 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Examples of python menu recursive query and data conversion to json
Examples of python menu recursive query and data conversion to json
Examples of python menu recursive query and data conversion to json
This article mainly introduces the python recursive query menu and converts it into a json instance. It has certain reference value. Interested friends can refer to it.
I recently needed to write a menu in python, and it took me two or three days to get it done. Now I record it here, and friends who need it can learn from it.
Note: The article quotes the complete non-executable code and only excerpts the key parts of the code
Environment
Database: mysql
python:3.6
Table structure
CREATE TABLE `tb_menu` ( `id` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '唯一标识', `menu_name` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '菜单名称', `menu_url` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '菜单链接', `type` varchar(1) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '类型', `parent` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '父级目录id', `del_flag` varchar(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '删除标志 0:不删除 1:已删除', `create_time` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间', `update_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '更新时间', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='菜单表';
Python code
In the Menu object, there is a reference to the submenu list "subMenus", the type is list
Core code
def set_subMenus(id, menus):
"""
根据传递过来的父菜单id,递归设置各层次父菜单的子菜单列表
:param id: 父级id
:param menus: 子菜单列表
:return: 如果这个菜单没有子菜单,返回None;如果有子菜单,返回子菜单列表
"""
# 记录子菜单列表
subMenus = []
# 遍历子菜单
for m in menus:
if m.parent == id:
subMenus.append(m)
# 把子菜单的子菜单再循环一遍
for sub in subMenus:
menus2 = queryByParent(sub.id)
# 还有子菜单
if len(menus):
sub.subMenus = set_subMenus(sub.id, menus2)
# 子菜单列表不为空
if len(subMenus):
return subMenus
else: # 没有子菜单了
return NoneTest Method
def test_set_subMenus(self):
# 一级菜单
rootMenus = queryByParent('')
for menu in rootMenus:
subMenus = queryByParent(menu.id)
menu.subMenus = set_subMenus(menu.id, subMenus) Note: The basic process is: first query the first-level menu, and then pass the id of the menu at this level and the submenu list of this level menu to the set_subMenus method, and recursively perform the submenu list. Lower-level menu settings;
supports passing the menu ID to query all submenus under the menu. If you pass a null character, the query starts from the root directory
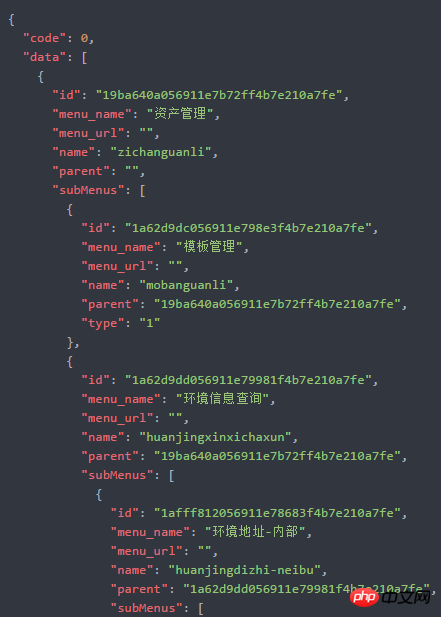
In the "rootMenus" object, you can see the complete menu tree structure
Convert to Json
The ORM framework I use is: sqlalchemy. The Menu object queried directly from the database will report an error when it is converted to Json. A DTO class needs to be redefined to convert the Menu object into a Dto object.
MenuDto
class MenuDto():
def init(self, id, menu_name, menu_url, type, parent, subMenus):
super().init()
self.id = id
self.menu_name = menu_name
self.menu_url = menu_url
self.type = type
self.parent = parent
self.subMenus = subMenus
def str(self):
return '%s(id=%s,menu_name=%s,menu_url=%s,type=%s,parent=%s)' % (
self.class.name, self.id, self.menu_name, self.menu_url, self.type, self.parent)
repr = strSo, the method of recursively setting submenus is redefined
def set_subMenuDtos(id, menuDtos):
"""
根据传递过来的父菜单id,递归设置各层次父菜单的子菜单列表
:param id: 父级id
:param menuDtos: 子菜单列表
:return: 如果这个菜单没有子菜单,返回None;如果有子菜单,返回子菜单列表
"""
# 记录子菜单列表
subMenuDtos = []
# 遍历子菜单
for m in menuDtos:
m.name = to_pinyin(m.menu_name)
if m.parent == id:
subMenuDtos.append(m)
# 把子菜单的子菜单再循环一遍
for sub in subMenuDtos:
menus2 = queryByParent(sub.id)
menusDto2 = model_list_2_dto_list(menus2,
"MenuDto(id='', menu_name='', menu_url='', type='', parent='', subMenus='')")
# 还有子菜单
if len(menuDtos):
if len(menusDto2):
sub.subMenus = set_subMenuDtos(sub.id, menusDto2)
else: # 没有子菜单,删除该节点
sub.delattr('subMenus')
# 子菜单列表不为空
if len(subMenuDtos):
return subMenuDtos
else: # 没有子菜单了
return NoneRemarks:
When a menu has no submenu, delete the "subMenus" attribute, otherwise a null value will appear when converting to Json
- ## The model_list_2_dto_list method can convert the Menu list into a MenuDto list
- to_pinyin is a method of converting Chinese characters into pinyin. You don’t need to pay attention here.
The method of View layer returning Json
def get(self):
param = request.args
id = param['id']
# 如果id为空,查询的是从根目录开始的各级菜单
rootMenus = queryByParent(id)
rootMenuDtos = model_list_2_dto_list(rootMenus,
"MenuDto(id='', menu_name='', menu_url='', type='', parent='', subMenus='')")
# 设置各级子菜单
for menu in rootMenuDtos:
menu.name = to_pinyin(menu.menu_name)
subMenus = queryByParent(menu.id)
if len(subMenus):
subMenuDtos = model_list_2_dto_list(subMenus,
"MenuDto(id='', menu_name='', menu_url='', type='', parent='', subMenus='')")
menu.subMenus = set_subMenuDtos(menu.id, subMenuDtos)
else:
menu.delattr('subMenus')
menus_json = json.dumps(rootMenuDtos, default=lambda o: o.dict, sort_keys=True, allow_nan=false,
skipkeys=true)
# 需要转字典,否则返回的字符串会带有“\”
menus_dict = json_dict(menus_json)
return fullResponse(menus_dict)
fullResponse
from flask import jsonify
def fullResponse(data='', msg='', code=0):
if msg == '':
return jsonify({'code': code, 'data': data})
elif data == '':
return jsonify({'code': code, 'msg': msg})
else:
return jsonify({'code': code, 'msg': msg, 'data': data})search result
The above is the detailed content of Examples of python menu recursive query and data conversion to json. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1421
1421
 52
52
 1315
1315
 25
25
 1266
1266
 29
29
 1239
1239
 24
24
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang is better than Python in terms of performance and scalability. 1) Golang's compilation-type characteristics and efficient concurrency model make it perform well in high concurrency scenarios. 2) Python, as an interpreted language, executes slowly, but can optimize performance through tools such as Cython.
 How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Running Python code in Notepad requires the Python executable and NppExec plug-in to be installed. After installing Python and adding PATH to it, configure the command "python" and the parameter "{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}" in the NppExec plug-in to run Python code in Notepad through the shortcut key "F6".



