
Modifying the user mode can be achieved using the usermod command.
1. Introduction to common usermod commands:
-a: Only used with -G to add users to affiliated groups.
-d: Modify the directory when the user logs in. For example, when a general user logs in, the preset home directory will be entered by default. Sometimes it is more complicated to enter for the convenience of login. When entering the path, you can use this option to set the directory when entering.
-g: Modify the group to which the user belongs.
-G: Modify the additional groups to which the user belongs; you can use this option when changing the user's sudo permissions.
-s: Modify the shell version used after user login
2. Sudo permissions
There are two ways for users to obtain sudo permissions
1. Modify the /etc/sudoers file and add the user name to the sudo permission group, for example
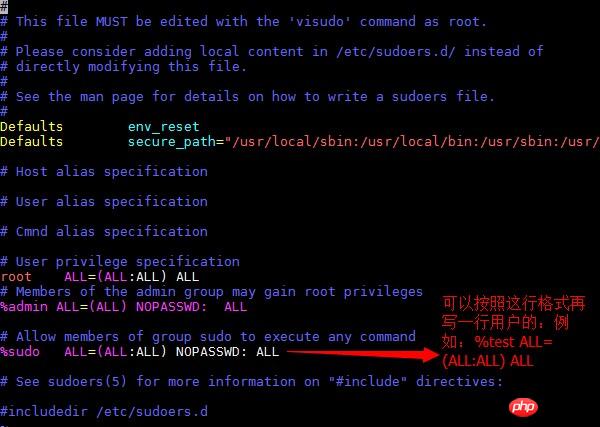
2. The second method is to modify the user affiliation group:
You can use usermod or gpasswd to modify
(1) Use usermod to modify
$ sudo usermod -a -G sudo tt
The modified results can be viewed in /etc/group, and you can see that the sudo column contains tt
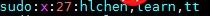
FILES
/etc/group
Group account information.
/etc/gshadow
Secure group account information.
/etc/passwd
User account information.
/etc/shadow
Secure user account information.-A Set the group administrator list
For example: Add tt as a sudo group member:sudo gpasswd -a tt sudo
sudo gpasswd -d tt sudo
The above is the detailed content of Linux user management (2) about modifying user mode (picture). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




