 Backend Development
Backend Development
 XML/RSS Tutorial
XML/RSS Tutorial
 XML—Detailed explanation of DTD for XML document constraints
XML—Detailed explanation of DTD for XML document constraints
XML—Detailed explanation of DTD for XML document constraints
1. A brief introduction to XML file constraints and DTD
We write documents to constrain the writing specifications of an XML document. This Call it an XML constraint.
Commonly used constraint technologies are:
Basic concepts of DTD:
- ##XML DTD
- XML Schema
document type definitionDTD files are generally used in conjunction with XML files, mainly for constraints XML file. The XML file introduces the DTD file, so that XML can customize tags but is constrained by the DTD file. For example, in the previous section, XML was used to describe information about a class. If we defined a
tag for each student, there would be no syntax error, but it would not be semantically correct. How could students use area? To describe it? At this time we need to use a DTD file to constrain this XML.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="gb2312"?><class>
<stu id="001">
<name>杨过</name>
<sex>男</sex>
<age>20</age>
<面积>100</面积>
</stu></class>1.1 DTD constraint quick start case
Basic syntax:<!ELEMENT 元素名 类型>
<!ELEMENT 班级 (学生+)><!ELEMENT 学生 (名字,年龄,介绍)><!ELEMENT 名字 (#PCDATA)><!ELEMENT 年龄 (#PCDATA)><!ELEMENT 介绍 (#PCDATA)>
The second line indicates that the student's sub-elements are name, age, introduction
There are no sub-elements under the name, then #PCDATA indicates that any text can be placed in the name.
The age and introduction are similar.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><!--引入dtd文件,约束这个xml--><!DOCTYPE 班级 SYSTEM "myClass.dtd"><班级>
<学生>
<名字>周小星</名字>
<年龄>23</年龄>
<介绍>学习刻苦</介绍>
</学生>
<学生>
<名字>林晓</名字>
<年龄>25</年龄>
<介绍>是一个好学生</介绍>
</学生> </班级>If it is written as PUBLIC, it means The imported DTD file comes from the Internet.
, open For this XML file, the browser still does not report an error.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><!--引入dtd文件,约束这个xml--><!DOCTYPE 班级 SYSTEM "myClass.dtd"><班级>
<学生>
<名字>周小星</名字>
<年龄>23</年龄>
<介绍>学习刻苦</介绍>
<面积>100平米</面积>
</学生>
<学生>
<名字>林晓</名字>
<年龄>25</年龄>
<介绍>是一个好学生</介绍>
</学生> </班级>programmatically verify the correctness of the XML document.
Browsers above IE5 have a built-in XML parsing tool: Microsoft.XMLDOM. Developers can write JavaScript code, use this parsing tool to load XML files, and perform DTD verification on XML files. We write myXmlTools.html to verify this XML, as follows:<html>
<head>
<!--自己编写一个简单的解析工具,去解析XML DTD是否配套-->
<script language="javascript">
// 创建xml文档解析器对象
var xmldoc = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLDOM"); // 开启xml校验
xmldoc.validateOnParse = "true"; // 装载xml文档,即指定校验哪个XML文件
xmldoc.load("myClass.xml");
document.writeln("错误信息:"+xmldoc.parseError.reason+"<br>");
document.writeln("错误行号:"+xmldoc.parseError.line); </script>
</head>
<body>
</body></html>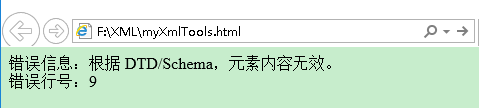
.
2.DTD details
2.1 Declaration and reference of DTD document
1.Internal DTD document
<!DOCTYPE 根元素 [定义内容]>
2. External DTD document
The imported external DTD document is divided into two types: (1) When the referenced DTD file When it is a local file, use the SYSTEM mark and write the "DTD file path" as follows:<!DOCTYPE 根元素 SYSTEM "DTD文件路径">
<!DOCTYPE 根元素 PUBLIC "DTD名称" "DTD文件的URL">
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems,Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN" "http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd">
2.2 Basic DTD syntax: <!ELEMENT NAME CONTENT>
Copy after loginCopy after login
Among them: <!ELEMENT NAME CONTENT>
- ELEMENT is a keyword and cannot The modified
- NAME represents the element name
- CONTENT is the element type and must be capitalized! There are three ways to write the content of CONTENT:
(1)EMPTY-indicates that the element cannot contain sub-elements and text, but can have attributes.(2)ANY——Indicates that the element can contain any element content defined in the
DTD (3) #PCDATA - can contain any character data, but cannot contain any sub-elements
2.3 Combination type of DTD elements:
DTD This is stipulated in:<!ELEMENT 家庭(人+,家电*)>
<家庭>
<人 名字="张晓明" 性别="男" 年龄="25"/>
<人 名字="李小钢" 性别="男" 年龄="36" 爱好="作个教育家和伟人"/>
<家电 名称="彩电" 数量="3"/></家庭>| Use | Example | Example description | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| is used to group elements | (Gu Long | Jin Yong), (Wang Shuo | Yu Jie) | is divided into two groups | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| in the listed objects Select one of | (man|woman) | means that a man or a woman must appear, and at least one of the two must be selected | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The object must appear once or multiple times | (member+) | means that the member must appear, but multiple members can appear | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This object is allowed to appear 0 or more times | (Hobby*) | Hobby can appear two to multiple times | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The object must appear 0 or 1 time | (Rookie?) | The rookie can appear or not. If it appears, it can only appear at most Appear once | ##, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (watermelon, apple, banana) | means watermelon, Apples and bananas must appear in this order |
| 符号 | 用途 | 示例 | 示例说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| () | 用来给元素分组 | (古龙|金庸),(王朔|余杰) | 分成两组 |
| | | 在列出的对象中选择一个 | (男人|女人) | 表示男人或者女人必须出现,两者至少选其一 |
| + | 该对象必须出现一次或者多次 | (成员+) | 表示成员必须出现,而却可以出现多个成员 |
| * | 该对象允许出现0次或者多次 | (爱好*) | 爱好可以出现两次到多次 |
| ? | 该对象必须出现0次或者1次 | (菜鸟?) | 菜鸟可以出现,也可以不出现,如果出现的话,最多只能出现一次 |
| , | 对象必须按指定的顺序出现 | (西瓜,苹果,香蕉) | 表示西瓜、苹果、香蕉必须出现,并且按这个顺序出现 |
2.4 属性定义
DTD中属性的定义是这样的:
<!ATTLIST 元素名称
属性名称 类型 属性特点
属性名称 类型 属性特点...... >其中,属性的类型有下面5种:
(1) CDATA
(2) ID
(3) IDREF/IDREFS
(4) Enumerated
(5) ENTITY/ENTITIES
属性的特点有如下4种:
(1) #REQUIRED,表示这个属性必须给,不给就报错
(2) #IMPLIED,表示这个属性可以给也可以不给
(3) #FIXED value,表示这个属性必须给一个固定的value值
(4) Default value,表示这个属性如果没有值,就分配一个默认的value值
比如,我们想在学生这个子元素上加上地址这个属性,而且这个属性是必须的,示例如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><!DOCTYPE 班级 SYSTEM "myClass.dtd"><班级>
<学生 地址="香港">
<名字>周小星</名字>
<年龄>23</年龄>
<介绍>学习刻苦</介绍>
</学生>
<学生 地址="澳门">
<名字>林晓</名字>
<年龄>25</年龄>
<介绍>是一个好学生</介绍>
</学生> </班级>这个时候相应的DTD文件也要更新,不然就会报错,如下:
<!ELEMENT 班级 (学生+)><!ELEMENT 学生 (名字,年龄,介绍)><!ATTLIST 学生
地址 CDATA #REQUIRED><!ELEMENT 名字 (#PCDATA)><!ELEMENT 年龄 (#PCDATA)><!ELEMENT 介绍 (#PCDATA)>2.4.1 对于属性类型的详细解释
(1)属性类型-CDATA,表示属性值可以是任何字符(包括中文和数字)
<!ATTLIST 木偶
姓名 CDATA #REQUIRED><木偶 姓名="匹诺曹"/><木偶 姓名="PiNuocao"/><木偶 姓名="123"/>
(2)属性类型-ID,表明该属性的取值必须是唯一的,但是属性的值不能是以数字开头!
<!ELEMENT 公司职员 ANY><!ATTLIST 公司职员
编号 ID #REQUIRED
姓名 CDATA #REQUIRED><公司职员 编号="Z001" 姓名="张三"/><公司职员 编号="Z002" 姓名="李思"/>
(3)属性类型-IDREF/IDREFS
- IDREF属性的值指向文档中其它地方声明的ID类型的值
- IDREFS同IDREF,但是可以具有由空格分开的多个引用。
<!ELEMENT 家庭(人+)><!ELEMENT 人 EMPTY><!ATTLIST 人 relID ID #REQUIRED
paraentID IDREFS #IMPLIED
name CDATA #REQUIRED><家庭>
<人 relID="P_1" name="爸爸"/>
<人 relID="P_2" name="妈妈"/>
<人 relID="P_3" parentID="P_1 P_2" name="儿子"/></家庭>(4)属性类型-Enumerated,事先定义好一些值,属性的值必须在所列出的值的范围内。
<!ATTLIST person
婚姻状态 (single|married|porced|widowed) #IMPLIED><!ATTLIST person
性别 (男|女) #REQUIRED>(5)属性类型-ENTITY,实体
实体定义:
- 实体用于为一段内容创建一个别名,以后在XML文档中就可以使用别名引用这段内容了。
- 在DTD定义中,一条!ENTITY语句用于定义一个实体。
- 实体可分为两种类型:引用实体和参数实体。引用实体是被XML文档应用的,而参数实体是被DTD文件本身应用的。
①引用实体:
引用实体主要在XML文档中被应用
语法格式如下,引用实体的定义内容最好放在DTD文件的最后。
<!ENTITY 实体名称 "实体内容">
引用方式:&实体名称; 末尾要带上分号,这个引用将直接转变成实体内容
举例如下:
<!ENTITY copyright "I am a programmer">.... ©right;
②参数实体:
参数实体被DTD文件自身使用
语法格式为:
<!ENTITY % 实体名称 "实体内容">
引用方式为:%实体名称
举例:
<!ENTITY % TAG_NAME "姓名|EMAIL|电话|地址"><!ELEMENT 个人信息 (%TAG_NAME;|生日)><!ELEMENT 客户信息 (%TAG_NAME;|公司名)>
3.DTD实际案例
学习DTD的目标在于:
(1)要求我们能够看得懂DTD文件,
(2)我们可以根据给出的DTD写出对应的XML文件
下面我们看一个案例,下述的DTD文件是从W3School在线教程中的DTD案例中拿过来的,细看每一行,我们都应该能够看得懂。
<!ENTITY AUTHOR "John Doe"><!ENTITY COMPANY "JD Power Tools, Inc."><!ENTITY EMAIL "jd@jd-tools.com"> <!ELEMENT CATALOG (PRODUCT+)> <!ELEMENT PRODUCT(SPECIFICATIONS+,OPTIONS?,PRICE+,NOTES?)> <!ATTLIST PRODUCTNAME CDATA #IMPLIEDCATEGORY (HandTool|Table|Shop-Professional) "HandTool"PARTNUM CDATA #IMPLIEDPLANT (Pittsburgh|Milwaukee|Chicago) "Chicago"INVENTORY (InStock|Backordered|Discontinued) "InStock"> <!ELEMENT SPECIFICATIONS (#PCDATA)> <!ATTLIST SPECIFICATIONSWEIGHT CDATA #IMPLIEDPOWER CDATA #IMPLIED> <!ELEMENT OPTIONS (#PCDATA)> <!ATTLIST OPTIONSFINISH (Metal|Polished|Matte) "Matte" ADAPTER (Included|Optional|NotApplicable) "Included"CASE (HardShell|Soft|NotApplicable) "HardShell"> <!ELEMENT PRICE (#PCDATA)> <!ATTLIST PRICEMSRP CDATA #IMPLIEDWHOLESALE CDATA #IMPLIEDSTREET CDATA #IMPLIEDSHIPPING CDATA #IMPLIED> <!ELEMENT NOTES (#PCDATA)>
然后我们可以根据该DTD编写如下最简单的XML文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><!DOCTYPE CATALOG SYSTEM "product.dtd"><CATALOG>
<PRODUCT NAME="康帅傅矿泉水" CATEGORY="Table" PARTNUM="12" PLANT="Chicago">
<SPECIFICATIONS WEIGHT="20" POWER="18">这里是细节</SPECIFICATIONS>
<PRICE>25</PRICE>
<PRICE>28</PRICE>
</PRODUCT></CATALOG>然后我们用Microsoft.XMLDOM校验该XML,会发现没有任何错误。但是要注意编码。
以上就是XML—XML文件约束之DTD详解的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Can I open an XML file using PowerPoint?
Feb 19, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Can I open an XML file using PowerPoint?
Feb 19, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Can XML files be opened with PPT? XML, Extensible Markup Language (Extensible Markup Language), is a universal markup language that is widely used in data exchange and data storage. Compared with HTML, XML is more flexible and can define its own tags and data structures, making the storage and exchange of data more convenient and unified. PPT, or PowerPoint, is a software developed by Microsoft for creating presentations. It provides a comprehensive way of
 Using Python to merge and deduplicate XML data
Aug 07, 2023 am 11:33 AM
Using Python to merge and deduplicate XML data
Aug 07, 2023 am 11:33 AM
Using Python to merge and deduplicate XML data XML (eXtensibleMarkupLanguage) is a markup language used to store and transmit data. When processing XML data, sometimes we need to merge multiple XML files into one, or remove duplicate data. This article will introduce how to use Python to implement XML data merging and deduplication, and give corresponding code examples. 1. XML data merging When we have multiple XML files, we need to merge them
 Filtering and sorting XML data using Python
Aug 07, 2023 pm 04:17 PM
Filtering and sorting XML data using Python
Aug 07, 2023 pm 04:17 PM
Implementing filtering and sorting of XML data using Python Introduction: XML is a commonly used data exchange format that stores data in the form of tags and attributes. When processing XML data, we often need to filter and sort the data. Python provides many useful tools and libraries to process XML data. This article will introduce how to use Python to filter and sort XML data. Reading the XML file Before we begin, we need to read the XML file. Python has many XML processing libraries,
 Convert XML data to CSV format in Python
Aug 11, 2023 pm 07:41 PM
Convert XML data to CSV format in Python
Aug 11, 2023 pm 07:41 PM
Convert XML data in Python to CSV format XML (ExtensibleMarkupLanguage) is an extensible markup language commonly used for data storage and transmission. CSV (CommaSeparatedValues) is a comma-delimited text file format commonly used for data import and export. When processing data, sometimes it is necessary to convert XML data to CSV format for easy analysis and processing. Python is a powerful
 Import XML data into database using PHP
Aug 07, 2023 am 09:58 AM
Import XML data into database using PHP
Aug 07, 2023 am 09:58 AM
Importing XML data into the database using PHP Introduction: During development, we often need to import external data into the database for further processing and analysis. As a commonly used data exchange format, XML is often used to store and transmit structured data. This article will introduce how to use PHP to import XML data into a database. Step 1: Parse the XML file First, we need to parse the XML file and extract the required data. PHP provides several ways to parse XML, the most commonly used of which is using Simple
 Python implements conversion between XML and JSON
Aug 07, 2023 pm 07:10 PM
Python implements conversion between XML and JSON
Aug 07, 2023 pm 07:10 PM
Python implements conversion between XML and JSON Introduction: In the daily development process, we often need to convert data between different formats. XML and JSON are common data exchange formats. In Python, we can use various libraries to convert between XML and JSON. This article will introduce several commonly used methods, with code examples. 1. To convert XML to JSON in Python, we can use the xml.etree.ElementTree module
 Handling errors and exceptions in XML using Python
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:25 PM
Handling errors and exceptions in XML using Python
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:25 PM
Handling Errors and Exceptions in XML Using Python XML is a commonly used data format used to store and represent structured data. When we use Python to process XML, sometimes we may encounter some errors and exceptions. In this article, I will introduce how to use Python to handle errors and exceptions in XML, and provide some sample code for reference. Use try-except statement to catch XML parsing errors When we use Python to parse XML, sometimes we may encounter some
 Python parsing special characters and escape sequences in XML
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:46 PM
Python parsing special characters and escape sequences in XML
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:46 PM
Python parses special characters and escape sequences in XML XML (eXtensibleMarkupLanguage) is a commonly used data exchange format used to transfer and store data between different systems. When processing XML files, you often encounter situations that contain special characters and escape sequences, which may cause parsing errors or misinterpretation of the data. Therefore, when parsing XML files using Python, we need to understand how to handle these special characters and escape sequences. 1. Special characters and



