


一、给弹性元素设置增长因子
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style1.css"> <title>给弹性元素设置增长因子</title> </head> <body> <h3>不设置弹性因子(默认为0)</h3> <div class="container flex demo1"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <hr> <h3>将全部剩余空间分配给指定元素</h3> <div class="container flex demo2"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <hr> <h3>将全部剩余空间平均分配给指定元素</h3> <div class="container flex demo3"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <hr> <h3>剩余空间按弹性因子比例在弹性元素之间分配</h3> <div class="container flex demo4"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <hr> <h3>弹性因子为小数也适用,因为是按比例分配</h3> <div class="container flex demo5"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <hr> <h3>当弹性元素宽度不同时</h3> <div class="container flex demo6"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> </body> </html>
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
@import "public.css";
/* 增长因子适用场景:
1.弹性容器设置了自定义宽度;
2.弹性元素设置了自定义宽度;
3.弹性容器不允许换行。
4.弹性元素总宽度在主轴方向上小于弹性容器宽度,有剩余空间 */
.container{
width: 550px;
}
.item{
width: 100px;
}
/* 不设置增长因子(默认) */
.demo1>.item{
flex-grow: 0;
}
/* 将全部剩余空间分配给指定元素 */
.demo2>.item:first-of-type{
flex-grow:0;
}
.demo2>.item:nth-of-type(2){
flex-grow:0;
}
.demo2>.item:last-of-type{
flex-grow:1;
}
/* 将全部剩余空间平均分配给指定元素 */
.demo3>.item:first-of-type{
flex-grow:1;
}
.demo3>.item:nth-of-type(2){
flex-grow:1;
}
.demo3>.item:last-of-type{
flex-grow:1;
}
/* 将全部剩余空间平均分配给指定元素 */
.demo4>.item:first-of-type{
flex-grow:1;
}
.demo4>.item:nth-of-type(2){
flex-grow:1;
}
.demo4>.item:last-of-type{
flex-grow:3;
}
/* 弹性因子为小数也适用,因为是按比例分配 */
/* 注意:弹性因子之和需大于等于1才能将剩余空间完全分配 */
.demo5>.item:first-of-type{
flex-grow:0.2;
}
.demo5>.item:nth-of-type(2){
flex-grow:0.2;
}
.demo5>.item:last-of-type{
flex-grow:0.6;
}
/* 当弹性元素宽度不同时 */
.demo6>.item:first-of-type{
flex-grow:1;
width:100px
}
.demo6>.item:nth-of-type(2){
flex-grow:1;
width: 200px;
}
.demo6>.item:last-of-type{
flex-grow:3;
width: 150px;
}
/* 计算:
弹性因子之和:1+1+3=5;
剩余空间:550-(100+200+150)=100;
每个弹性元素分配到的剩余空间分别是:(1/5)x100、(1/5)x100、(3/5)x100 */点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
.container{
border: 1px solid rgb(245, 175, 175);
background-color: rgb(233, 245, 167);
margin: 15px;
}
.flex{
display: flex;
}
.item{
padding: 25px;
border: 1px solid rgb(70, 42, 97);
color: black;
box-sizing: border-box;
background-color: rgb(176, 233, 111);
}点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

手抄:


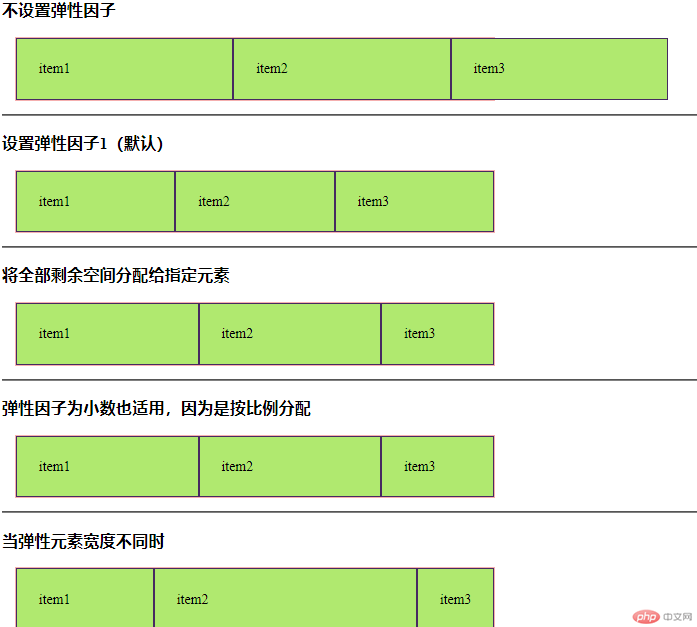
二、设置弹性元素的缩减因子
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style2.css"> <title>设置弹性元素的缩减因子</title> </head> <body> <h3>不设置弹性因子</h3> <div class="container flex demo0"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <hr> <h3>设置弹性因子1(默认)</h3> <div class="container flex demo1"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <hr> <h3>将全部剩余空间分配给指定元素</h3> <div class="container flex demo2"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <hr> <!-- <h3>将全部剩余空间平均分配给指定元素</h3> <div class="container flex demo3"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <hr> <h3>剩余空间按弹性因子比例在弹性元素之间分配</h3> <div class="container flex demo4"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <hr> --> <h3>弹性因子为小数也适用,因为是按比例分配</h3> <div class="container flex demo5"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <hr> <h3>当弹性元素宽度不同时</h3> <div class="container flex demo6"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> </body> </html>
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
@import "public.css";
/*
缩减因子使用场景:
1. 弹性元素设置了自定义宽度
2. 弹性容器设置了自定义宽度
3. 弹性元素总宽度在主轴上超过了弹性容器的宽度
4. 弹性容器不允许换行
*/
.container{
width: 550px;
}
.item{
width: 250px;
}
/* 不设置缩减因子,不缩减 */
.demo0>.item{
flex-shrink: 0;
}
/* 设置缩减因子为1,所有弹性元素自动缩减 */
.demo1>.item{
flex-shrink: 1;
}
/* 当三个缩减因子不相等时 */
.demo2>.item:first-of-type{
flex-shrink:1;
}
.demo2>.item:nth-of-type(2){
flex-shrink:1;
}
.demo2>.item:last-of-type{
flex-shrink:3;
}
/* 计算:
多余缩减空间:250x3-550=200
每个元素缩减空间分别为:(1/5)x200、(1/5)x200、(3/5)x200 */
/* 将全部剩余空间平均分配给指定元素
.demo3>.item:first-of-type{
flex-shrink:1;
}
.demo3>.item:nth-of-type(2){
flex-shrink:1;
}
.demo3>.item:last-of-type{
flex-shrink:1;
} */
/* 将全部剩余空间平均分配给指定元素
.demo4>.item:first-of-type{
flex-shrink:1;
}
.demo4>.item:nth-of-type(2){
flex-shrink:1;
}
.demo4>.item:last-of-type{
flex-shrink:3;
} */
/* 弹性因子为小数也适用,负数无效 */
/* 注意:弹性因子之和需大于等于1才能将剩余空间完全分配 */
.demo5>.item:first-of-type{
flex-shrink:0.2;
}
.demo5>.item:nth-of-type(2){
flex-shrink:0.2;
}
.demo5>.item:last-of-type{
flex-shrink:0.6;
}
/* 当弹性元素宽度不同时 */
/*
特别提示:
1. 缩减因子的前掉是每个元素必须是等宽的(在主轴上空间相等)
2. 如果不相等, 必须按一定的比例, 来调整这个元素的缩减因子
*/
.demo6>.item:first-of-type{
flex-shrink:1;
width:200px
}
.demo6>.item:nth-of-type(2){
flex-shrink:1;
width: 400px;
}
.demo6>.item:last-of-type{
flex-shrink:3;
width: 150px;
}
/* 计算:
a=200/(1x200+1x400+3x150);
每个弹性元素缩减的宽度为:200x(1xa)、400x(1xa)、150x(3xa) */点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
手抄:
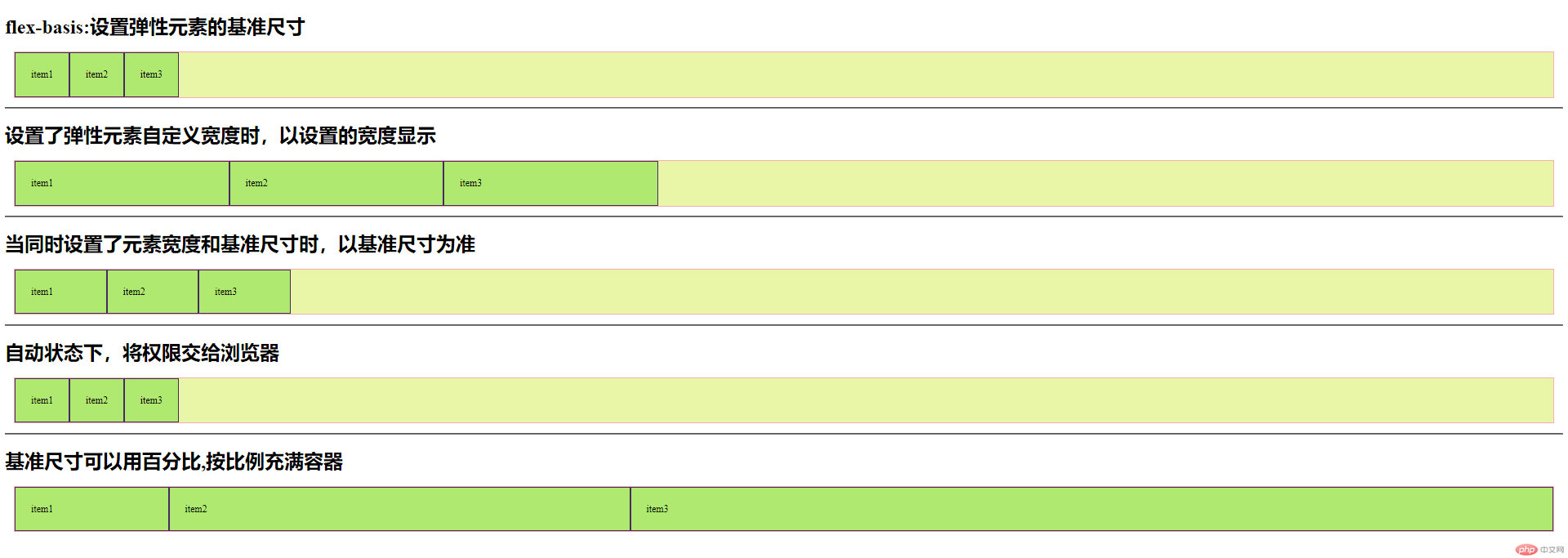
三、给弹性元素设置基准值
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style3.css"> <title>给弹性元素设置基准值</title> </head> <body> <h1>flex-basis:设置弹性元素的基准尺寸</h1> <div class="container flex demo1"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <hr> <h1>设置了弹性元素自定义宽度时,以设置的宽度显示</h1> <div class="container flex demo2"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <hr> <h1>当同时设置了元素宽度和基准尺寸时,以基准尺寸为准</h1> <div class="container flex demo3"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <hr> <h1>自动状态下,将权限交给浏览器</h1> <div class="container flex demo4"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <hr> <h1>基准尺寸可以用百分比,按比例充满容器</h1> <div class="container flex demo5"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> </body> </html>
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
@import "public.css";
/*
元素基准使用场景:
flex-basis 属性定义了在分配多余空间之前,
项目占据的主轴空间(main size),
浏览器根据这个属性,计算主轴是否有多余空间
1. 没有为弹性元素设置宽度
2. 为元素设置的宽度不满足当前需求
3.为每个弹性元素设置初始值/状态
*/
/* 在未设置元素自定义宽度时,以元素内容显示 */
.demo1>.item{
flex-basis: content;
}
/* 设置了弹性元素自定义宽度时,以设置的宽度显示 */
.demo2>.item{
width: 350px;
}
/* 当同时设置了元素宽度和基准尺寸时,以基准尺寸为准 */
.demo3>.item{
width: 350px;
flex-basis:150px;
}
/* 自动状态下,将权限交给浏览器
如果给元素设置了宽度,则按其显示
如果元素的宽度也是auto,或者没有定义,则按flex-basis:content显示 */
.demo4>.item{
flex-basis:auto;
}
/* 基准尺寸可以用百分比,按比例充满容器 */
.demo5>.item:first-of-type{
flex-basis:10%;
}
.demo5>.item:nth-of-type(2){
flex-basis:30%;
}
.demo5>.item:last-of-type{
flex-basis:60%;
}点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
手抄:

四、简化弹性元素的基本设置
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style4.css"> <title>简化弹性元素的基本设置</title> </head> <body> <h1>简化弹性元素的基本设置</h1> <h3>1.根据宽度计算,允许缩减适应容器</h3> <div class="container flex demo1"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(2): 根据宽度计算,元素完全弹性以适应容器</h3> <div class="container flex demo2"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(3): 元素完全失去弹性, 以原始大小呈现</h3> <div class="container flex demo3"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(4): 一个数值表示增长因子,其它值默认: flex: 1 1 auto</h3> <div class="container flex demo4"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(5): 第三个有具体数值时, 以它为计算标准</h3> <div class="container flex demo5"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> <h3>(6): 单独设置某一个元素弹性大小 </h3> <div class="container flex demo6"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> </body> </html>
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
@import "public.css";
.container{
width: 550px;
}
/* flex:flex-grow flex-shrink fllex-basis
flex:可简化flex-grow flex-shrink fllex-basis这三个属性
例如flex:0 0 auto,表示不增长、不缩减、宽度自动 */
/*根据width,height计算,并且允许缩减大小适应容器*/
.demo1 > .item {
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
flex: initial;
/*等价于初始值*/
flex: 0 1 auto;
}
.demo2 > .item {
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
flex: auto;
/*等价于*/
/*flex: 1 1 auto;*/
}
.demo3 > .item {
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
flex: none;
/*等价于: */
flex: 0 0 auto;
}
/*一个数值代表增长因子*/
.demo4 > .item {
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
flex: 1;
/*等价于*/
/*如果有多余空间,允许元素在主轴上伸缩*/
/*flex-grow: 1;*/
/*等价于:*/
/*flex: 1 1 auto;*/
}
.demo5 > .item {
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
flex: 1 0 200px;
}
.demo6 > .item {
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
}
.demo6 > .item:first-of-type {
flex: 1 1 50%;
}
/*
实际上最后一个参数: 30%是无效的, 任何数都不会发生变化
因为第一个是1,表示可增长, 即将剩余空间全部分配给它,其它二个默认增长因子为0
*/点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

手抄:

五、单独设置元素在交叉轴上排列方式
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>单独设置元素在交叉轴上排列方式</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style5.css"> </head> <body> <h1>单独设置元素在交叉轴上排列方式</h1> <div class="container flex"> <span class="item">item1</span> <span class="item">item2</span> <span class="item">item3</span> </div> </body> </html>
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
@import "public.css";
.container{
width: 500px;
height: 300px;
flex-flow: column nowrap;
align-items:flex-end;
}
.item{
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
}
/* 单独调整第一个元素 */
.item:first-of-type{
align-self:flex-start;
}
/* 单独调整最后一个元素 */
.item:first-of-type{
align-self:center;
}
/* 将第二个元素设置自动扩展 */
.item:nth-last-of-type(2){
background-color: #fff;
width: auto;
align-self: stretch;
}
/*这个属性很实用, 例如我们经常会将导航上用户登录/注册按钮单独放在右侧,就可以用到它*/点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

手抄:

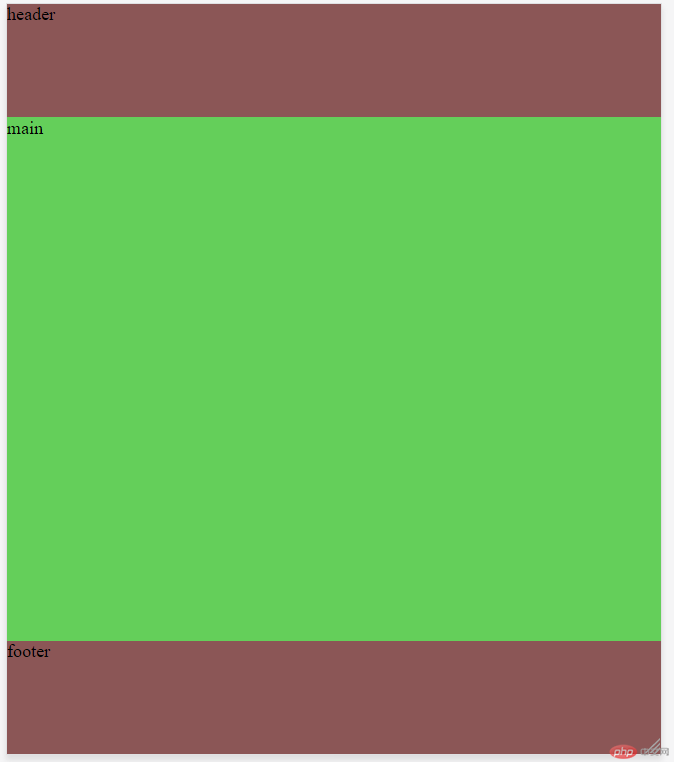
六、移动端首页样式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>移动端首页样式</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
body{
height: 100vh;
display: flex;
flex-flow: column nowrap;
}
header,footer{
min-height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(139, 86, 86);
flex: 0 0 auto;
}
main{
background-color: rgb(100, 207, 90);
/* 视口高度 */
height: 90vh;
flex:1;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<header>header</header>
<main>main</main>
<footer>footer</footer>
</body>
</html>点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
手抄:

七、order用法
order 属性 设置或检索弹性盒模型对象的子元素出现的順序。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>order</title>
<style>
.container{
display: flex;
}
.item1{
order:4;
background-color: rgb(241, 20, 20);
margin: 15px;
}
.item2{
order: 3;
background-color: rgb(130, 250, 18);
margin: 15px;
}
.item3{
order: 2;
background-color: rgb(12, 133, 247);
margin: 15px;
}
.item4{
order: 1;
background-color: rgb(228, 18, 228);
margin: 15px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>order 属性 设置或检索弹性盒模型对象的子元素出现的順序。</h1>
<div class="container">
<div class="item1">item1</div>
<div class="item2">item2</div>
<div class="item3">item3</div>
<div class="item4">item4</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

手抄:
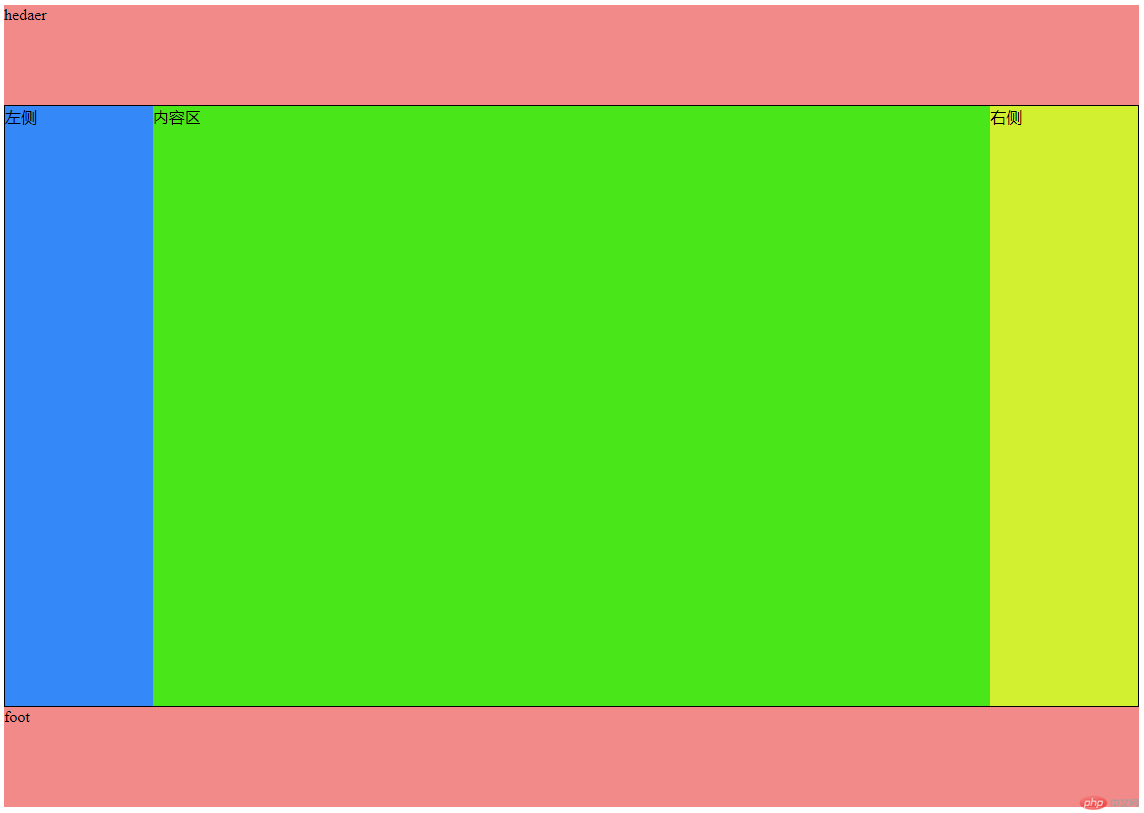
八、用flex改写圣杯布局
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style8.css"> <title>用flex改写圣杯布局</title> </head> <body> <header>hedaer</header> <main> <article>内容区</article> <aside class="left">左侧</aside> <aside class="right">右侧</aside> </main> <footer>foot</footer> </body> </html>
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
body,main{
display: flex;
}
body{
flex-direction: column;
}
header,footer{
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(243, 138, 138);
}
main{
box-sizing: border-box;
border: 1px solid black;
flex-flow: row nowrap;
}
article{
order: 2;
width: 100%;
min-height: 600px;
background-color: rgb(73, 231, 25);
}
.left{
width: 200px;
order: 1;
background-color: rgb(52, 136, 247);
}
.right{
width: 200px;
order: 3;
background-color: rgb(211, 240, 48);
}点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

手抄:
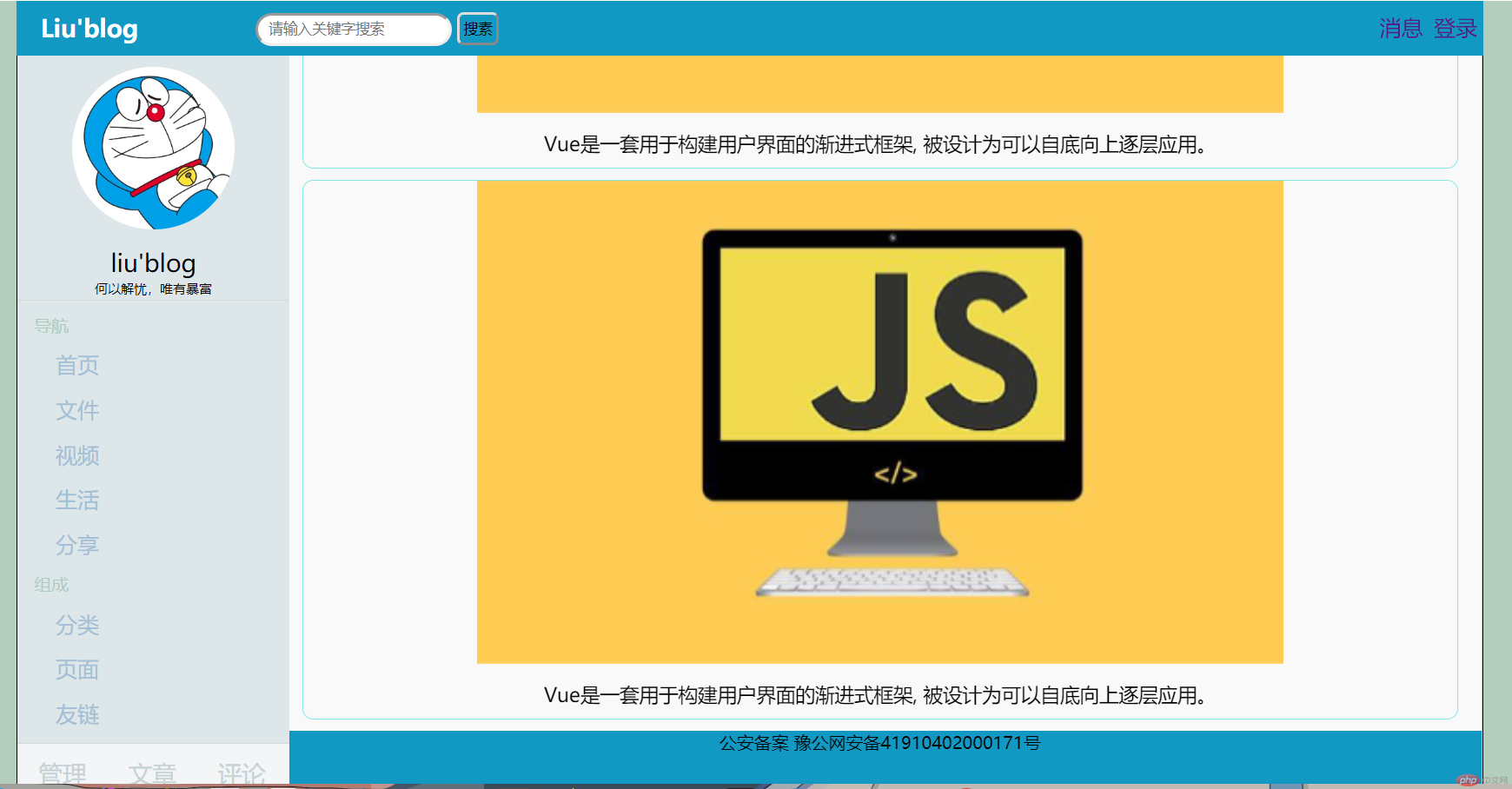
九、简易首页设计
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style9.css"> <title>简易首页</title> </head> <body> <header> <div class="hl1"> <a href="">Liu'blog</a> </div> <form action="" id="form"> <div class="fh"> <input id="inp" type="text" placeholder="请输入关键字搜索"> <button>搜素</button> </div> </form> <ul> <li><a href="">消息</a></li> <li> <a href="">登录</a> </li> </ul> </header> <main> <article> <ol class="ahead"> <li><a href="">首页</a></li> <li>/ <a href="">正文</a> </li> <div class="fx"> 分享到 QQ\微信\微博 </div> </ol> <section> <div class="ss"> <img src="imgs/2.jpg" width="742px" alt=""> <p>Vue是一套用于构建用户界面的渐进式框架, 被设计为可以自底向上逐层应用。</p> </div> </section> <section> <div class="ss"> <img src="imgs/2.jpg" width="742px" alt=""> <p>Vue是一套用于构建用户界面的渐进式框架, 被设计为可以自底向上逐层应用。</p> </div> </section> <section> <div class="ss"> <img src="imgs/2.jpg" width="742px" alt=""> <p>Vue是一套用于构建用户界面的渐进式框架, 被设计为可以自底向上逐层应用。</p> </div> </section> <footer>公安备案 豫公网安备41910402000171号</footer> </article> <aside class="left"> <div class="l1"> <a href=""> <div class="tx"> <div class="tp"> <img src="imgs/1.jpg" width="150px" height="150px" alt=""> </div> </div> </a> <p class="s1">liu'blog</p> <p class="s2">何以解忧,唯有暴富</p> </div> <!-- <aside class="right"> <div class="rhead"> <a href="">热门</a> <a href="">评论</a> <a href="">随机</a> </div> <div class="contain"> <p>热门文章</p> </div> </aside> --> <nav style="border-bottom: 1px solid rgb(218, 215, 215);"> <p class="dh">导航</p> <ul> <li> <a href="">首页</a> </li> <li> <a href="">文件</a> </li> <li> <a href="">视频</a> </li> <li> <a href="">生活</a> </li> <li> <a href="">分享</a> </li> </ul> <p class="dh">组成</p> <ul> <li> <a href="">分类</a> </li> <li> <a href="">页面</a> </li> <li> <a href="">友链</a> </li> </ul> </nav> <div class="lfoot"> <div class="lf1"> <a href="">管理</a> </div> <div class="lf1"> <a href="">文章</a> </div> <div class="lf1"> <a href="">评论</a> </div> </div> </aside> </main> </body> </html>
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
body,main{
display: flex;
}
body{
flex-direction: column;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
header,footer{
height: 50px;
background-color: #1199C4;
}
main{
box-sizing: border-box;
border: 1px solid black;
flex-flow: row nowrap;
}
article{
order: 2;
width: 100%;
min-height: 600px;
background-color: #F9F9F9;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.left{
width: 250px;
order: 1;
background-color:#DDE6E9;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
border: 1px;
}
.right{
width: 220px;
order: 3;
background-color: #DDE6E9;
}
.tp{
text-align: center;
margin: 10px auto;
}
.tp>img{
border-radius: 500px;
}
.s1{
text-align: center;
font-size: 22px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.s2{
text-align: center;
font-size: 12px;
margin: 2px auto;
}
.l1{
border-bottom: 1px solid rgb(218, 215, 215);
background-color:#DDE6E9;
margin-top: 0;
}
nav{
margin-top: 12px;
padding-left: 6px;
}
.dh{
color: #AECDBE;
text-align: left;
}
nav{
padding-left: 15px;
}
nav>ul{
margin: 8px auto;
padding-left: 15px;
}
nav>ul>li{
list-style-type: none;
margin: 5px auto;
background-color:#DDE6E9;
display: block;
}
nav>ul>li>a{
text-decoration: none;
display: block;
color: #A3BFD6;
font-size: 20px;
padding: 5px;
}
nav>ul>li>a:hover{
color: white;
background-color:#E4EAEC;
}
.lfoot{
background-color:#f3f5f6;
height: 55px;
text-align: center;
}
.lf1{
width: 33%;
float: left;
line-height: 55px;
}
.lf2{
width: 33%;
float: left;
line-height: 55px;
}
.lf3{
width: 33%;
float: left;
line-height: 55px;
}
.lfoot>.lf1>a{
text-decoration: none;
color: rgb(199, 210, 214);
}
.lfoot>.lf1>a:hover{
color: black;
font-size: 20px;
}
.hl1{
background-color: #1199c4;
height: 50px;
width: 220px;
position: fixed;
}
.hl1>a{
line-height: 50px;
text-decoration: none;
text-align: center;
padding: 0 22px;
font-size: 22px;
font-weight: 700;
height: auto;
color: white;
float: left;
display: block !important;
}
*{
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.fh{
margin-left: 220px;
/* display: block; */
overflow: visible;
height: auto;
/* display: inline-table */
}
#form{
/* display: inline-block; */
/* height: 55px;
width: 120px; */
margin-top: 10px ;
margin-bottom: 10px;
width: auto;
/* display: inline-block; */
float: left !important;
width: auto;
padding-top: 0;
padding-bottom: 0;
margin-right: 0;
margin-left: 0;
border: 0;
-webkit-box-shadow: none;
box-shadow: none;
}
#inp{
border-radius: 550px;
padding: 5px 10px;
/* float: left; */
}
button{
padding: 4px;
border-radius: 6px;
background: 0 0;
}
header{
position: fixed;
width: 1350px;
}
header>ul{
float: right !important;
list-style: none;
}
header>ul>li{
float: left;
display: block;
}
header>ul>li>a{
text-decoration: none;
line-height: 50px;
font-size: 20px;
padding: 5px;
}
header>ul>li>a:hover{
background-color: rgb(95, 202, 235);
}
.ahead{
list-style-type: none;
margin: 12px 12px;
border:2px solid #dee5e7;
height: 33px;
border-radius: 12px;
padding: 0 13px;
}
a{
text-decoration: none;
font-size: 22px;
}
ol>li{
float: left;
}
.fx{
float: right;
margin-right: 12px;
}
body{
padding:0 100px;
background-color: #B3CEBC;
}
section{
margin: 10px 22px;
}
.ss{
margin: 10px auto;
text-align: center;
border: 1px solid rgb(134, 233, 233);
border-radius: 10px;
}
section>img{
margin-top: 8px;
}
section>.ss>p{
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: 12px;
display: inline-block;
margin-top: 12px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
.left{
margin-top: 49.5px;
position: fixed;
}
.right{
margin-top:50.5px;
width: 320px;
float: right;
}
article{
margin-left: 240px;
text-align: center;
}
.rhead{
height: 10px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
/* .rhead>ul{
list-style-type: none;
text-align: center;
width: 100%;
}
.rhead>ul>li{
float: left;
margin: 10px 5px;
}
.rhead>ul>li>a{
font-size: 17px;
background-color: rgb(216, 241, 237);
line-height: 10px;
}
.rhead>ul>li>a:hover{
font-size:19px ;
} */
main{
width: 1350px;
}
.contain{
margin-top: 60px;
margin-bottom: 5px;
border-top: 1px solid black;
padding-top: 6px;
padding-left: 8px;
}点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
十、总结
增长因子适用场景:1.弹性容器设置了自定义宽度;2.弹性元素设置了自定义宽度;3.弹性容器不允许换行。4.弹性元素总宽度在主轴方向上小于弹性容器宽度,有剩余空间;用flex-gorw设置。
缩减因子使用场景:1. 弹性元素设置了自定义宽度2. 弹性容器设置了自定义宽度3. 弹性元素总宽度在主轴上超过了弹性容器的宽度4. 弹性容器不允许换行。用flex-shrink设置。
增长因子与缩减因子在弹性元素的宽度不同时,计算方法是不同的;
元素基准使用场景:flex-basis 属性定义了在分配多余空间之前,项目占据的主轴空间(main size),浏览器根据这个属性,计算主轴是否有多余空间1. 没有为弹性元素设置宽度2. 为元素设置的宽度不满足当前需求3.为每个弹性元素设置初始值/状态
flex:可简化flex-grow flex-shrink fllex-basis这三个属性例如flex:0 0 auto,表示不增长、不缩减、宽度自动 ;
单独调整一个元素用align-self,属性值有flex-start、center、stretch;
order属性设置或检索弹性盒模型对象的子元素出现的順序;
最后应用已学知识做了一个简单的首页,flex真的很强大。