
1. Workflow
<script>'Not Safe'</script>
c. Other users see this page containing malicious scripts and execute them to obtain the user's cookies, etc. Sensitive information.
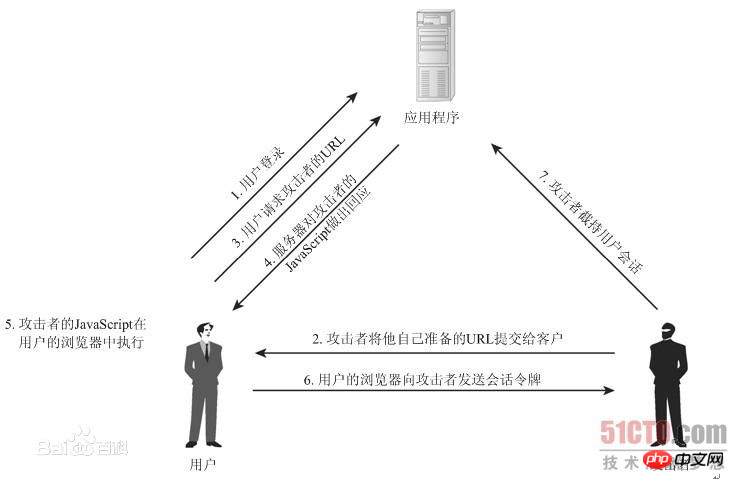
2. Example - Failure to prevent XSS attacks

1 pinglu = [] # 评论列表 2 3 #提交表单 4 def commit(request): 5 if request.method == 'GET': 6 return render(request, 'commit.html') 7 else: 8 com = request.POST.get('commit') 9 pinglu.append(com)10 return redirect('/index.html/')11 12 13 #查看评论页面14 def index(request):15 return render(request, 'index.html', {'commit': pinglu})
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>Title</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <h1>评论</h1> 9 <form action="/commit.html/" method="post">10 <input type="text" name="commit">11 <input type="submit" value="sumbit"> {{ error }}12 </form>13 </body>14 </html>
 commit.html
commit.html
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>Title</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <h1>评论</h1> 9 {% for item in commit %}10 <div>{{ item|safe }}</div>11 {# item后加safe,默认数据安全,django不会做特殊处理#}12 {% endfor %}13 </body>14 </html>
 index.html
In the above example, if you enter the following content on the commit.html page and submit:
index.html
In the above example, if you enter the following content on the commit.html page and submit:
<script> alert('恶意脚本') </script>3. Prevent XSS attacks 
{# <div>{{ item|safe }}</div>#}<div>{{ item }}</div>
def commit(request):if request.method == 'GET':return render(request, 'commit.html')else:
com = request.POST.get('commit')if '<script>' in com: # 过滤“<script>”关键字,防止恶意代码的提交return render(request, 'commit.html', {'error': '此条评论有毒,已被和谐'})else:
pinglu.append(com)return redirect('/index.html/') 2. CSRF
2. CSRF
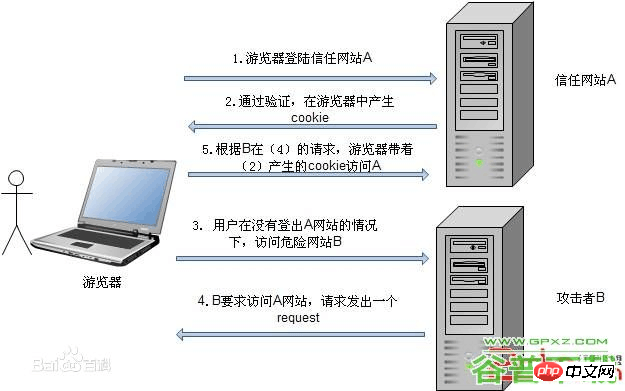
CSRF (Cross-site request forgery) cross-site request forgery, also known as "One Click Attack" or Session Riding, often abbreviated as CSRF or XSRF, is a malicious exploitation of a website. Although it sounds like cross-site scripting (XSS), it is very different from XSS, which exploits trusted users within a site, while CSRF exploits trusted websites by disguising requests from trusted users. Compared with XSS attacks, CSRF attacks tend to be less popular (so resources to prevent them are also quite scarce) and difficult to prevent, so they are considered more dangerous than XSS.
The attack works by including links or scripts in pages accessed by authorized users:
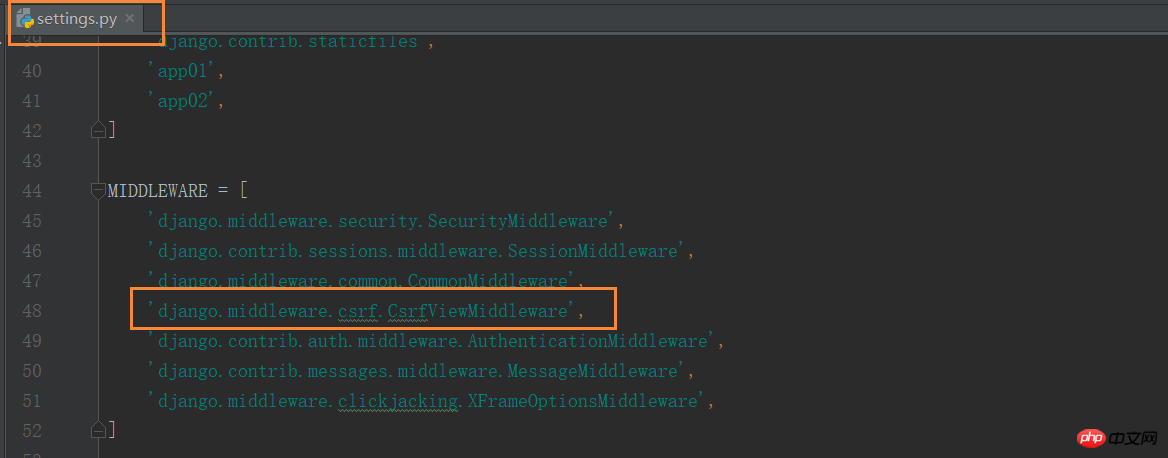
 Django implements the function of preventing cross-site request forgery for users, which is completed through the middleware django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware. The anti-cross-site request forgery function in Django is divided into global and local.
Django implements the function of preventing cross-site request forgery for users, which is completed through the middleware django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware. The anti-cross-site request forgery function in Django is divided into global and local.
from django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_exempt,csrf_protect
@csrf_protect,为当前函数强制设置防跨站请求伪造功能,即便settings中没有设置全局中间件
@csrf_exempt,取消当前函数防跨站请求伪造功能,即便settings中设置了全局中间件。
form表单中添加{% csrf_token %}
若form表单中未添加{% csrf_token %},则会报403错误。
#settings.py中打开MIDDLEWARE设置'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',


1 from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse, redirect2 3 def csrf_test(request):4 if request.method == 'GET':5 return render(request, 'csrf_test.html')6 else:7 return HttpResponse('ok')

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>csef_test</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <form action="/csrf_test.html/" method="post"> 9 <input type="text" name="user" id="user">10 <input type="submit" value="submit">11 </form>12 13 </body>14 </html>
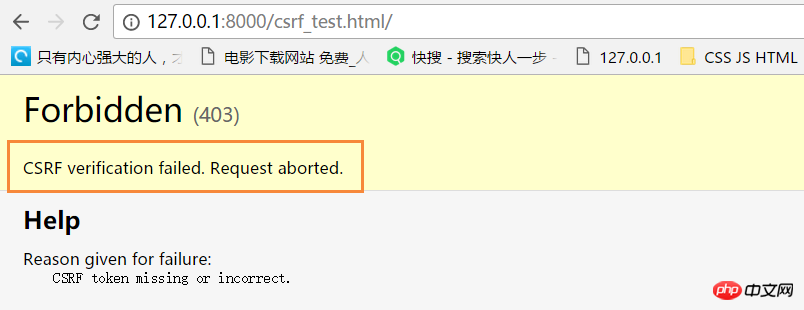
修改csef_test.html:


1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>csef_test</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <form action="/csrf_test.html/" method="post"> 9 {% csrf_token %}10 <input type="text" name="user" id="user">11 <input type="submit" value="submit">12 </form>13 14 </body>15 </html>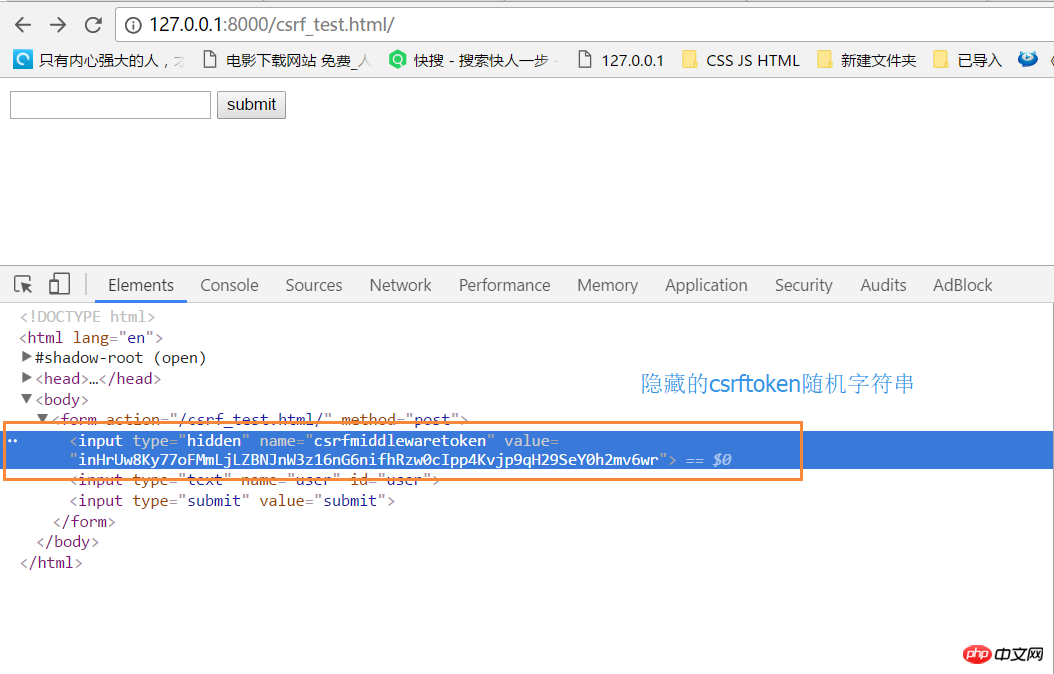
全站禁用,即将settings.py中的 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware' 注释掉即可
基于FBV视图的局部禁用和使用

1 #settings.py 2 #启用 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware', 3 4 5 from django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_exempt 6 7 8 @csrf_exempt 9 def csrf_test(request):10 if request.method == 'GET':11 return render(request, 'csrf_test.html')12 else:13 return HttpResponse('ok')

1 #settings.py 2 #禁用 #'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware', 3 4 5 from django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_protect 6 7 8 @csrf_protect 9 def csrf_test(request):10 if request.method == 'GET':11 return render(request, 'csrf_test.html')12 else:13 return HttpResponse('ok')基于CBV视图的(只能局部使用或禁用类,不能在类方法里局部使用或禁用


1 #settings.py 2 #禁用 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware', 3 4 5 from django.views import View 6 from django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_protect 7 from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator 8 9 10 @method_decorator(csrf_protect, name='dispatch')11 class Foo(View):12 def get(self, request):13 pass14 15 def post(self, request):16 pass
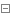
1 #settings.py 2 #启用 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware', 3 4 5 from django.views import View 6 from django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_exempt 7 from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator 8 9 10 @method_decorator(csrf_exempt, name='dispatch')11 class Foo(View):12 def get(self, request):13 pass14 15 def post(self, request):16 pass
Ajax提交数据时,携带CSRF


1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>csef_test</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <form action="/csrf_test.html/" method="post"> 9 {% csrf_token %}10 <input type="text" name="user" id="user">11 {# <input type="submit" value="submit">#}12 <a onclick="submitForm();">Ajax提交表单</a>13 </form>14 15 <script src="/static/jquery-3.2.1.js"></script>16 <script>17 function submitForm() {18 var csrf = $("input[name='csrfmiddlewaretoken']").val()19 var user = $("#user").val()20 $.ajax({21 url: '/csrf_test.html/',22 type: 'POST',23 data: {"user": user, "csrfmiddlewaretoken": csrf},24 success: function (arg) {25 console.log(arg);26 }27 })28 }29 </script>30 </body>31 </html>

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>csef_test</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <form action="/csrf_test.html/" method="post"> 9 {% csrf_token %}10 <input type="text" name="user" id="user">11 {# <input type="submit" value="submit">#}12 <a onclick="submitForm();">Ajax提交表单</a>13 </form>14 15 <script src="/static/jquery-3.2.1.js"></script>16 {#专门处理cookie的插件,提取cookie字符串#}17 <script src="/static/jquery.cookie.js"></script>18 19 {#csrf数据放于data中#}20 {#<script>#}21 {# function submitForm() {#}22 {# var csrf = $("input[name='csrfmiddlewaretoken']").val();#}23 {# var user = $("#user").val();#}24 {# $.ajax({#}25 {# url: '/csrf_test.html/',#}26 {# type: 'POST',#}27 {# data: {"user": user, "csrfmiddlewaretoken": csrf},#}28 {# success: function (arg) {#}29 {# console.log(arg);#}30 {# }#}31 {# })#}32 {# }#}33 {#</script>#}34 35 {#csrf数据放于请求头中#}36 <script>37 function submitForm() {38 var csrf = $.cookie('csrftoken');39 var user = $("#user").val();40 $.ajax({41 url: '/csrf_test.html/',42 type: 'POST',43 headers: {'X-CSRFToken': csrf},44 data: {"user": user},45 success: function (arg) {46 console.log(arg);47 }48 })49 }50 </script>51 52 53 54 </body>55 </html>注意:{% csrf_token %}和cookie中的csrftoken值不一样。
form表单中的隐藏csrf_token

cookie中

The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to XSS and CSRF. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




