
- Determine whether it is still a maximum heap after insertion
- If not, reconstruct the heap
insert(key) {
this.data[this.size] = key;
this.size++
if (this.isHeap()) {
return;
}
this.rebuildHeap();
}- Delete an element in the array
- Heap length-1
- Determine whether it is a heap
- If not, then reconstruct the heap
delete(index) {
if (index >= this.size) {
return;
}
this.data.splice(index, 1);
this.size--;
if (this.isHeap()) {
return;
}
this.rebuildHeap();
}/**
* 最大堆
*/
function left(i) {
return i * 2 + 1;
}
function right(i) {
return i * 2 + 2;
}
function swap(A, i, j) {
const t = A[i];
A[i] = A[j];
A[j] = t;
}
class Heap {
constructor(arr) {
this.data = [...arr];
this.size = this.data.length;
}
/**
* 重构堆
*/
rebuildHeap() {
const L = Math.floor(this.size / 2);
for (let i = L - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
this.maxHeapify(i);
}
}
isHeap() {
const L = Math.floor(this.size / 2);
for (let i = L - 1; i >= 0; i++) {
const l = this.data[left(i)] || Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
const r = this.data[right(i)] || Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
const max = Math.max(this.data[i], l, r);
if (max !== this.data[i]) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
sort() {
for (let i = this.size - 1; i > 0; i--) {
swap(this.data, 0, i);
this.size--;
this.maxHeapify(0);
}
}
insert(key) {
this.data[this.size++] = key;
if (this.isHeap()) {
return;
}
this.rebuildHeap();
}
delete(index) {
if (index >= this.size) {
return;
}
this.data.splice(index, 1);
this.size--;
if (this.isHeap()) {
return;
}
this.rebuildHeap();
}
/**
* 堆的其他地方都满足性质
* 唯独跟节点,重构堆性质
* @param {*} i
*/
maxHeapify(i) {
let max = i;
if (i >= this.size) {
return;
}
// 求左右节点中较大的序号
const l = left(i);
const r = right(i);
if (l this.data[max]) {
max = l;
}
if (r this.data[max]) {
max = r;
}
// 如果当前节点最大,已经是最大堆
if (max === i) {
return;
}
swap(this.data, i, max);
// 递归向下继续执行
return this.maxHeapify(max);
}
}
module.exports = Heap;Copy after login
SummaryThe heap is over here, the heap is Binary trees are relatively simple and are often used for sorting and priority queues. The core of the heap is the max-heapify operation and the three properties of the heap. /**
* 最大堆
*/
function left(i) {
return i * 2 + 1;
}
function right(i) {
return i * 2 + 2;
}
function swap(A, i, j) {
const t = A[i];
A[i] = A[j];
A[j] = t;
}
class Heap {
constructor(arr) {
this.data = [...arr];
this.size = this.data.length;
}
/**
* 重构堆
*/
rebuildHeap() {
const L = Math.floor(this.size / 2);
for (let i = L - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
this.maxHeapify(i);
}
}
isHeap() {
const L = Math.floor(this.size / 2);
for (let i = L - 1; i >= 0; i++) {
const l = this.data[left(i)] || Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
const r = this.data[right(i)] || Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
const max = Math.max(this.data[i], l, r);
if (max !== this.data[i]) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
sort() {
for (let i = this.size - 1; i > 0; i--) {
swap(this.data, 0, i);
this.size--;
this.maxHeapify(0);
}
}
insert(key) {
this.data[this.size++] = key;
if (this.isHeap()) {
return;
}
this.rebuildHeap();
}
delete(index) {
if (index >= this.size) {
return;
}
this.data.splice(index, 1);
this.size--;
if (this.isHeap()) {
return;
}
this.rebuildHeap();
}
/**
* 堆的其他地方都满足性质
* 唯独跟节点,重构堆性质
* @param {*} i
*/
maxHeapify(i) {
let max = i;
if (i >= this.size) {
return;
}
// 求左右节点中较大的序号
const l = left(i);
const r = right(i);
if (l this.data[max]) {
max = l;
}
if (r this.data[max]) {
max = r;
}
// 如果当前节点最大,已经是最大堆
if (max === i) {
return;
}
swap(this.data, i, max);
// 递归向下继续执行
return this.maxHeapify(max);
}
}
module.exports = Heap;The above is the detailed content of Introduction to binary trees (binary heaps) in JavaScript (code examples). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1671
1671
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1329
1329
 25
25
 1276
1276
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
 Compare complex data structures using Java function comparison
Apr 19, 2024 pm 10:24 PM
Compare complex data structures using Java function comparison
Apr 19, 2024 pm 10:24 PM
When using complex data structures in Java, Comparator is used to provide a flexible comparison mechanism. Specific steps include: defining the comparator class, rewriting the compare method to define the comparison logic. Create a comparator instance. Use the Collections.sort method, passing in the collection and comparator instances.
 Java data structures and algorithms: in-depth explanation
May 08, 2024 pm 10:12 PM
Java data structures and algorithms: in-depth explanation
May 08, 2024 pm 10:12 PM
Data structures and algorithms are the basis of Java development. This article deeply explores the key data structures (such as arrays, linked lists, trees, etc.) and algorithms (such as sorting, search, graph algorithms, etc.) in Java. These structures are illustrated through practical examples, including using arrays to store scores, linked lists to manage shopping lists, stacks to implement recursion, queues to synchronize threads, and trees and hash tables for fast search and authentication. Understanding these concepts allows you to write efficient and maintainable Java code.
 In-depth understanding of reference types in Go language
Feb 21, 2024 pm 11:36 PM
In-depth understanding of reference types in Go language
Feb 21, 2024 pm 11:36 PM
Reference types are a special data type in the Go language. Their values do not directly store the data itself, but the address of the stored data. In the Go language, reference types include slices, maps, channels, and pointers. A deep understanding of reference types is crucial to understanding the memory management and data transfer methods of the Go language. This article will combine specific code examples to introduce the characteristics and usage of reference types in Go language. 1. Slices Slices are one of the most commonly used reference types in the Go language.
 PHP data structure: The balance of AVL trees, maintaining an efficient and orderly data structure
Jun 03, 2024 am 09:58 AM
PHP data structure: The balance of AVL trees, maintaining an efficient and orderly data structure
Jun 03, 2024 am 09:58 AM
AVL tree is a balanced binary search tree that ensures fast and efficient data operations. To achieve balance, it performs left- and right-turn operations, adjusting subtrees that violate balance. AVL trees utilize height balancing to ensure that the height of the tree is always small relative to the number of nodes, thereby achieving logarithmic time complexity (O(logn)) search operations and maintaining the efficiency of the data structure even on large data sets.
 Full analysis of Java collection framework: dissecting data structure and revealing the secret of efficient storage
Feb 23, 2024 am 10:49 AM
Full analysis of Java collection framework: dissecting data structure and revealing the secret of efficient storage
Feb 23, 2024 am 10:49 AM
Overview of Java Collection Framework The Java collection framework is an important part of the Java programming language. It provides a series of container class libraries that can store and manage data. These container class libraries have different data structures to meet the data storage and processing needs in different scenarios. The advantage of the collection framework is that it provides a unified interface, allowing developers to operate different container class libraries in the same way, thereby reducing the difficulty of development. Data structures of the Java collection framework The Java collection framework contains a variety of data structures, each of which has its own unique characteristics and applicable scenarios. The following are several common Java collection framework data structures: 1. List: List is an ordered collection that allows elements to be repeated. Li
 Hash table-based data structure optimizes PHP array intersection and union calculations
May 02, 2024 pm 12:06 PM
Hash table-based data structure optimizes PHP array intersection and union calculations
May 02, 2024 pm 12:06 PM
The hash table can be used to optimize PHP array intersection and union calculations, reducing the time complexity from O(n*m) to O(n+m). The specific steps are as follows: Use a hash table to map the elements of the first array to a Boolean value to quickly find whether the element in the second array exists and improve the efficiency of intersection calculation. Use a hash table to mark the elements of the first array as existing, and then add the elements of the second array one by one, ignoring existing elements to improve the efficiency of union calculations.
 PHP SPL data structures: Inject speed and flexibility into your projects
Feb 19, 2024 pm 11:00 PM
PHP SPL data structures: Inject speed and flexibility into your projects
Feb 19, 2024 pm 11:00 PM
Overview of the PHPSPL Data Structure Library The PHPSPL (Standard PHP Library) data structure library contains a set of classes and interfaces for storing and manipulating various data structures. These data structures include arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, and sets, each of which provides a specific set of methods and properties for manipulating data. Arrays In PHP, an array is an ordered collection that stores a sequence of elements. The SPL array class provides enhanced functions for native PHP arrays, including sorting, filtering, and mapping. Here is an example of using the SPL array class: useSplArrayObject;$array=newArrayObject(["foo","bar","baz"]);$array
 Comparison of Golang and Node.js in backend development
Jun 03, 2024 pm 02:31 PM
Comparison of Golang and Node.js in backend development
Jun 03, 2024 pm 02:31 PM
Go and Node.js have differences in typing (strong/weak), concurrency (goroutine/event loop), and garbage collection (automatic/manual). Go has high throughput and low latency, and is suitable for high-load backends; Node.js is good at asynchronous I/O and is suitable for high concurrency and short requests. Practical cases of the two include Kubernetes (Go), database connection (Node.js), and web applications (Go/Node.js). The final choice depends on application needs, team skills, and personal preference.