PHP operates MySQL database
PHP connection to MySQL
Before we access the MySQL database, we need to connect to the database server first. To connect to the server, we use the mysqli_connect() function.
Before using this function, let’s first take a look at the syntax of this function:
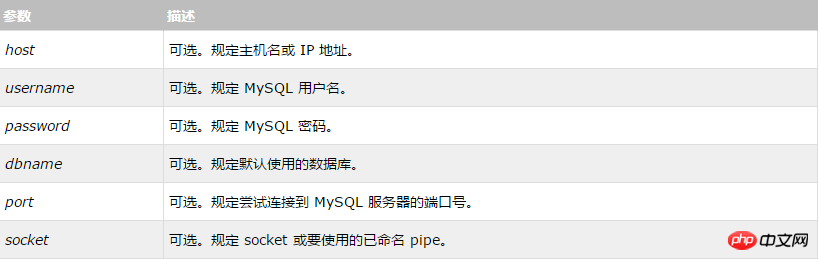
mysqli_connect(host,username,password,dbname,port,socket);
Parameter description
Return value
If the connection is successful Returns an object representing a connection to the MySQL server.
Here, I am using the wamp integrated mysql database. We use the above method to connect to our database. (The default user name is root, and the password is empty);
$conn=mysqli_connect("localhost","root","");
if(!$conn){
die("Connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());//如果连接失败输出一条消息,并退出当前脚本}Create database
mysqli_query()
In php, execute the mysql statement, The mysqli_query() method must be used. So before creating a database, let's first take a look at the usage of mysqli_query():
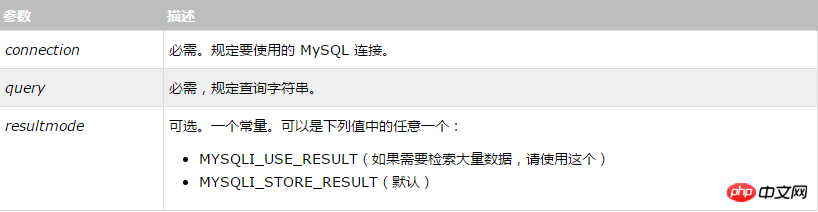
mysqli_query(connection,query,resultmode);
Parameter description
Return value
For successful SELECT, SHOW, DESCRIBE or EXPLAIN query, a mysqli_result object will be returned. For other successful queries, TRUE will be returned. On failure, returns FALSE.
Create database
Create a database using the CREATE DATABASE statement, and this statement needs to be executed through the mysqli_query() method to take effect. (Note: In PHP, all mysql statements need to be executed through this method to take effect, so they will not be explained again below)
Next we will do this in our local database, Create a database named test01
= ('localhost','root','' = "CREATE DATABASE test01"(,After executing the above statement, we can use the show databases statement to check whether the database has been created successfully. ()
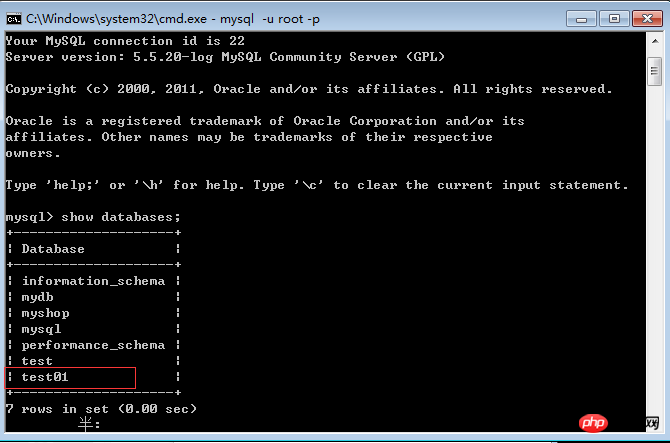
Open cmd, enter mysql -u username -p and press Enter to enter the password according to the prompts. At this time, you can enter the console of the mysql database. If after typing, it prompts that mysql is not an internal or external command, then we only need to find the installation directory (bin directory) of mysql and copy it, and then use this path as a variable value to configure the environment variable. You can
Enter the show databases statement. At this time, you can see that the test01 database we just created already exists, as shown below
Create data table
Select database
After the database is created, we will start to create the data table. Before creating the table, we must first select the method to create the table. Database, we use the mysqli_select_db() method to select the database. Similarly, before using this method, let’s first take a look at the usage of this method:
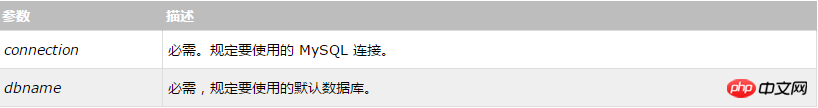
mysqli_select_db(connection,dbname);
Parameter description:
Returns TRUE if successful and FALSE if failed. Now let's use this method and select the table we just created.
mysqli_select_db($conn,'test01');//选择数据库
Create data table
Create a table using the CREATE TABLE table name statement. Next we use this statement to create an admin table
$sql="CREATE TABLE admin ( id INT(6) UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, username VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL, password CHAR(6) NOT NULL, email VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL )";mysqli_query($conn,$sql); //创建数据库
NOT NULL - Each row must contain a value (cannot be empty), null values are not allowed.
UNSIGNED - Use unsigned numeric types, 0 and positive numbers
AUTO INCREMENT - Set the value of the MySQL field every time when adding a record Automatically increase by 1
PRIMARY KEY - Set the unique identifier of each record in the data table. Usually the PRIMARY KEY of the column is set to the ID value, used with AUTO_INCREMENT.
Insert data
After creating the database and table, we can add data to the table.
INSERT INTO statement is usually used to add new records to the MySQL table:
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3,...) VALUES (value1, value2, value3,...)
Example:
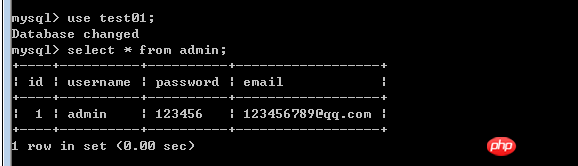
$sql="INSERT INTO admin(username,password,email) VALUES('admin','123456','123456789@qq.com')";mysqli_query($conn,$sql);Complete execution After that, we can check whether the newly created piece of data exists in the database. As you can see from the picture on the right, this piece of data has been successfully created in our table.
Deleting data
Use the DELETE FROM statement to delete records from the database table.
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE some_column = some_value
$sql="DELETE FROM admin WHERE username='admin'";mysqli_query($conn,$sql);
Update data
The UPDATE statement is used to update existing records in the database table.
UPDATE table_name SET column1=value, column2=value2,... WHERE some_column=some_value
实例:
$sql="UPDATE admin SET email='309123793@qq.com'"; mysqli_query($conn,$sql);
读取数据
SELECT 语句用于从数据表中读取数据:
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name
实例:
$sql = "SELECT id, username, email FROM admin"; mysqli_query($conn,$sql);
ORDER BY 关键词
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name ORDER BY column_name(s) ASC|DESC
说明:默认为升序排列,如果需要降序排列,请使用 DESC 关键字。
$sql="SELECT * FROM admin ORDER BY username";
mysqli_query($conn,$sql);
The above is the detailed content of PHP operates MySQL database. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1317
1317
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1246
1246
 24
24
 MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin are powerful database management tools. 1) MySQL is used to create databases and tables, and to execute DML and SQL queries. 2) phpMyAdmin provides an intuitive interface for database management, table structure management, data operations and user permission management.
 Explain the purpose of foreign keys in MySQL.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Explain the purpose of foreign keys in MySQL.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:17 AM
In MySQL, the function of foreign keys is to establish the relationship between tables and ensure the consistency and integrity of the data. Foreign keys maintain the effectiveness of data through reference integrity checks and cascading operations. Pay attention to performance optimization and avoid common errors when using them.
 The Compatibility of IIS and PHP: A Deep Dive
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The Compatibility of IIS and PHP: A Deep Dive
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:01 AM
IIS and PHP are compatible and are implemented through FastCGI. 1.IIS forwards the .php file request to the FastCGI module through the configuration file. 2. The FastCGI module starts the PHP process to process requests to improve performance and stability. 3. In actual applications, you need to pay attention to configuration details, error debugging and performance optimization.
 Compare and contrast MySQL and MariaDB.
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Compare and contrast MySQL and MariaDB.
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:08 AM
The main difference between MySQL and MariaDB is performance, functionality and license: 1. MySQL is developed by Oracle, and MariaDB is its fork. 2. MariaDB may perform better in high load environments. 3.MariaDB provides more storage engines and functions. 4.MySQL adopts a dual license, and MariaDB is completely open source. The existing infrastructure, performance requirements, functional requirements and license costs should be taken into account when choosing.
 SQL vs. MySQL: Clarifying the Relationship Between the Two
Apr 24, 2025 am 12:02 AM
SQL vs. MySQL: Clarifying the Relationship Between the Two
Apr 24, 2025 am 12:02 AM
SQL is a standard language for managing relational databases, while MySQL is a database management system that uses SQL. SQL defines ways to interact with a database, including CRUD operations, while MySQL implements the SQL standard and provides additional features such as stored procedures and triggers.
 What happens if session_start() is called multiple times?
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:06 AM
What happens if session_start() is called multiple times?
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Multiple calls to session_start() will result in warning messages and possible data overwrites. 1) PHP will issue a warning, prompting that the session has been started. 2) It may cause unexpected overwriting of session data. 3) Use session_status() to check the session status to avoid repeated calls.
 Composer: Aiding PHP Development Through AI
Apr 29, 2025 am 12:27 AM
Composer: Aiding PHP Development Through AI
Apr 29, 2025 am 12:27 AM
AI can help optimize the use of Composer. Specific methods include: 1. Dependency management optimization: AI analyzes dependencies, recommends the best version combination, and reduces conflicts. 2. Automated code generation: AI generates composer.json files that conform to best practices. 3. Improve code quality: AI detects potential problems, provides optimization suggestions, and improves code quality. These methods are implemented through machine learning and natural language processing technologies to help developers improve efficiency and code quality.
 MySQL: The Database, phpMyAdmin: The Management Interface
Apr 29, 2025 am 12:44 AM
MySQL: The Database, phpMyAdmin: The Management Interface
Apr 29, 2025 am 12:44 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin can be effectively managed through the following steps: 1. Create and delete database: Just click in phpMyAdmin to complete. 2. Manage tables: You can create tables, modify structures, and add indexes. 3. Data operation: Supports inserting, updating, deleting data and executing SQL queries. 4. Import and export data: Supports SQL, CSV, XML and other formats. 5. Optimization and monitoring: Use the OPTIMIZETABLE command to optimize tables and use query analyzers and monitoring tools to solve performance problems.




