
This article mainly introduces the relevant information on string processing of python data cleaning. Friends who need it can refer to it
Preface
Data cleaning is a Complex and tedious (kubi) work, it is also the most important link in the entire data analysis process. Some people say that 80% of the time of an analysis project is cleaning data. This sounds strange, but it is true in actual work. There are two purposes of data cleaning. The first is to make the data available through cleaning. The second is to make the data more suitable for subsequent analysis. In other words, there is "dirty" data that needs to be washed, and clean data that needs to be washed as well.
In data analysis, especially text analysis, character processing requires a lot of energy, so understanding character processing is also a very important ability for data analysis.
String processing methods
First of all, let’s understand what the basic methods are.
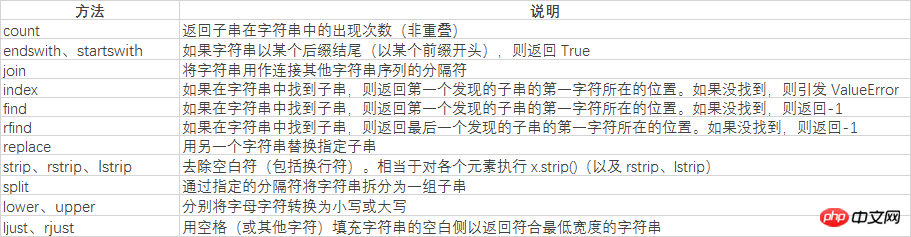
First of all, let’s understand The split method of string below
str='i like apple,i like bananer' print(str.split(','))
The result of splitting the character str with commas:
['i like apple', 'i like bananer']
print(str.split(' '))
The result of splitting based on spaces:
['i', 'like', 'apple,i', 'like', 'bananer']
print(str.index(',')) print(str.find(','))
Both search results are:
12
If the index cannot be found, the index returns an error, and find returns -1
print(str.count('i'))
The result is :
4
connt is used to count the frequency of the target string
print(str.replace(',', ' ').split(' '))
The result is:
[' i', 'like', 'apple', 'i', 'like', 'bananer']
Here replace replaces commas with spaces and then uses spaces to split the string. Just enough to get every word out.
In addition to conventional methods, the more powerful character processing tool feeregular expression is none other than.
Regular expression
Before using regular expressions, we need to understand the many methods in regular expressions.
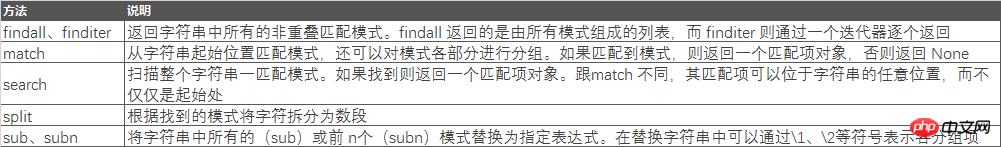
Let me look at the use of the next method. First, understand the difference between the match and search methods.
str = "Cats are smarter than dogs" pattern=re.compile(r'(.*) are (.*?) .*') result=re.match(pattern,str) for i in range(len(result.groups())+1): print(result.group(i))
The result is:
Cats are smarter than dogs
Cats
smarter
Under this form of pettern matching rule, the return results of the match and search methods are the same
At this time, if the pattern is changed to
pattern=re.compile(r'are (.*?) .*')
match, none will be returned, and the search result will be:
are smarter than dogs
smarter
Next let’s learn about the use of other methods
str = "138-9592-5592 # number" pattern=re.compile(r'#.*$') number=re.sub(pattern,'',str) print(number)
The result is:
138-9592-5592
The above is done by The content after the # sign is replaced with nothing to achieve the purpose of extracting the number.
We can also further replace the crossbar of the number
print(re.sub(r'-*','',number))
The result is:
13895925592
We You can also use the find method to print out the found string
str = "138-9592-5592 # number" pattern=re.compile(r'5') print(pattern.findall(str))
The result is:
['5', '5', '5']
The overall content of regular expressions is relatively large, and we need to have a sufficient understanding of the rules for matching strings. The following are the specific matching rules.

Vectorized stringFunction
When cleaning up the scattered data to be analyzed, you often need to do some String normalization work.
data = pd.Series({'li': '120@qq.com','wang':'5632@qq.com',
'chen': '8622@xinlang.com','zhao':np.nan,'sun':'5243@gmail.com'})
print(data)The result is:

You can make preliminary judgments on the data through some integrated methods, such as using contains to determine whether each data contains key The result of the word
print(data.str.contains('@'))
is:

You can also split the string and extract the required string
data = pd.Series({'li': '120@qq.com','wang':'5632@qq.com',
'chen': '8622@xinlang.com','zhao':np.nan,'sun':'5243@gmail.com'})
pattern=re.compile(r'(\d*)@([a-z]+)\.([a-z]{2,4})')
result=data.str.match(pattern) #这里用fillall的方法也可以result=data.str.findall(pattern)
print(result)The result For:
chen [(8622, xinlang, com)]
li [(120, qq, com)]
sun [(5243, gmail, com)]
wang [(5632, qq, com)]
zhao NaN
dtype: object
To join at this time we need to extract the name in front of the mailbox
print(result.str.get(0))
The result is:

Or the domain name to which the email address belongs
print(result.str.get(1))
The result is:

data = pd.Series({'li': '120@qq.com','wang':'5632@qq.com',
'chen': '8622@xinlang.com','zhao':np.nan,'sun':'5243@gmail.com'})
print(data.str[:6])
Finally we understand the vectorized string method

Summary
[Related recommendations]
2. Python object-oriented video tutorial
3. Python basic introductory tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of examples of cleaning strings in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




