


1、浮动原理
html页面中默认的元素排序被称为文档流,从上到下,从左到右依次排序。要实现网页的布局就要打破默认的文档流,重新给元素定位。让元素脱离html文档流的方法就是浮动和定位。
浮动(float)使元素脱离了html文档流,实现了左右方向的自由移动。可以把默认的文档流认为是一层,加了浮动(float)之后的元素是另外一层,这个浮动的一层“漂浮”在默认文档流的上面。
浮动对前面的元素没有影响,对后面的元素有影响,会覆盖后面的元素。所以为了使后面的元素能正常显示,需要浮动或者清除(clear)前面浮动元素的作用。
2、清除子元素浮动对父元素高度折叠的影响
对于嵌套的盒子,子元素的浮动会引起父元素高度折叠。如下实例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>清除子元素浮动引起的塌陷</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css3.css"/> </head> <body> <div class="box1"> <div class="box2"> box2 </div> </div> </body> </html>
两个盒子原始的样式是这么写的:
.box1{
width: 400px;
outline: 1px dashed red;
}
.box2{
width: inherit;
height: 400px;
background-color: aqua;
}此时页面显示如图
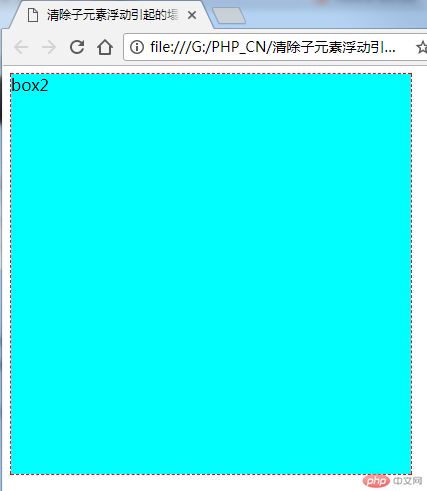
给box2加一个浮动
.box1{
width: 400px;
outline: 1px dashed red;
}
.box2{
width: inherit;
height: 400px;
background-color: aqua;
}
.box2{
float: left;
}这时候因为子元素box2浮动,所以父元素box1里面就没有内容了,整个边框就缩成了一条线,如图:
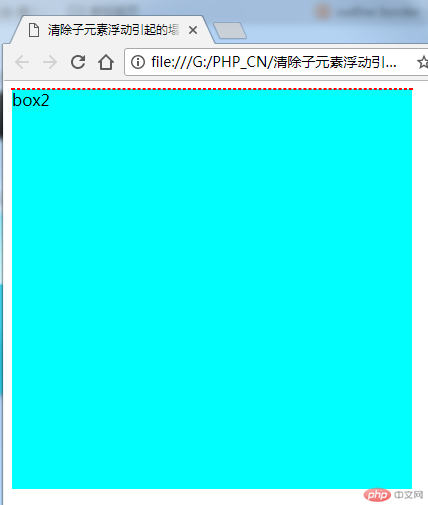
这就是子元素浮动造成的父元素在高度上的折叠,清除的方法很简单,在父元素的样式里加上overflow:hidden即可
.box1{
width: 400px;
outline: 1px dashed red;
}
.box2{
width: inherit;
height: 400px;
background-color: aqua;
}
.box2{
float: left;
}
.box1{
overflow: hidden;
}这个时候页面又恢复正常了
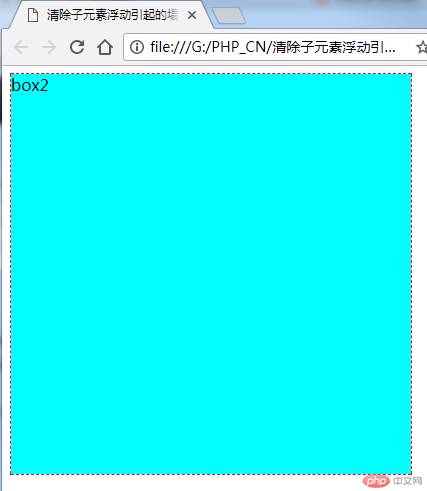
flow是流量的意思,over是超过,overflow本意就是超过流量了。通俗点说就是装不下了,流出来了,就好像家里的洗手盆都会有个溢出口,如果放水忘记关水龙头了,水会从这个溢出口流进下水管道,而不至于从面板上溢出来流的满地都是。
很显然,在上面这个例子中,因为子元素box2浮动了,脱离了默认的文档流,父元素box1里面就没东西了,框子缩成了一条线。反过来看,就是父元素装不下子元素了,子元素溢出了。hidden是隐藏的意思,把这种溢出的现象隐藏起来,也就消除掉了。此例中,父元素box1的高度是没有指定的,而子元素box2有高度,所以浏览器会理解box1的高度要足够大,才能够“不溢出”。此时,父元素box1又可以框住box2了。
3、定位
定位也是一种让元素布局的方法,定位有4种:
1、静态定位(static),也就是html页面的默认的定位,文档流;
2、相对定位(relative),元素仍在文档流,也就是说对后面的元素的位置没有影响,相对它原来的位置发生偏移;
3、绝对定位(absolute),元素脱离的文档流,对后面的元素的位置是有影响的,相对离它最近的一个有位置的元素进行定位;
4、固定定位(fixed),始终相对于浏览器窗口进行定位,也脱离了文档流。
写一个实例,有个5个盒子
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>定位</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css4.css"/> </head> <body> <div class="box1">1</div> <div class="box2">2</div> <div class="box3">3</div> <div class="box4">4</div> <div class="box5">5</div> </body> </html>
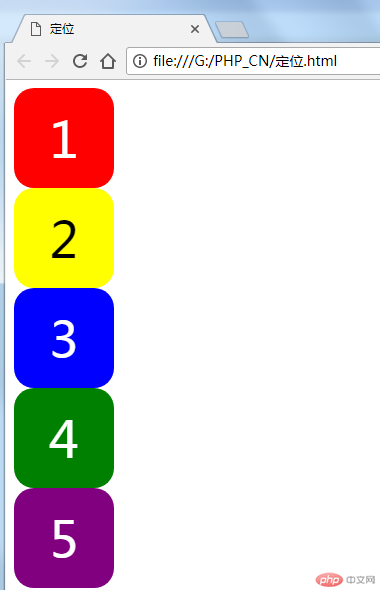
首先用相对定位,使5个盒子摆成一个十字架,5在中间,1/2/3/4呈顺时针排列,样式如下:
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
border-radius: 20%;
font-size: 50px;
color: white;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
border-radius: 20%;
font-size: 50px;
color: black;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: blue;
border-radius: 20%;
font-size: 50px;
color: white;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
}
.box4{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
border-radius: 20%;
font-size: 50px;
color: white;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
}
.box5{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: purple;
border-radius: 20%;
font-size: 50px;
color: white;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
}
/* 相对定位 */
.box1{
position: relative;
left: 100px;
}
.box2{
position: relative;
left: 200px;
}
.box3{
position: relative;
left: 100px;
}
.box4{
position: relative;
top: -200px;
}
.box5{
position: relative;
left: 100px;
top: -300px;
}
浏览器里的效果如下图
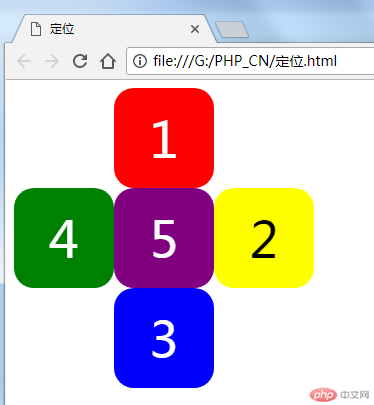
再用绝对定位实现一次
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>绝对定位</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css5.css"/> </head> <body> <div class="parent"> <div class="box1">1</div> <div class="box2">2</div> <div class="box3">3</div> <div class="box4">4</div> <div class="box5">5</div> </div> </body> </html>
给5个盒子加一个父级盒子“parent”,为了看得更清楚,给parent加一个框
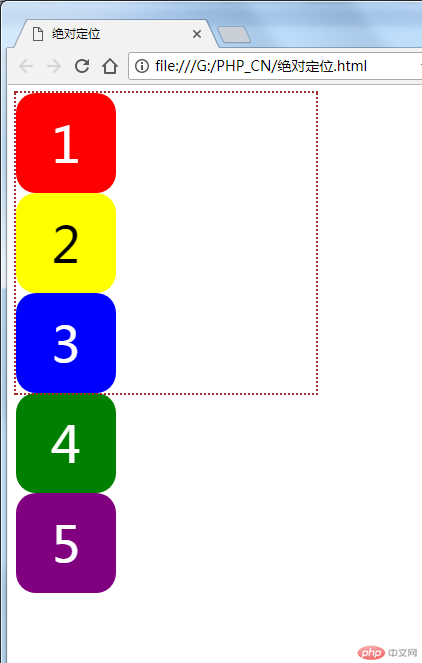
用绝对定位来摆一个十字架,首先要给父级盒子一个定位,其次要注意绝对定位是脱离了文档流的定位,会对后面的元素位置产生影响,css代码如下:
.parent{
/* 设置定位父级的定位属性 */
position: relative;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
outline: 2px dotted brown;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
border-radius: 20%;
font-size: 50px;
color: white;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
border-radius: 20%;
font-size: 50px;
color: black;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: blue;
border-radius: 20%;
font-size: 50px;
color: white;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
}
.box4{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
border-radius: 20%;
font-size: 50px;
color: white;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
}
.box5{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: purple;
border-radius: 20%;
font-size: 50px;
color: white;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
}
/* 绝对定位 */
.box1{
position: absolute;
left: 100px;
}
.box2{
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
top: 100px;
}
.box3{
position: absolute;
left: 100px;
top: 200px;
}
.box4{
position: absolute;
top: 100px;
}
.box5{
position: absolute;
left: 100px;
top: 100px;
}
同样把十字架画成了。
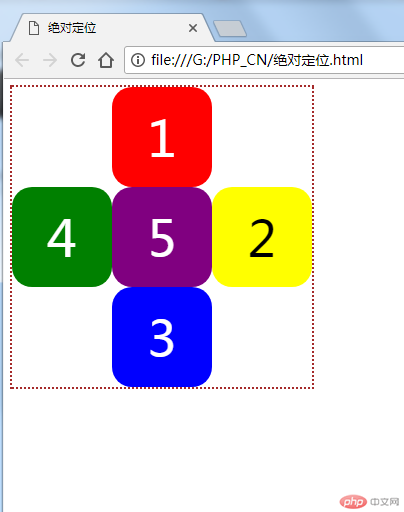
4、用绝对定位和浮动定位实现三列布局。
实例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>绝对定位三列布局</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css6.css"> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="header">头部</div> <div class="main"> <div class="left">左边</div> <div class="content">内容</div> <div class="right">右边</div> </div> <div class="footer">底部</div> </div> </body> </html>
绝对定位要注意的是,元素脱离了文档流,对后面元素的位置产生影响,样式文件如下:
.container{
width: 1000px;
background-color: blue;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.header{
height: 80px;
background-color: lightcoral;
}
.footer{
height: 80px;
width: inherit;
background-color: lightgray;
}
.main{
background-color: lightgreen;
margin: 5px auto;
}
.left{
background-color: lightpink;
width: 200px;
min-height: 800px;
}
.content{
background-color: lightskyblue;
width: 600px;
min-height: 800px;
}
.right{
background-color: lightsalmon;
width: 200px;
min-height: 800px;
}
/* 绝对定位 */
.main{
/* 给定位父级元素设置定位属性 */
position: relative;
}
.left{
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
}
.right{
position: absolute;
right: 0;
top: 0;
}
.content{
position: absolute;
margin: 0 200px;
}
.footer{
position: absolute;
bottom: 0;
}实现的效果如下:
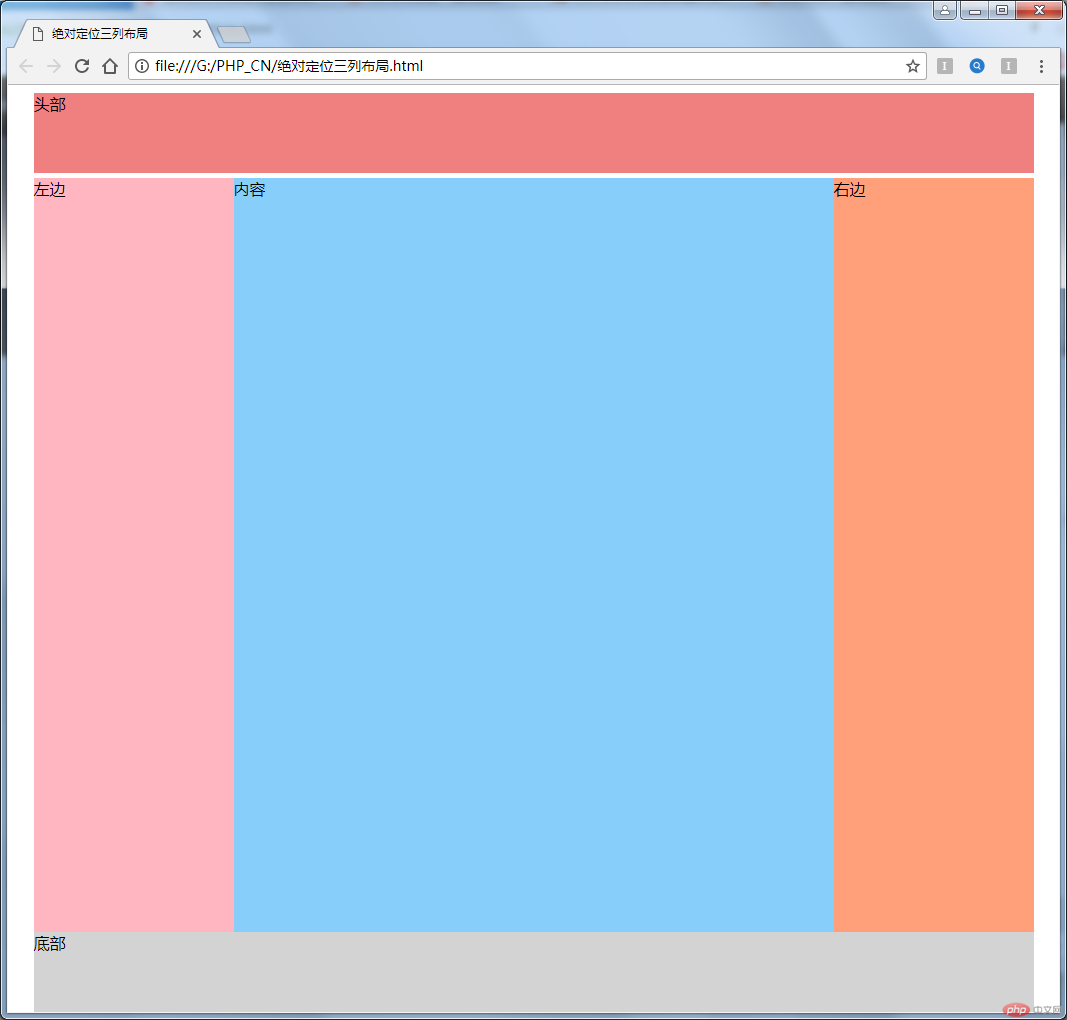 此处代码不是完全按老师示例去写的,footer和header分开写的,遇到一个问题就是right定位完了之后,footer跑到了顶上,这时候给了footer一个绝对定位bottom 0,发现main的下margin 5px消失了,main跟footer之间没有空隙了。
此处代码不是完全按老师示例去写的,footer和header分开写的,遇到一个问题就是right定位完了之后,footer跑到了顶上,这时候给了footer一个绝对定位bottom 0,发现main的下margin 5px消失了,main跟footer之间没有空隙了。
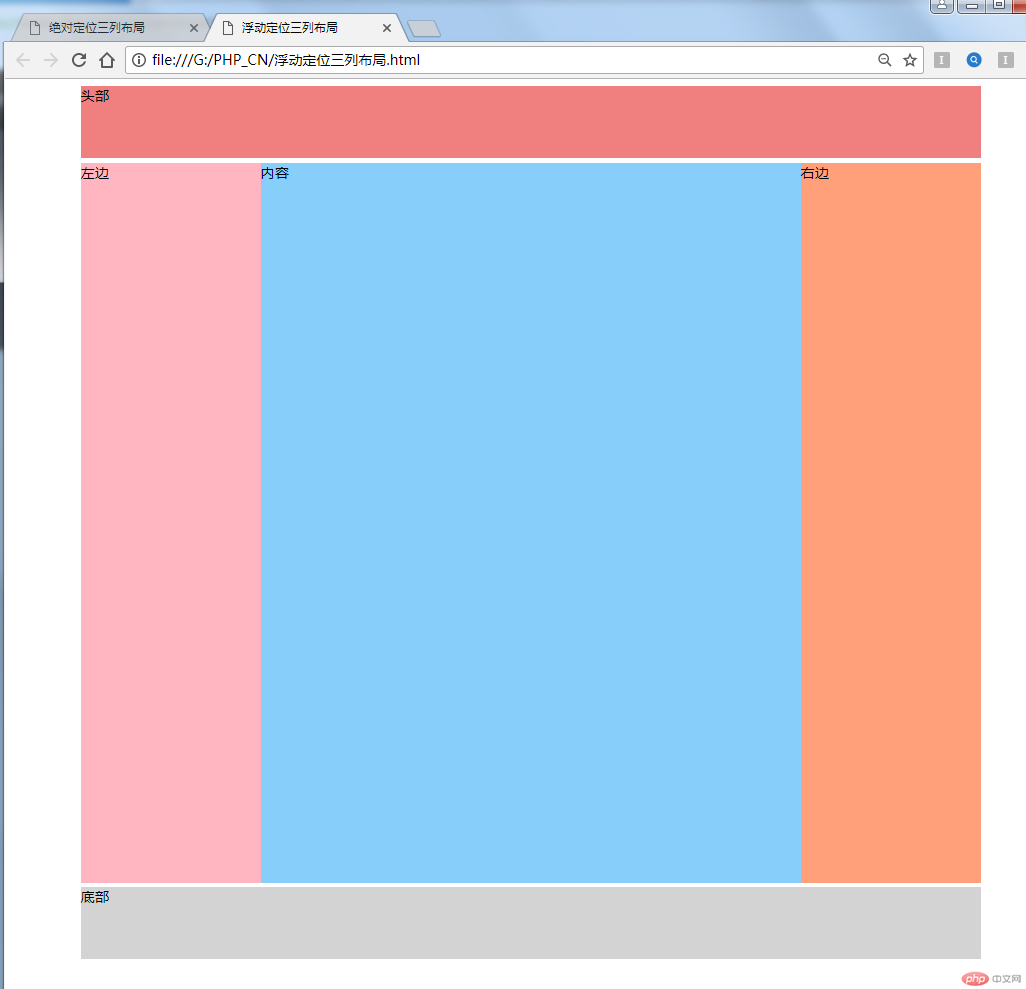
用浮动定位,注意为了避免子元素浮动引起父元素高度方向塌陷,所以要用到 overflow:hidden,实例样式文件如下:
.container{
width: 1000px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.header{
height: 80px;
background-color: lightcoral;
}
.footer{
height: 80px;
width: inherit;
background-color: lightgray;
}
.main{
background-color: lightgreen;
margin: 5px auto;
overflow: hidden;
}
.left{
background-color: lightpink;
width: 200px;
min-height: 800px;
}
.content{
background-color: lightskyblue;
min-height: 800px;
}
.right{
background-color: lightsalmon;
width: 200px;
min-height: 800px;
}
/* 浮动定位 */
.left{
float: left;
}
.right{
float: right;
}
.content{
float: left;
width: 600px;
}运行效果如图
总结:
相对定位不影响前后元素的定位,还在文档流当中,只是元素相对自己的位置发生了便宜。绝对定位和浮动都会让元素脱离文档流,影响后面元素的位置。overflow:hidden 语句在子元素发生浮动时,可以避免父级元素在高度方面的塌陷。