


相邻选择器选中的是紧挨着的下一个元素,用 #id + * 号表示。
兄弟选择器选择的是从本身开始以后的元素,用 #id + ~ 号表示。
Nth-child(): 伪类:子元素选择器。
Nth-of-type():伪类:类型选择器。
如果关注点是位置,用nth-child()
如果既关注位置也关注类型,用nth-of-type()
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="static/css/style.css"> <title>选择器</title> </head> <body> <ul> <li class="bg-one">1</li> <li id="bg-one">2</li> <li class="bg-one">3</li> <li class="bg-one">4</li> <li id="bg-two">5</li> <li>6</li> <li>7</li> <li>8</li> <li>9</li> <li>10</li> </ul> </body> </html>
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
ul {
margin: 0;
padding-left: 0;
border: 1px dashed lightcoral;
}
ul li {
list-style-type: none;
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: #8abeb7;
border: 1px solid red;
line-height: 50px;
/*水平和垂直居中*/
text-align: center;
border-radius: 50%;
/*将一个块级元素转为内联元素*/
display: inline-block;
}
/*相邻选择器, #bg-one 这个id属性,用 *是选中后边的最相邻的*/
#bg-one + * {
/*background-color: aqua;*/
}
/*兄弟选择器,#bg-two这个id属性后的都是属于兄弟选择器的选择范围*/
#bg-two ~ * {
/*background-color: green;*/
}
/*nth-child() 伪类:子元素选择器 ()中是索引从1开始*/
ul :nth-child(7) {
background-color: red;
}
/*nth-of-type() 伪类:类型选择器*/
ul li:nth-of-type(8) {
background-color: hotpink;
color: white;
}点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
通过实例:将图片显示在容器中间 来演示padding对盒子大小影响以及解决方案
a) 当padding撑开盒子的时候,可以通过直接还原宽度来还原原本的效果

还原后效果:

此方式为:通过手工修改盒子宽度实现图片居中
方式2:宽度分离,通过添加一个中间层实现图片居中
<div><div></div></div>
方式3:box-sizing: border-box;来限制盒子
代码汇总:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="static/css/style1.css"> <title>padding</title> </head> <body> <!--将图片显示在容器中间--> <div class="box1"> <img src="images/jww.jpg" alt="吉娃娃" width="200px"> </div> <!--宽度分离 通过添加一个中间层实现图片居中--> <div class="wrap"> <div class="box2"> <img src="images/jww.jpg" alt="吉娃娃" width="200px"> </div> </div> <!--box-sizing--> <div class="box3"> <img src="images/jww.jpg" alt="吉娃娃" width="200px"> <a href="https://www.w3school.com.cn/cssref/pr_box-sizing.asp">点我看box-sizing用法</a> </div> </body> </html>
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
/*通过手工修改宽度数值实现图片居中*/
.box1 {
width: 300px;
border: 1px solid hotpink;
background-color: aquamarine;
}
.box1 {
padding: 50px;
width: 200px;
}
/*宽度分离*/
.wrap {
width: 300px;
}
.box2 {
padding: 50px;
background-color: aqua;
border: 1px solid coral;
}
/*box-sizing*/
.box3 {
width: 300px;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding:50px;
background-color: lightcoral;
border: 1px solid slateblue;
}点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
margin中的同级塌陷, 嵌套传递与自动挤压
同级塌陷:指垂直方向上的高度塌陷
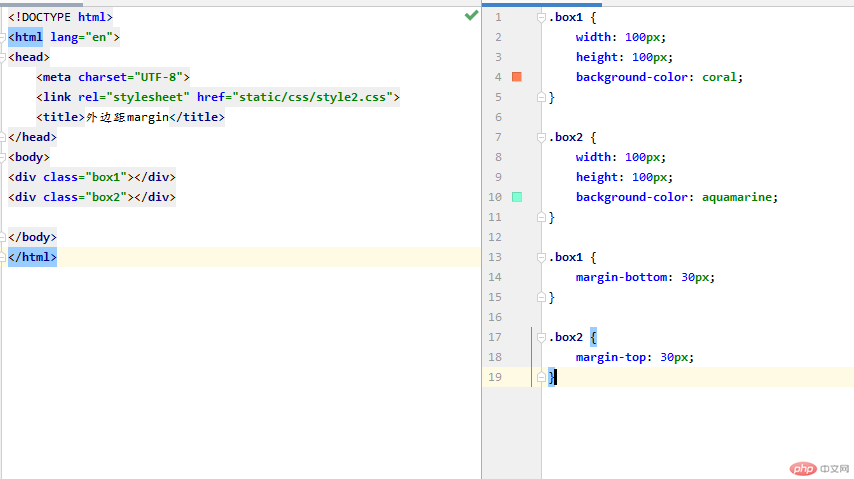
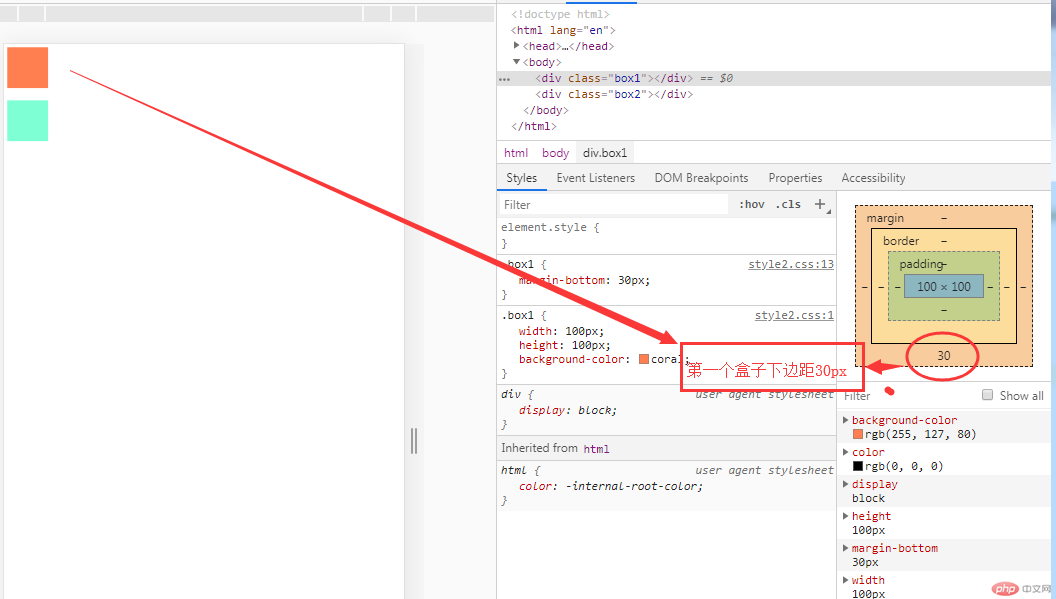
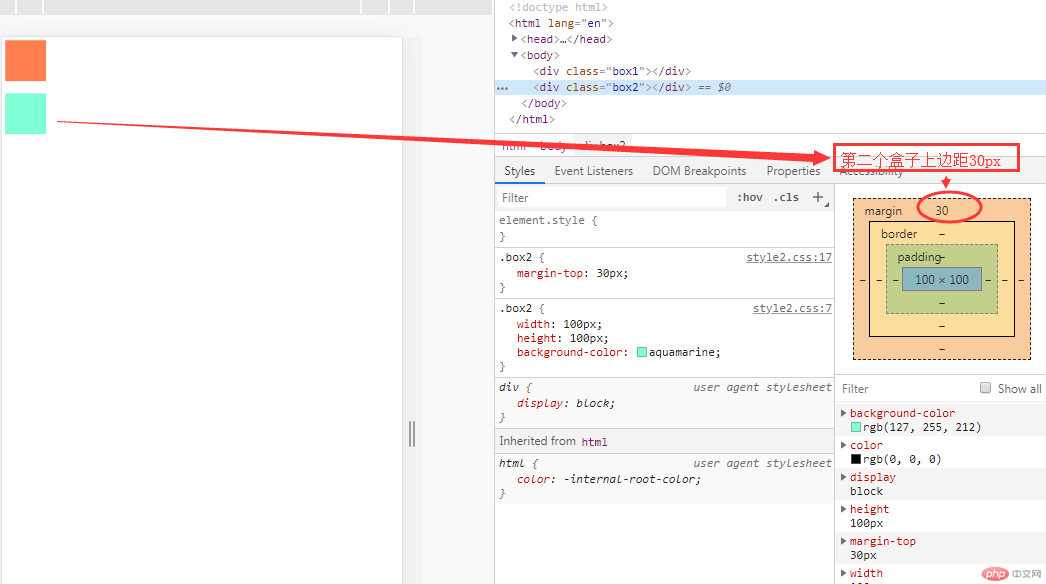
通过修改 box1的上边距像素为50px,发现下边的盒子陷入到上边盒子的边距里面去了,谁向谁塌陷,遵循谁大以谁为准。
嵌套传递:是一个嵌套级的关系,子元素的外边距会自动传递到父元素上
举例: <div class=”box3”>
<div class=”box4”></div>
</div>
传递前效果:
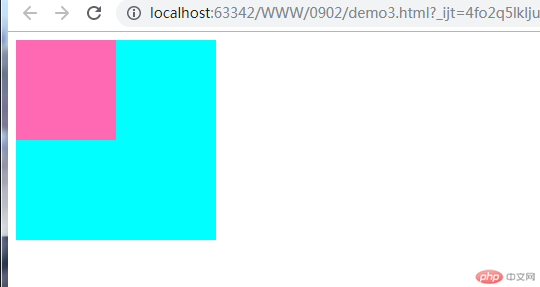
传递后效果:
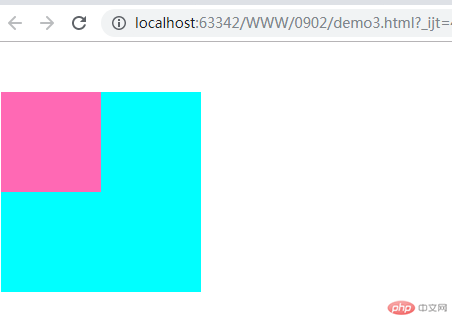
自动挤压:某一个元素设置外边距的时候,会尽可能的自动挤压,尽可能的将位置留给对方尽可能的扩大。
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="static/css/style2.css"> <title>外边距margin</title> </head> <body> <!--同级塌陷--> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> <!--嵌套传递--> <div class="box3"> <div class="box4"></div> </div> <!--自动挤压--> <div class="box5"></div> </body> </html>
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
/*!*同级塌陷*!*/
/*.box1 {*/
/* width: 100px;*/
/* height: 100px;*/
/* background-color: coral;*/
/*}*/
/*.box2 {*/
/* width: 100px;*/
/* height: 100px;*/
/* background-color: aquamarine;*/
/*}*/
/*.box1 {*/
/* margin-bottom: 30px;*/
/*}*/
/*.box2 {*/
/* margin-top: 30px;*/
/*}*/
.box3 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: aqua;
}
.box4 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: hotpink;
}
/*此处子元素会传递到父元素*/
.box4 {
/*margin-top: 50px;*/
}
/*通过修改父元素内边距距离和整体高度实现*/
.box3 {
padding-top: 50px;
height: 150px;
}
.box5 {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: #008856;
}
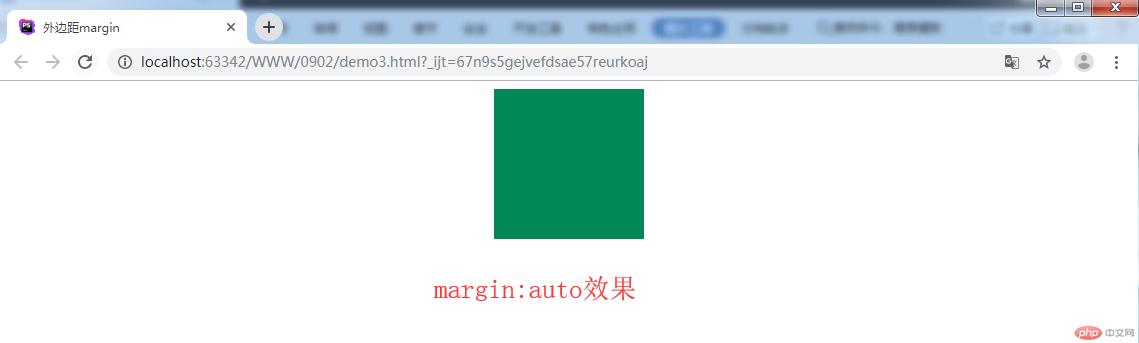
.box5 {
margin:auto;
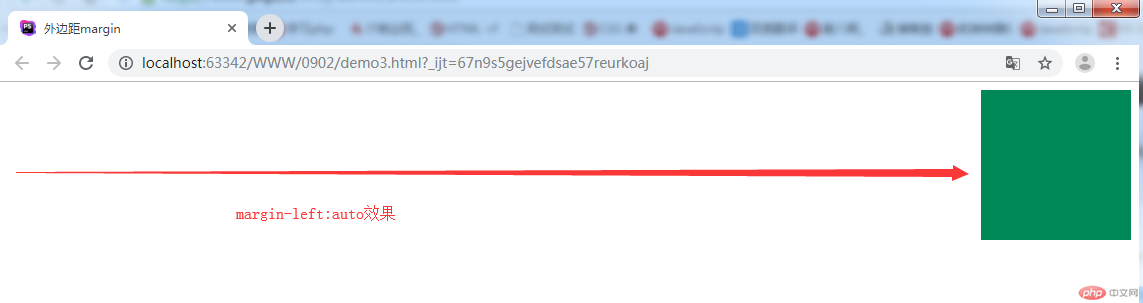
/*比如要求做坐外边赋值auto,会自动给左侧尽力空出位置,挤压到右侧*/
/*margin-left: auto;*/
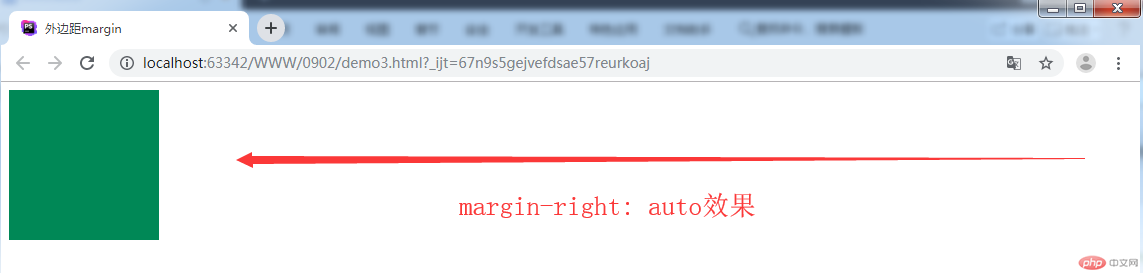
/*当赋值右外边auto,自动尽力挤压到左侧*/
/*margin-right: auto;*/
}点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
总结:
1.
相邻选择器选中的是紧挨着的下一个元素,用 #id + * 号表示。
兄弟选择器选择的是从本身开始以后的元素,用 #id + ~ 号表示。
Nth-child(): 伪类:子元素选择器。
Nth-of-type():伪类:类型选择器。
如果关注点是位置,用nth-child()
如果既关注位置也关注类型,用nth-of-type()
2.
padding的展示方式影响了盒子的效果,可以通过多种方式实现最终效果。
3.
同级塌陷:指垂直方向上的高度塌陷
嵌套传递:是一个嵌套级的关系,子元素的外边距会自动传递到父元素上
自动挤压:某一个元素设置外边距的时候,会尽可能的自动挤压,尽可能的将位置留给对方尽可能的扩大。