About the analysis of PHP pipeline plug-in League\Pipeline
This article mainly introduces the analysis of the PHP pipeline plug-in League\Pipeline, which has certain reference value. Now I share it with you. Friends in need can refer to it
Pipeline design pattern
The water pipe is too long, and if one part is broken, it will leak, and it is not conducive to bending and turning in complex environments. Therefore, we will divide the water pipes into very short pipes, and then maximize the size of the pipes to have different functions, adapt to local conditions, and assemble them together to meet a variety of different needs.
This leads to the design pattern of Pipeline, which is to cut complex and lengthy processes into small processes and tasks. Each minimally quantified task can be reused to form complex and diverse processes by assembling different small tasks.
Finally, introduce the "input" into the pipeline, operate (process, filter) the input according to each small task, and finally output the results that meet the needs.
Today I mainly study "Pipeline", and by the way, I recommend a PHP plug-in: league/pipeline.
gulp
The first time I learned about the concept of "pipe" came from the use of gulp.

gulp is an automatic task runner based on NodeJS. She can automatically complete Javascript, Test, check, merge, compress, format, automatically refresh the browser, generate deployment files for sass, less and other files, and monitor the files to repeat the specified steps after changes. In terms of implementation, she draws on the pipe idea of the Unix operating system. The output of the previous level directly becomes the input of the next level, making the operation very simple.
var gulp = require('gulp');
var less = require('gulp-less');
var minifyCSS = require('gulp-csso');
var concat = require('gulp-concat');
var sourcemaps = require('gulp-sourcemaps');
gulp.task('css', function(){
return gulp.src('client/templates/*.less')
.pipe(less())
.pipe(minifyCSS())
.pipe(gulp.dest('build/css'))
});
gulp.task('js', function(){
return gulp.src('client/javascript/*.js')
.pipe(sourcemaps.init())
.pipe(concat('app.min.js'))
.pipe(sourcemaps.write())
.pipe(gulp.dest('build/js'))
});
gulp.task('default', [ 'html', 'css', 'js' ]);The above two task are mainly to parse, compress, output and other process operations on less and all js files, and then save them. to the corresponding folder; the output of each step is the input of the next step, just like the flow of water in a pipe.
IlluminatePipeline
The middleware in the Laravel framework is implemented using Illuminate\Pipeline. I originally wanted to write about my interpretation of the source code of "Laravel Middleware". But I found that there are already many posts on the Internet that explain it, so this article will briefly talk about how to use Illuminate\Pipeline.
Write a demo
public function demo(Request $request)
{
$pipe1 = function ($payload, Closure $next) {
$payload = $payload + 1;
return $next($payload);
};
$pipe2 = function ($payload, Closure $next) {
$payload = $payload * 3;
return $next($payload);
};
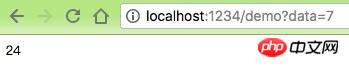
$data = $request->input('data', 0);
$pipeline = new Pipeline();
return $pipeline
->send($data)
->through([$pipe1, $pipe2])
->then(function ($data) {
return $data;
});
}
gulp and Illuminate\Pipeline just tells us that "Pipeline" is widely used. If we were asked to write a similar plug-in ourselves, I think it wouldn't be difficult.
League\Pipeline plug-in and take a look at its source code to see how it is implemented.
Brief description
This package provides a plug and play implementation of the Pipeline Pattern. It's an architectural pattern which encapsulates sequential processes. When used, it allows you to mix and match operation, and pipelines, to create new execution chains. The pipeline pattern is often compared to a production line, where each stage performs a certain operation on a given payload/subject. Stages can act on, manipulate, decorate, or even replace the payload.If you find yourself passing results from one function to another to complete a series of tasks on a given subject, you might want to convert it into a pipeline.https://pipeline. thephpleague.com/
Install plug-in
composer require league/pipeline
Write a demo
use League\Pipeline\Pipeline;
// 创建两个闭包函数
$pipe1 = function ($payload) {
return $payload + 1;
};
$pipe2 = function ($payload) {
return $payload * 3;
};
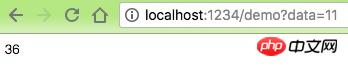
$route->map(
'GET',
'/demo',
function (ServerRequestInterface $request, ResponseInterface $response
) use ($service, $pipe1, $pipe2) {
$params = $request->getQueryParams();
// 正常使用
$pipeline1 = (new Pipeline)
->pipe($pipe1)
->pipe($pipe2);
$callback1 = $pipeline1->process($params['data']);
$response->getBody()->write("<h1 id="正常使用">正常使用</h1>");
$response->getBody()->write("<p>结果:$callback1</p>");
// 使用魔术方法
$pipeline2 = (new Pipeline())
->pipe($pipe1)
->pipe($pipe2);
$callback2 = $pipeline2($params['data']);
$response->getBody()->write("<h1 id="使用魔术方法">使用魔术方法</h1>");
$response->getBody()->write("<p>结果:$callback2</p>");
// 使用 Builder
$builder = new PipelineBuilder();
$pipeline3 = $builder
->add($pipe1)
->add($pipe2)
->build();
$callback3 = $pipeline3($params['data']);
$response->getBody()->write("<h1 id="使用-Builder">使用 Builder</h1>");
$response->getBody()->write("<p>结果:$callback3</p>");
return $response;
}
);Run result


Interpretation of the source code
The entire plug-in only has these files: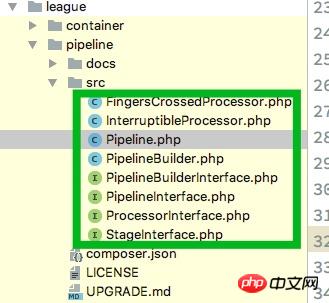
PipelineInterface
<?php declare(strict_types=1);
namespace League\Pipeline;
interface PipelineInterface extends StageInterface
{
/**
* Create a new pipeline with an appended stage.
*
* @return static
*/
public function pipe(callable $operation): PipelineInterface;
}
interface StageInterface
{
/**
* Process the payload.
*
* @param mixed $payload
*
* @return mixed
*/
public function __invoke($payload);
}mixed __invoke ([ $... ] )
当尝试以调用函数的方式调用一个对象时,__invoke() 方法会被自动调用。如:
<?php class CallableClass
{
function __invoke($x) {
var_dump($x);
}
}
$obj = new CallableClass;
$obj(5);
var_dump(is_callable($obj));
?>返回结果:
int(5) bool(true)
Pipeline
<?php declare(strict_types=1);
namespace League\Pipeline;
class Pipeline implements PipelineInterface
{
/**
* @var callable[]
*/
private $stages = [];
/**
* @var ProcessorInterface
*/
private $processor;
public function __construct(ProcessorInterface $processor = null, callable ...$stages)
{
$this->processor = $processor ?? new FingersCrossedProcessor;
$this->stages = $stages;
}
public function pipe(callable $stage): PipelineInterface
{
$pipeline = clone $this;
$pipeline->stages[] = $stage;
return $pipeline;
}
public function process($payload)
{
return $this->processor->process($payload, ...$this->stages);
}
public function __invoke($payload)
{
return $this->process($payload);
}
}其中核心类 Pipeline 的作用主要就是两个:
添加组装各个管道「pipe」;
组装后,引水流动,执行 process($payload),输出结果。
Processor
接好各种管道后,那就要「引水入渠」了。该插件提供了两个基础执行类,比较简单,直接看代码就能懂。
// 按照 $stages 数组顺利,遍历执行管道方法,再将结果传入下一个管道,让「水」一层层「流动」起来
class FingersCrossedProcessor implements ProcessorInterface
{
public function process($payload, callable ...$stages)
{
foreach ($stages as $stage) {
$payload = $stage($payload);
}
return $payload;
}
}
// 增加一个额外的「过滤网」,经过每个管道后的结果,都需要 check,一旦满足则终止,直接输出结果。
class InterruptibleProcessor implements ProcessorInterface
{
/**
* @var callable
*/
private $check;
public function __construct(callable $check)
{
$this->check = $check;
}
public function process($payload, callable ...$stages)
{
$check = $this->check;
foreach ($stages as $stage) {
$payload = $stage($payload);
if (true !== $check($payload)) {
return $payload;
}
}
return $payload;
}
}
interface ProcessorInterface
{
/**
* Process the payload using multiple stages.
*
* @param mixed $payload
*
* @return mixed
*/
public function process($payload, callable ...$stages);
}我们完全也可以利用该接口,实现我们的方法来组装管道和「过滤网」。
PipelineBuilder
最后提供了一个 Builder,这个也很好理解:
class PipelineBuilder implements PipelineBuilderInterface
{
/**
* @var callable[]
*/
private $stages = [];
/**
* @return self
*/
public function add(callable $stage): PipelineBuilderInterface
{
$this->stages[] = $stage;
return $this;
}
public function build(ProcessorInterface $processor = null): PipelineInterface
{
return new Pipeline($processor, ...$this->stages);
}
}
interface PipelineBuilderInterface
{
/**
* Add an stage.
*
* @return self
*/
public function add(callable $stage): PipelineBuilderInterface;
/**
* Build a new Pipeline object.
*/
public function build(ProcessorInterface $processor = null): PipelineInterface;
}总结
无论是对不同技术的横向理解,还是基于 Laravel 或者某些开源插件,我们都能学习到技术之上的通用原理和方法。再将这些原理和方法反作用于我们的实际代码开发中。
最近闲来没事,自己参考 Laravel 去写个简易框架,也将League\Pipeline 引入到框架中使用。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网!
相关推荐:
关于利用Vue-laravel前端和后端分离写一个博客的方法
The above is the detailed content of About the analysis of PHP pipeline plug-in League\Pipeline. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1663
1663
 14
14
 1420
1420
 52
52
 1315
1315
 25
25
 1266
1266
 29
29
 1239
1239
 24
24
 Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel is a PHP framework for easy building of web applications. It provides a range of powerful features including: Installation: Install the Laravel CLI globally with Composer and create applications in the project directory. Routing: Define the relationship between the URL and the handler in routes/web.php. View: Create a view in resources/views to render the application's interface. Database Integration: Provides out-of-the-box integration with databases such as MySQL and uses migration to create and modify tables. Model and Controller: The model represents the database entity and the controller processes HTTP requests.
 Solve caching issues in Craft CMS: Using wiejeben/craft-laravel-mix plug-in
Apr 18, 2025 am 09:24 AM
Solve caching issues in Craft CMS: Using wiejeben/craft-laravel-mix plug-in
Apr 18, 2025 am 09:24 AM
When developing websites using CraftCMS, you often encounter resource file caching problems, especially when you frequently update CSS and JavaScript files, old versions of files may still be cached by the browser, causing users to not see the latest changes in time. This problem not only affects the user experience, but also increases the difficulty of development and debugging. Recently, I encountered similar troubles in my project, and after some exploration, I found the plugin wiejeben/craft-laravel-mix, which perfectly solved my caching problem.
 Laravel user login function
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
Laravel user login function
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
Laravel provides a comprehensive Auth framework for implementing user login functions, including: Defining user models (Eloquent model), creating login forms (Blade template engine), writing login controllers (inheriting Auth\LoginController), verifying login requests (Auth::attempt) Redirecting after login is successful (redirect) considering security factors: hash passwords, anti-CSRF protection, rate limiting and security headers. In addition, the Auth framework also provides functions such as resetting passwords, registering and verifying emails. For details, please refer to the Laravel documentation: https://laravel.com/doc
 Laravel and the Backend: Powering Web Application Logic
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:29 AM
Laravel and the Backend: Powering Web Application Logic
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:29 AM
How does Laravel play a role in backend logic? It simplifies and enhances backend development through routing systems, EloquentORM, authentication and authorization, event and listeners, and performance optimization. 1. The routing system allows the definition of URL structure and request processing logic. 2.EloquentORM simplifies database interaction. 3. The authentication and authorization system is convenient for user management. 4. The event and listener implement loosely coupled code structure. 5. Performance optimization improves application efficiency through caching and queueing.
 Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Article summary: This article provides detailed step-by-step instructions to guide readers on how to easily install the Laravel framework. Laravel is a powerful PHP framework that speeds up the development process of web applications. This tutorial covers the installation process from system requirements to configuring databases and setting up routing. By following these steps, readers can quickly and efficiently lay a solid foundation for their Laravel project.
 How to learn Laravel How to learn Laravel for free
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
How to learn Laravel How to learn Laravel for free
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
Want to learn the Laravel framework, but suffer from no resources or economic pressure? This article provides you with free learning of Laravel, teaching you how to use resources such as online platforms, documents and community forums to lay a solid foundation for your PHP development journey from getting started to master.
 What versions of laravel are there? How to choose the version of laravel for beginners
Apr 18, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
What versions of laravel are there? How to choose the version of laravel for beginners
Apr 18, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
In the Laravel framework version selection guide for beginners, this article dives into the version differences of Laravel, designed to assist beginners in making informed choices among many versions. We will focus on the key features of each release, compare their pros and cons, and provide useful advice to help beginners choose the most suitable version of Laravel based on their skill level and project requirements. For beginners, choosing a suitable version of Laravel is crucial because it can significantly impact their learning curve and overall development experience.
 How to view the version number of laravel? How to view the version number of laravel
Apr 18, 2025 pm 01:00 PM
How to view the version number of laravel? How to view the version number of laravel
Apr 18, 2025 pm 01:00 PM
The Laravel framework has built-in methods to easily view its version number to meet the different needs of developers. This article will explore these methods, including using the Composer command line tool, accessing .env files, or obtaining version information through PHP code. These methods are essential for maintaining and managing versioning of Laravel applications.




