 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 PHP object-oriented advanced design pattern: decorator pattern
PHP object-oriented advanced design pattern: decorator pattern
PHP object-oriented advanced design pattern: decorator pattern
What is the decorator pattern?
If you make changes to part or functionality of an existing object, but do not need to modify the structure of the original object, then using the decorator design pattern is most suitable.
Decorator pattern application problems and solutions:
When we first learn about object-oriented programming, the first obstacle is often understanding the parent-child relationship in inheritance. relation. Over time, we will become more familiar with this programming method. When faced with a new challenge, experienced object-oriented programmers immediately extend more functionality to an object. However, just as everything has a degree, only moderate use can ensure the good development of this kind of work.
The code base should have a limit on the number of class hierarchies. If objects begin to require too many subclasses, the corresponding code sacrifices programmer understanding and maintainability. Generally, I try to ensure that there are no more than 3 parent-child relationships for an object. I found that as long as more parent-child relationships are created, the code becomes confusing and uncontrollable. In addition, using ordinary paper cannot produce a UML diagram representation of any object in the application.
However, I don't want to prevent the use of class extensions. In fact, we often extend objects using appropriate solutions. However, for some problems, using classes based on the decorator design pattern is a better solution.
The decorator design pattern is suitable for situations where programmers spend a lot of time: changes are quick and small, and have little impact on the rest of the application. The goal of designing a class using the decorator design pattern is to apply incremental changes to a base object without having to override any existing functionality. Decorators are built in such a way that it should be possible to insert one or more decorators that change or "decorate" the target object directly into the main code flow without affecting other code flows.
UML
The UML diagram below details a class design using the decorator design pattern.
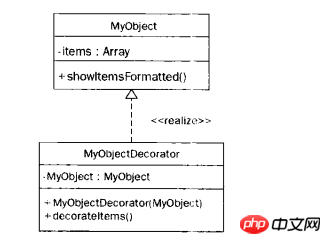
The following description of the above picture:
1.MyObject is a base class with existing functionality. This class contains a public array named items and a public method named show ItemsFormatted().
2. The show ItemsFormatted() method is responsible for accepting the items array, formatting the array using predefined functionality and submitting the output.
3.The MyObjectDecorator class contains a private instance of MyObject and two public methods: MyObjectDecorator() and decorateItems().
4.The MyObjectDecorator() method represents the constructor, which accepts a MyObject type parameter and stores it internally.
5. The decorateItems() method can modify the items array of the MyObject instance.
Let’s look at the following example. In order to calculate the value of an area, we write the code as follows:
// 区域抽象类
abstract class Area
{
abstract public function treasure();
}
//森林类,价值100
class Forest extends Area
{
public function treasure()
{
return 100;
}
}
//沙漠类,价值10
class Desert extends Area
{
function function treasure()
{
return 10;
}
}The above code seems to have no problem, but if you need to give an area What should I do to calculate the value of the destroyed forest? Should I add a DamageForest subclass? Obviously it is not feasible, because there are likely to be many other classes with overlapping types, which will lead to duplicate code in the class and more and more subclasses.
The decorator pattern uses composition and delegation instead of inheritance to solve the above problems. Let's look at the following improved code:
// 区域抽象类
abstract class Area
{
abstract public function treasure();
}
//森林类,价值100
class Forest extends Area
{
public function treasure()
{
return 100;
}
}
//沙漠类,价值10
class Desert extends Area
{
function function treasure()
{
return 10;
}
}
//区域类的装饰器类
abstract class AreaDecorateor extends Area
{
protected $_area = null;
public function __construct(Area $area)
{
$this->_area = $area;
}
}
//被破坏了后的区域,价值只有之前的一半
class Damaged extends AreaDecorateor
{
public function treasure()
{
return $this->_area->treasure() * 0.5;
}
}
//现在我们来获取被破坏的森林类的价值
$damageForest = new Damaged(new Forest());
echo $damageForest->treasure(); //返回50The above is the detailed content of PHP object-oriented advanced design pattern: decorator pattern. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1668
1668
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1329
1329
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
 PHP Advanced Features: Best Practices in Object-Oriented Programming
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:39 PM
PHP Advanced Features: Best Practices in Object-Oriented Programming
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:39 PM
OOP best practices in PHP include naming conventions, interfaces and abstract classes, inheritance and polymorphism, and dependency injection. Practical cases include: using warehouse mode to manage data and using strategy mode to implement sorting.
 The difference between design patterns and architectural patterns in Java framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:59 PM
The difference between design patterns and architectural patterns in Java framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:59 PM
In the Java framework, the difference between design patterns and architectural patterns is that design patterns define abstract solutions to common problems in software design, focusing on the interaction between classes and objects, such as factory patterns. Architectural patterns define the relationship between system structures and modules, focusing on the organization and interaction of system components, such as layered architecture.
 In-depth understanding of PHP object-oriented programming: Debugging techniques for object-oriented programming
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:50 PM
In-depth understanding of PHP object-oriented programming: Debugging techniques for object-oriented programming
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:50 PM
By mastering tracking object status, setting breakpoints, tracking exceptions and utilizing the xdebug extension, you can effectively debug PHP object-oriented programming code. 1. Track object status: Use var_dump() and print_r() to view object attributes and method values. 2. Set a breakpoint: Set a breakpoint in the development environment, and the debugger will pause when execution reaches the breakpoint, making it easier to check the object status. 3. Trace exceptions: Use try-catch blocks and getTraceAsString() to get the stack trace and message when the exception occurs. 4. Use the debugger: The xdebug_var_dump() function can inspect the contents of variables during code execution.
 Analysis of the Decorator Pattern in Java Design Patterns
May 09, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
Analysis of the Decorator Pattern in Java Design Patterns
May 09, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
The decorator pattern is a structural design pattern that allows dynamic addition of object functionality without modifying the original class. It is implemented through the collaboration of abstract components, concrete components, abstract decorators and concrete decorators, and can flexibly expand class functions to meet changing needs. In this example, milk and mocha decorators are added to Espresso for a total price of $2.29, demonstrating the power of the decorator pattern in dynamically modifying the behavior of objects.
 PHP Design Patterns: Test Driven Development in Practice
Jun 03, 2024 pm 02:14 PM
PHP Design Patterns: Test Driven Development in Practice
Jun 03, 2024 pm 02:14 PM
TDD is used to write high-quality PHP code. The steps include: writing test cases, describing the expected functionality and making them fail. Write code so that only the test cases pass without excessive optimization or detailed design. After the test cases pass, optimize and refactor the code to improve readability, maintainability, and scalability.
 Application of design patterns in Guice framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 10:49 PM
Application of design patterns in Guice framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 10:49 PM
The Guice framework applies a number of design patterns, including: Singleton pattern: ensuring that a class has only one instance through the @Singleton annotation. Factory method pattern: Create a factory method through the @Provides annotation and obtain the object instance during dependency injection. Strategy mode: Encapsulate the algorithm into different strategy classes and specify the specific strategy through the @Named annotation.
 Application of design patterns in Spring MVC framework
Jun 02, 2024 am 10:35 AM
Application of design patterns in Spring MVC framework
Jun 02, 2024 am 10:35 AM
The SpringMVC framework uses the following design patterns: 1. Singleton mode: manages the Spring container; 2. Facade mode: coordinates controller, view and model interaction; 3. Strategy mode: selects a request handler based on the request; 4. Observer mode: publishes and listen for application events. These design patterns enhance the functionality and flexibility of SpringMVC, allowing developers to create efficient and maintainable applications.
 What are the advantages and disadvantages of using design patterns in java framework?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using design patterns in java framework?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
The advantages of using design patterns in Java frameworks include: enhanced code readability, maintainability, and scalability. Disadvantages include complexity, performance overhead, and steep learning curve due to overuse. Practical case: Proxy mode is used to lazy load objects. Use design patterns wisely to take advantage of their advantages and minimize their disadvantages.



