


1. 实例演示相邻选择器与兄弟选择器,并分析异同
相邻选择器 与 兄弟选择器 实例结果 GIF
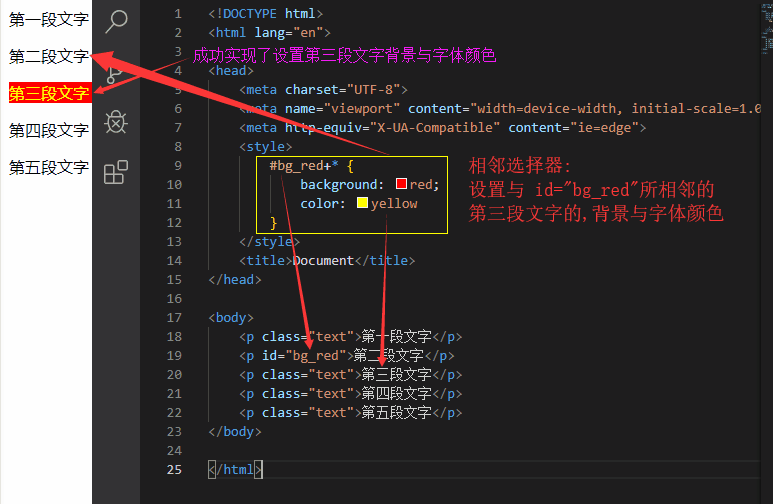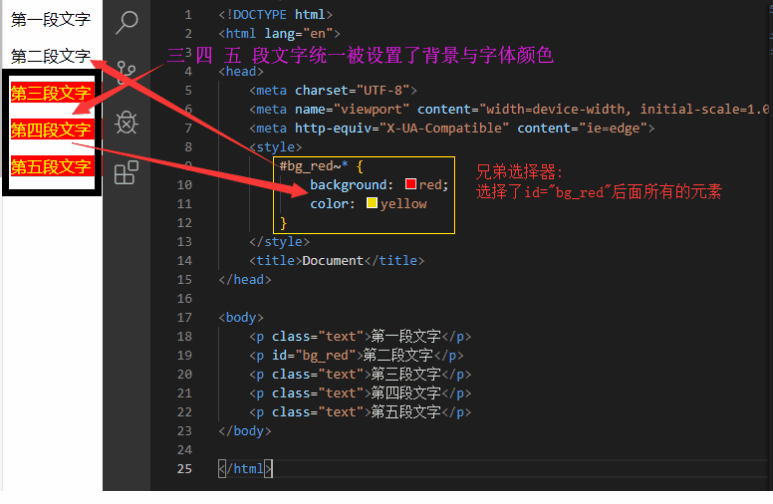
相邻选择器实例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<style>
#bg_red+* {
background: red;
color: yellow
}
</style>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="text">第一段文字</p>
<p id="bg_red">第二段文字</p>
<p class="text">第三段文字</p>
<p class="text">第四段文字</p>
<p class="text">第五段文字</p>
</body>
</html>点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
兄弟选择器实例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<style>
#bg_red~* {
background: red;
color: yellow
}
</style>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="text">第一段文字</p>
<p id="bg_red">第二段文字</p>
<p class="text">第三段文字</p>
<p class="text">第四段文字</p>
<p class="text">第五段文字</p>
</body>
</html>点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
分析:
如果需要选择紧接在另一个元素后的元素,可以使用相邻选择器, #bg_red+* {color:red} 选择紧接在id="bg_red"后面的元素
需要选择在另一个元素后面所有的元素,使用兄弟选择器 #bg_red~* {color:red}选择在id="bg_red"后面所有的元素
2. 实例演示:nth-child() 和 :nth-of-type()选择器,并分析异同
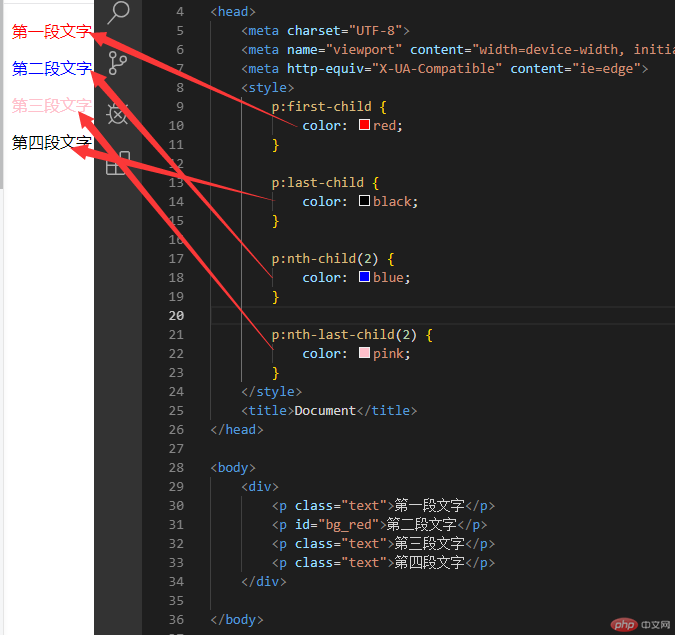
first-child last-child nth-child nth-last-child 实例
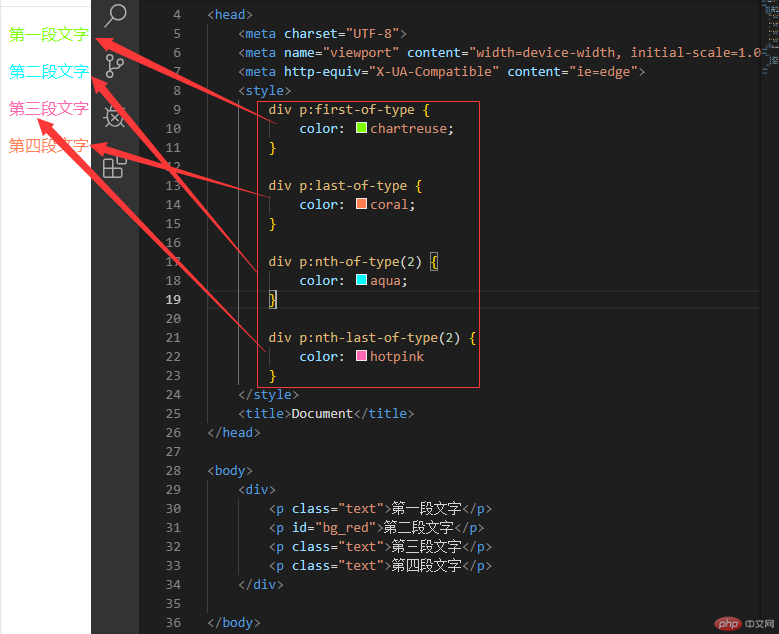
first-of-type last-of-type nth-of-type nth-last-of-type 实例
分析:
ntf-child 与 ntf-of-type 关注点各不相同
如果关注点 只是 数量 使用 ntf-child
如果既关注数量,又关注类型, 使用 ntf-of-type
3. 实例演示:padding 对盒子大小的影响与解决方案, 使用宽度分离或box-sizing
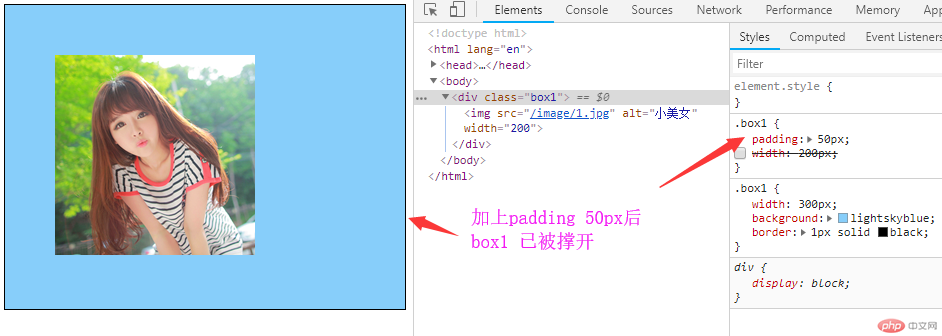
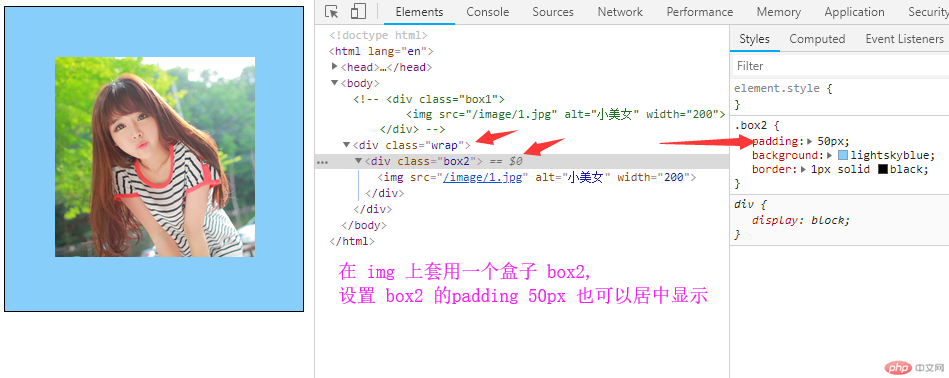
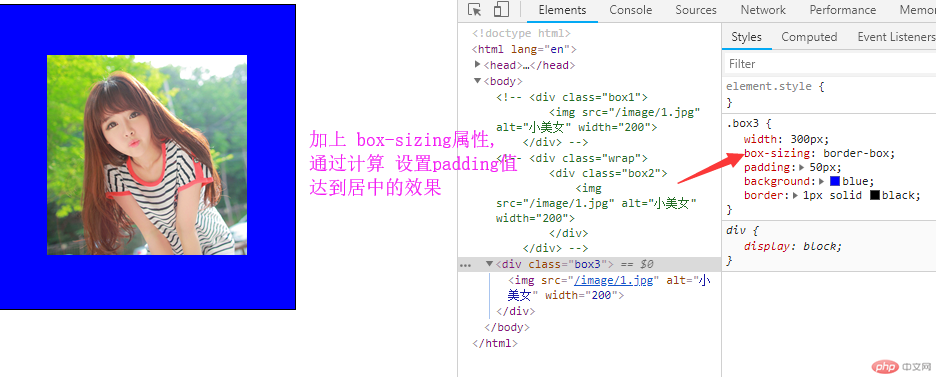
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="style/style.css"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div class="box1"> <img src="/image/1.jpg" alt="小美女" width="200"> </div> <div class="wrap"> <div class="box2"> <img src="/image/1.jpg" alt="小美女" width="200"> </div> </div> <div class="box3"> <img src="/image/1.jpg" alt="小美女" width="200"> </div> </body> </html>
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
4. 实例演示: margin中的同级塌陷, 嵌套传递与自动挤压, 并提出解决方案或应用场景
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<style>
.box1 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: blue;
}
.box2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
}
.box1 {
margin-bottom: 50px;
}
.box2 {
margin-top: 30px;
}
</style>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
</body>
</html>点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
同级塌陷在布局的时候会出现 数值小的会被大的吞掉,,解决办法 只设置一边的,
比如上面盒子的margin-bottom设置50px,下盒子的margin-top设置20px
只要设置其中的一个盒子的上top或者下bottom边距为70px,就可以解决
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<style>
.box1 {
/* box-sizing: border-box;
padding-top: 50px; */
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background: green;
}
.box2 {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background: pink;
}
.box1 {
padding-top: 50px;
height: 250px;
}
</style>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
嵌套传递指的是 在父元素未设置上边距的时候,子元素如果设置了上边距,会传递给父元素,造成这种情况
解决办法是,给父元素添加 boder-sizing属性 设置 padding值