
This article mainly introduces the principle of Oracle paging query in detail, and analyzes the implementation method from the example test data. This article analyzes the basic knowledge of Oracle paging query in detail from the data query principle and paging implementation method. The following is this article Content:
Reason 1
Oracle generates rowmun and rowid fields for each table by default. We call these fields pseudo columns
1 Create a test table
CREATE TABLE TEST( ID NUMBER, NAME VARCHAR2(20) )
2 Insert test data
INSERT INTO TEST VALUES (1,'张三'); INSERT INTO TEST VALUES (2,'李四'); INSERT INTO TEST VALUES (3,'王五'); INSERT INTO TEST VALUES (4,'赵六'); INSERT INTO TEST VALUES (5,'郑七'); INSERT INTO TEST VALUES (6,'胡八'); INSERT INTO TEST VALUES (7,'刘九');
3 Check the table fields and confirm that the built-in fields
select rowid,rownum,id,name from TEST;
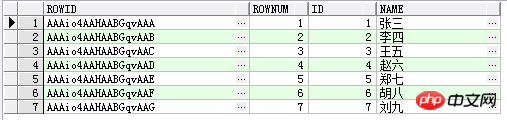
4 rowid are generally not used. , used internally by Oracle to store the physical location of rows. Related to paging is rownum, which is the row number
二
1 Query rows less than 5 and get four results
select rowid,rownum,id,name from test where rownum <5;

2 Query rows greater than 2 and less than 5
select rownum,id,name from test where rownum>2 and rownum <5;
I found nothing, what’s the reason?,
rownum has the following characteristics:
1 ROWNUM is only applicable to less than or less than Equal, if equal judgment is made, it can only be equal to 1;
2 ROWNUM is the number of rows allocated sequentially by the Oracle system. The first row returned is allocated 1, the second row is 2, and so on. ;
3 ROWNUM always starts from 1
4 The first data row number is 1 and does not meet the condition of >2, then the first row is removed, and the previous second row It becomes the new first row, and so on, until the last row, the condition is never satisfied, so not even a single piece of data can be found.
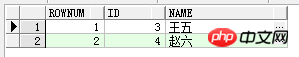
3 Correct way to write it: Because > cannot be used, use the inner query to query the row number as a result set, and use the inner result set for comparison in the outer layer.
select rownum,id,name from ( select rownum rn, u.* from test u where rownum<5) un where un.rn>2
4 If paging is performed, for example, there are three rows per page, you need to query the second page, it is equivalent to checking 4, 5, 6 items, starting line 4 = (page number-1) * length of each page + 1, ending line 6 = page number * length of each page
select rownum,id,name from ( select rownum rn , t.* from test t where rownum <=6) n where n.rn>=4

select rownum,id,name from (
select rownum rn, n.* from
(
select * from test --最内层循环该怎么写怎么写
) n where rownum <=6 --小于限制写在第二层
)
where rn>=4Oracle paging function example implemented in PHP
##php+oracle paging class_PHP tutorialoracle paging query sql principles and statementsThe above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the basic principles of Oracle paging query. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




