
Before, when I saw the partition, I pinched it, it was so tall. Yesterday I finally learned what partitioning is, but it’s nothing more than that. To summarize today, a good memory is not as good as a bad writing.
MySQL Supports partitioning function starting from 5.1. One sentence for partitioning is: Divide a table into multiple areas (pages/files) according to certain rules (range/list/hash/key, etc.) for storage. For mysql application development, there is no difference between partitioning and non-partitioning (that is, it is transparent to the application). It's like "breaking it into pieces" in a breakout battle. MySQL supports most storage engines (such as MyISAM, InnoDB, Memory, etc.) to create partitions, but does not support MERGE and CSV to create partitions. All partitions in the same partition table must be of the same storage engine. Make an example:
#创建一个5个hash分区的myisam表 CREATE TABLE `test`.`partition_t1`( `id` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, `username` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, `email` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, `birth_date` DATE NOT NULL ) ENGINE=MYISAM PARTITION BY HASH(MONTH(birth_date)) PARTITIONS 5;
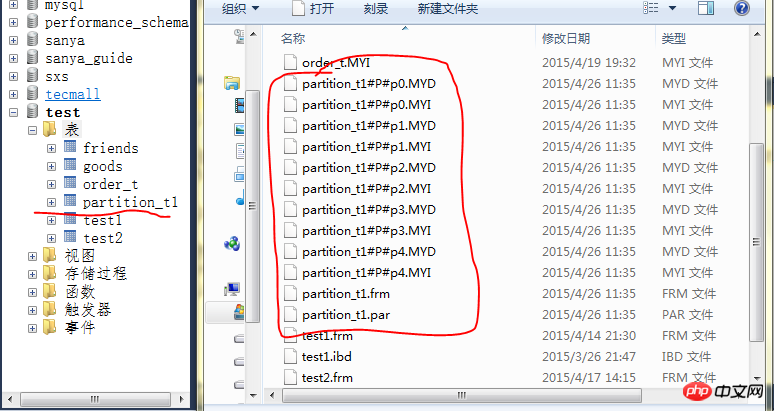
Example result
Can store more data (maximum limit of a single file in the system)
Optimize the query, in the where clause, if the partition condition is included, only one needs to be scanned Or partially partition to improve query efficiency. When it comes to functions such as sum(), it can be processed in parallel on the partitions and the results are finally summarized.
For expired or unnecessary data, you can delete related partitions to quickly delete the data.
By distributing data queries across multiple disks, the concurrency capability of a single table is improved, and the disk I/O performance is also improved.
is divided into 4 types:
range partition: based on a given The continuous interval range of the data is allocated to different partitions.
List partitioning: similar to range partitioning, the difference is that list is partitioned based on the enumerated value list, and range is partitioned based on the range.
Hash partition: Based on the given number of partitions, allocate data to different partitions (modulo/linear)
key partition: Similar to hash partitioning.
In MySQL5.1, range, list, and hash partitioning require that the partition key must be int. MySQL 5.5 and above supports non-integer range and list partitions, namely: range columns and list columns.
Note: No matter what kind of partitioning, there is either no primary key/unique key on the partition table, or one of the partition keys must be a primary key/unique key.
Range partitioning uses value ranges (intervals) to divide partitions. The intervals must be continuous and cannot overlap each other. Use values less thanOperator performs partition definition.
Example 1:
CREATE TABLE `test`.`partition_t2`( `id` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, `username` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, `email` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, `birth_date` DATE NOT NULL ) ENGINE=MYISAM PARTITION BY RANGE(id)( PARTITION t21 VALUES LESS THAN (10), PARTITION t22 VALUES LESS THAN (20), PARTITION t23 VALUES LESS THAN MAXVALUE );
The above example defines a range partition table containing 3 partitions (t21, t22, t23). This is somewhat similar Same as the <a href="http://www.php.cn/code/5745.html" target="_blank">switch statement</a> in high-level languages. The explanation is as follows: when id<10, it is in the t21 partition; when 20>id>=10, it is in the t22 partition; when id>=20, it is in the t23 partition.
Example 2:
CREATE TABLE `test`.`partition_t3`( `id` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, `username` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, `email` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, `birth_date` DATE NOT NULL ) ENGINE=MYISAM PARTITION BY RANGE COLUMNS(birth_date)( PARTITION t31 VALUES LESS THAN ('1996-01-01'), PARTITION t32 VALUES LESS THAN ('2006-01-01'), PARTITION t33 VALUES LESS THAN ('2038-01-01') );
MySQL5.5 improves range partitioning and provides range columns partitioning to support non-integer partitioning.
list partition creates a discrete value list (similar to enum type data in mysql) to divide the partition, use values inoperator to partition. List partitions do not need to be declared in any particular order. Lists are similar to ranges in many ways.
CREATE TABLE `test`.`partition_t4`( `id` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, `username` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, `email` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, `birth_date` DATE NOT NULL ) ENGINE=MYISAM PARTITION BY LIST(id)( PARTITION t41 VALUES IN (1,2), PARTITION t42 VALUES IN (3,6), PARTITION t43 VALUES IN (5,4), PARTITION t44 VALUES IN (7,8) );
The above example is that when the id is 1 or 2, it is in the t41 partition; when the id is 3 or 6, it is in the t42 partition, and so on...
Hash partition is mainly used to disperse hotspot reads to ensure that data is distributed as evenly as possible among a predetermined number of partitions. When a table performs hash partitioning, MySQL applies a hash function to the partition key to determine which of the n partitions the data should be placed in. Hash partition supports two hash functions (partitioning methods): modulo algorithm (default hash partitioning method) and linear power-of-2 algorithm (liner hash partitioning) .
#顶部引例就是常规hash分区
mysql does not recommend using hashexpressions involving multiple columns.
Conventional hashing brings too much cost in partition management and is not suitable for the needs of flexible partitions. See: Consistent Hash Algorithm
Because of the management problems of conventional hash partitioning, all mysql introduces linear hash partitioning.
CREATE TABLE `test`.`partition_t5`( `id` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, `username` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, `email` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, `birth_date` DATE NOT NULL ) ENGINE=MYISAM PARTITION BY LINEAR HASH(id) PARTITIONS 5;
In the above example, a linear hash partition of 5 partitions is created.
Advantages of linear hash partitioning: MySQL can handle partition maintenance faster;
线性hash分区缺点:分区各个分区之间数据分布不太均衡。
hash分区允许用户自定义的表达式,而key分区不允许使用用户自定义的表达式。
hash分区只支持整数分区,key分区支持除了blob或text类型之外的其他数据类型分区。
与hash分区不同,创建key分区表的时候,可以不指定分区键,默认会选择使用主键/唯一键作为分区键,没有主键/唯一键,必须指定分区键。
CREATE TABLE `test`.`partition_t6`( `id` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, `username` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, `email` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, `birth_date` DATE NOT NULL ) ENGINE=MYISAM PARTITION BY LINEAR KEY(email) PARTITIONS 5;
columns 包括range columns与list columns 支持非整型的分区键。columns分区支持多列分区。
CREATE TABLE `test`.`partition_t7`(
`a` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
`b` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL
)
PARTITION BY RANGE COLUMNS(a,b)(
PARTITION p0 VALUES LESS THAN (0,10),
PARTITION p1 VALUES LESS THAN (10,10),
PARTITION p2 VALUES LESS THAN (10,20),
PARTITION p3 VALUES LESS THAN (10,35),
PARTITION p4 VALUES LESS THAN (10,MAXVALUE),
PARTITION p5 VALUES LESS THAN (MAXVALUE,MAXVALUE)
);判断依据:(a<10) or ((1=10) and (10<10))。
子分区是分区表中对每一个分区的再次分割,又被称为复合分区。MySQL从MySQL5.1开始支持对通过range和list的表再进行子分区,子分区即可以hash分区,也可以使用key分区。子分区适合保存非常大量的数据记录。
CREATE TABLE partition_t8(id INT,purchased DATE)
PARTITION BY RANGE(YEAR(purchased))
SUBPARTITION BY HASH(TO_DAYS(purchased))
SUBPARTITIONS 2(
PARTITION p0 VALUES LESS THAN (1990),
PARTITION p1 VALUES LESS THAN (2000),
PARTITION p2 VALUES LESS THAN MAXVALUE
);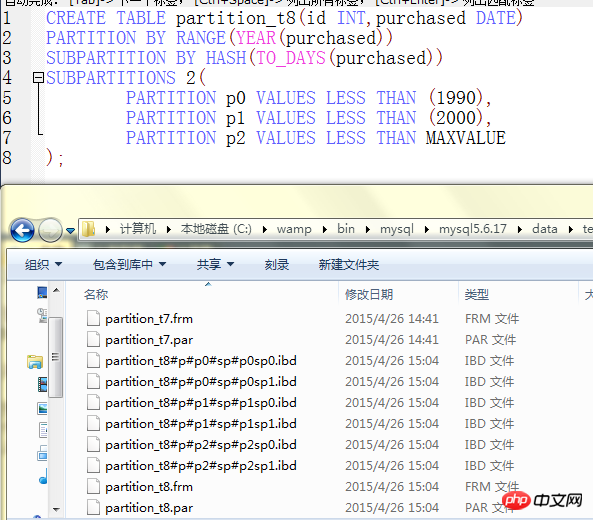
mysql子分区
MySQL5.1提供添加、删除、重定义、合并、拆分分区命令。
#删除分区
alter table partition_t8 drop partition p2;
#添加一个分区
alter table partition_t8 add partition(
partition p4 values less than (2030)
)
#重定义一个分区
alter table partition_t8 reorganize partition p3 into(
partition p2 values less than (2005),
partition p3 values less than (2015)
);只能从range分区列表最大端增加分区。
增加list分区,不能添加一个包含现有分区值列表中的任意值分区,也就是说对一个固定的分区键值,必须指定并且只能指定一个唯一的分区。
重新定义range分区,只能够重新定义相邻的分区,同时重新定义的分区区间必须和原分区区间覆盖相同的区间。
#减少分区数,(如将分区数减少到2) alter table partition_t8 coalesce partition 2; #增加分区数(如:为分区数增加了8) alter table partiton_t8 add partition partitions 8;
coalesce不能用来增加分区数量。
【相关推荐】
2. MySQL最新手册教程
3. 数据库设计那些事
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to partitions in mysql. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




