
#When we are developing, sometimes we need to upload and download pictures and files. For example, when registering an account, sometimes you need to upload a picture of your avatar. At this time, you need to use file processing, and there are many file styles, such as txt, word, excel, etc.
The way of operating files in PHP language and even other languages is essentially a stream operation. There are two types of streams in PHP (byte stream, binary stream), which are divided into input streams and output streams according to different output methods. 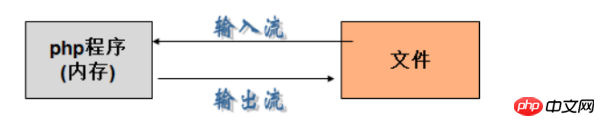
File streams are all referenced by memory. If the data is saved from memory to a file on disk, we call it an output stream. Conversely, if the data flows from a file to memory, we call it an output stream. input stream.
There are two ways to operate files in PHP
Local operation
Remote operation
Local operation is to add, delete, modify and check files on your own computer.
Remote operation is to access the server remotely and perform operations such as adding, deleting, modifying and checking files on the server.
You can see the functions for operating files from the help document:

Here are just some of the functions listed. For more functions, please see the help. document. You can see that there are a total of 81 functions in the help document, but we don’t need to master them all, just the commonly used ones.
When we operate the file, sometimes we need to know the relevant information of the file, such as the size of the file, the Type, file creation time, modification time, access time and other information, here the technology of reading file-related information will be used, which is divided into two forms in PHP to obtain file information.
<?php
//写一个变量记录文件的路径
$file_path = "D:/config.txt";
if(file_exists($file_path)){
//文件存在
if($fp = fopen($file_path,'r')){
//$type是一个存放文件信息的数组
$type = fstat($fp);
echo '<br>文件的字节是:' . $type['size'];
echo '<br>文件创建时间是:' . date('Y-m-d H:i:s',$type['ctime']);
echo '<br>文件访问时间是:' . date('Y-m-d H:i:s',$type['atime']);
echo '<br>文件修改时间是:' .date('Y-m-d H:i:s',$type['mtime']);
//关闭资源
fclose($fp);
}else{
echo '文件打开失败';
}
}else{
echo '文件不存在';
}
......结果.......
文件的字节是:22
文件创建时间是:2016-10-12 20:34:56
文件访问时间是:2016-10-12 20:34:56
文件修改时间是:2016-10-12 20:35:081. We first define a path to the file we access. This path can be a relative path or an absolute path.
2. Use the file_exists($path) function to determine whether the file exists. If it exists, it returns true. If it does not exist, it returns false.
3. Through fopen($path, access form), this function opens a file and returns a file. Pointer, pointing to the first row. The first parameter is the path of the file, the second parameter is the access form of the file, "r" means reading the file.
4. fstat (file pointer) obtains file information through the opened file pointer and returns an array, which contains some associative arrays with the values we want.
5. Remember to close the resource after using it, otherwise unexpected errors may sometimes occur.
<?php
$file_path = 'D:/config.txt';
echo '<br>文件的类型是:' . filetype($file_path);
echo '<br>文件的大小是:' . filesize($file_path);
echo '<br>文件的创建时间是:' . date('Y-m-d H:i:s',filectime($file_path));
echo '<br>文件的访问时间是:' .date('Y-m-d H:i:s',fileatime($file_path));
echo '<br>文件的修改时间是:' . date('Y-m-d H:i:s',filemtime($file_path));
.....结果.....
文件的类型是:file
文件的大小是:22
文件的创建时间是:2016-10-12 20:34:56
文件的访问时间是:2016-10-12 20:34:56
文件的修改时间是:2016-10-12 20:35:08This method is relatively simple. It directly obtains the relevant information of the file through functions, but the file should be opened at the bottom of each function. operate.
We often need to read the contents of the file when operating files. PHP provides three ways to read files.
<?php
header("Content-type:text/html;charset = utf-8");
$file_path = 'D:/config.txt';
if(file_exists($file_path)){
if($fp = fopen($file_path,'r')){
//获取文件的大小
$file_size = fstat($fp)['size'];
$content = fread($fp, $file_size);
//对文件中中文进行编码
$content = iconv('gbk', 'utf-8', $content);
//对换行符进行替换。
$content = str_replace("\r\n", "<br>", $content);
echo $content;
fclose($fp);
}else{
echo '文件打开失败';
}
}else{
echo '文件不存在';
}
......结果.......
这是一些配置文件信息。
user = abc;
password = 122;Define the full path of the file
file_exists($path) judgment Does the file exist?
fopen($path, access form) There are many access forms in this function. We only use three commonly used ones:
r, for reading the file, the file pointer points to the head
w, for writing the file, if the file exists, the file pointer points to the head, and Clear the contents and create the file if it does not exist.
a, perform a writing operation on a file. If the file exists, the file pointer points to the end, and the content inside will not be cleared. If the file does not exist, the file will be created.
fread(file pointer, size) This function is to perform file operations. By getting the file size, write the whole of a file. into $content.
iconv (input character set, output character set, string) This function encodes the function in the file and stores it in the file in gbk and in the page. It is utf-8,
str_replace (character to be replaced, ring character, string). This function converts the newline character in the file. The newline character in the file under Windows is "\r\n", the content of the file is displayed on the web page, and the line break character of the web page is "<\br>". Note that the escape characters must be enclosed in double quotes.
Close the file pointer resource
In the first way, read Fetching the file is to read the entire file at once. When the file is very large, this method is unreasonable. You can use the second method, using loop reading, reading a part first, merging, and then reading a part, merging.
<?php
$file_path = 'D:/config.txt';
if(file_exists($file_path)){
if($fp = fopen($file_path,'r')){
//文件太大,分字节度
$size = 1024;//每次读取1024个字节
$tmp_content = '';//存放一次读取的内容
$content = '';//存放总的内容。
while(!feof($fp)){
$tmp_content = fread($fp,$size);
$content .= $tmp_content;
}
$content = iconv('gbk', 'utf-8', $content);
$content = str_replace("\r\n", "<br>", $content);
echo $content;
fclose($fp);
}else{
echo '文件打开失败';
}
}else{
echo '文件不存在';
}
......结果.......
这是一些配置文件信息。
user = abc;
password = 122;- 从上面的代码中可以看出来,读取文件的内容是分块读取的,读取一次,拼接到总的内容上。
- feof(文件指针) 测试文件指针是否到了文件结束的位置,当文件指针指向最后则不用循环。
- 关闭文件指针资源
<?php
$file_path = 'D:/config.txt';
$content = file_get_contents($file_path);
$content = iconv('gbk','utf-8',$content);
$content = str_replace("\r\n","<br>",$content);
echo $content;
......结果.......
这是一些配置文件信息。
user = abc;
password = 122;第三种方式是最简单的一种方式,通过file_get_contents()方法进行整体的读取。
<?php
//定义文件的路径
$file_path = 'D:/test.txt';
if(!file_exists($file_path)){
//文件不存在
//fopen()函数使用w这种访问形式,
if($fp = fopen($file_path, 'w')){
$str = '';
for($i = 0; $i < 10; $i++){
$str .= "hello,php\r\n";
}
//向文件中写数据
fwrite($fp, $str);
fclose($fp);
}
}- 当文件不存在的使用使用fopen()打开文件是自动创建文件的,这里使用的文件访问形式是w,文件指针指向头部,清空文件里面的内容。
- 通过fread()函数想文件中写文件。
- 当文件存在的时候我们可以使用’a’这种访问形式进行对文件内容的追加写入。
<?php
//定义文件的路径
$file_path = 'D:/test.txt';
if(!file_exists($file_path)){
$str = '';
for($i = 0; $i < 10; $i++){
$str .= "hello,php\r\n";
}
file_put_contents($file_path, $str);
}- 使用file_put_contents()函数进行文件的写入,这个函数也是当文件不存在的时候,创建文件。
- 如果我们通过file_put_contents函数来追加新的内容到文件中,应该在使用file_put_contents函数时,带上第三个参数 FILE_APPEND 即可。
<?php
$file_path = 'D:/test.txt';
if(file_exists($file_path)){
if(unlink($file_path)){
echo '文件删除成功';
}else{
echo '文件删除失败';
}
}- 通过unlink(文件路径)函数删除文件。
<?php
$file_path = 'D:/test.txt';
$file_newPath = 'D:/newtest.txt';
if(file_exists($file_path)){
if(rename($file_path,$file_newPath)){
echo '文件名修改成功';
}else{
echo '文件名修改失败';
}
}- 修改文件的名字可以通过rename(
新的文件名)进行修改,当修改成功时返回true,失败返回false。这个函数还可以移动文件的位置。
在php文件编程中,目录也是一种文件,是一种比较特殊的文件,因此对目录的操作有固定的操作方法,主要的方法有三个 is_dir,rmdir,mkdir
is_dir 判断是否是一个目录
rmdir 删除一个目录,当目录下面有文件或目录的时候不能删除。
mkdir 创建一个目录
<?php
$dir_path = 'D:/test';
//判断目录是否存在
if(is_dir($dir_path)){
echo '目录存在';
}else{
//目录不存在,创建目录
if(mkdir($dir_path)){
echo '目录创建成功';
}else{
echo '目录创建失败';
}
}上面先判断目录是否存在,不存在使用mkdir()函数进行目录的创建。
上面的代码只能创建一级目录,当路径名字换成$dir_path = ‘D:/test/a/b/c/d’时,在test目录下还有目录,这时候用上面的方法就会报错,不能够创建多级目录。这时候也可以使用mkdir()函数进行创建,但是在函数中多了两个参数,这两个参数对于windows系统下开发是没有意义的。
<?php
$dir_path = 'D:/test/a/b/c/d';
//判断目录是否存在
if(is_dir($dir_path)){
echo '目录存在';
}else{
//目录不存在,创建目录
if(mkdir($dir_path,0777,true)){
echo '目录创建成功';
}else{
echo '目录创建失败';
}
}可以看到在创建目录的函数中添加了两个参数,就能创建多级目录。0777是在linux下的最大访问权限,而true是表示创建多级目录。
<?php
$dir_path = 'D:/test';
if(is_dir($dir_path)){
//目录存在
if(rmdir($dir_path)){
echo '目录删除成功';
}else{
echo '目录删除失败';
}
}- 通过rmdir(目录路径)删除目录。
- 删除目录时,下面没有目录或者文件的存在。
- rmdir()函数只能删除一个目录,不能删除多个目录,删除多个目录,可以使用递归删除。
<?php
//在这里test目录下的全目录是:D:/test/a/b/c/d
$dir_path = 'D:/test';
delDir($dir_path);
function delDir($dir_path){
//打开当前的目录
$dir = opendir($dir_path);
//通过readdir函数获取目录下的所有目录
while(false !== ($fileName = readdir($dir))){
//对当前的目录进行拼接
if($fileName != '.' && $fileName != '..'){
$dir_name = $dir_path . '/' . $fileName;
if(is_dir($dir_name)){
//是一个目录,通过递归在此判断。
delDir($dir_name);
//递归完成,当前目录下为空,删除目录。
}else if(is_file($dir_name)){
//是文件删除文件。
unlink($dir_name);
}
}
}
closedir($dir);
rmdir($dir_path);
}把文件删除的操作封装到函数中,如果目录下没有文件则while循环不会进入循环,而是直接删除目录。当有目录或文件时,可以在循环中递归的执行函数,知道遇到是文件或目录为空(基准条件)。
<?php
//当前需要复制的文件路径。
$file_path = 'D:/Desert.jpg';
//需要复制到哪的路径
$path = "E:/desert.jpg";
if(file_exists($file_path)){
if(copy($file_path,$path)){
echo '复制成功';
}else{
echo '复制失败';
}
}else{
echo '文件不存在';
}定义的文件的全路径
定义目标的路径。
利用copy函数直接进行复制拷贝,第一个参数是文件的路径,第二个参数是目标的路径。
<?php
$dir_path = 'D:/test';
isDir($dir_path);
function isDir($dir_path){
if(is_dir($dir_path)){
//存在文件
$dir = opendir($dir_path);
//打开目录
while(($fileName = readdir($dir)) !== false){
if($fileName != '.' && $fileName != '..'){
if(is_dir($dir_path . '/' . $fileName)){
echo '<br>目录名是:' . $fileName;
isDir($dir_path . '/' . $fileName);
}else if(is_file($dir_path . '/' . $fileName)){
echo '<br>文件名是:' . $fileName;
}
}
}
//关闭资源
closedir($dir);
}
}
......结果.......
目录名是:a
文件名是:a.txt
目录名是:b
目录名是:c
目录名是:d
文件名是:n.doc
文件名是:c.txt* 通过递归进行循环的判断一个目录下面的所有目录和文件,进行输出。
* 在每个目录下都隐藏着两个无用的目录,所以通过if判断把这两个无用的目录过滤掉。
<?php
$dir_path = 'D:/test';
echo getSize($dir_path);
function getSize($dir_path){
//定义字节。
$size = 0;
//判断是否目录
if(is_dir($dir_path)){
//打开目录
$dir = opendir($dir_path);
//判断每个目录是否存在。
while(false !== ($fileName = readdir($dir))){
//过滤无用的两个目录。
if($fileName != '.' && $fileName != '..'){
if(is_dir($dir_path . '/' . $fileName)){
//通过递归进行循环的获取字节大小。
$size += getSize($dir_path . '/' . $fileName);
}else if(is_file($dir_path . '/' . $fileName)){
$size +=filesize($dir_path . '/' . $fileName);
}
}
}
}
//关闭资源。
fclose($dir);
return $size;
}
.......结果.......
47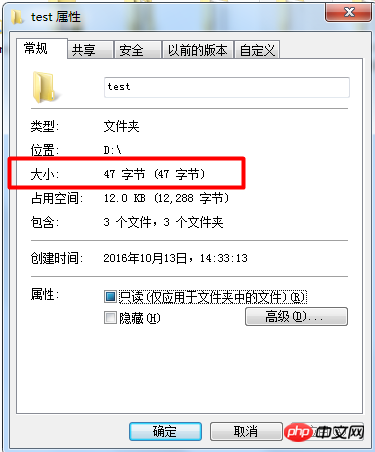
获取目录的字节通过递归完成。定义$size记录每个文件的大小,返回。
PHP中对于文件的操作还是很重要的,对于文件的操作要灵活的应用不同的函数。
以上就是PHP基础教程十五之文件、目录的操作的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!




