Correction status:qualified
Teacher's comments:一定要明白, 前后端交互的任何数据 , 都是字符串, 为什么有数据类型?是因为解释不同



JOSN 支持三种数据类型: 简单值, 对象, 数组
150, 3.24"Hello World!",必须使用双引号做为定界符true, falsenull注意: 不支持
undefined
<script>// JavaScript 变量能够保存多种数据类型:数值、字符串值、数组、对象等等var grade= 89; //数值var username = "admin"; //字符串var flag =false; //布尔值var cars = ["bmw","byd","PORcshe"]; //数组var x = { //对象name :"xiaoming",age : "58",}console.log(typeof grade,typeof username ,typeof flag,typeof cars,typeof x);</script>
特殊类型:null,undefined;
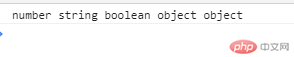
var role;var role = undefined;console.log(role);var title =null;console.log(title);// null,undefined 都有空/无得意义console.log(null ==undefined);// null表示空对象// undefined专用于表示对象类型变量的空/无console.log(typeof null);if(!null) console.log(null + "无")if(!undefined) console.log(undefined + "无")console.log(null+100); // null --->0console.log(undefined +100); //undefined ----->NaN
数组类型
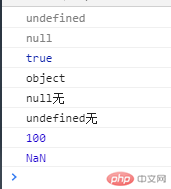
username = 'adimin';// js的数组 与 php类似var fruits = ['waterwelon','apple','orange','peach','pear']console.log(fruits);console.log(fruits.length); //返回5console.log(fruits[1]); // 返回appleconsole.log(typeof fruits); //返回object// 正确判断是否数组类型console.log(Array.isArray(fruits)); //返回ture// 遍历一个数组for(var i =0 ;i<fruits.length;i++){console.log(fruits[i]);}console.log("------------------")fruits.forEach(function(item,index,array){console.log(item);document.body.innerHTML += "<li> " + item +"</li>";})// php中获取数组部分元素slice(),js也有console.log(fruits.slice(0,3)); //["waterwelon", "apple", "orange"]console.log(fruits.slice(0)); //["waterwelon", "apple", "orange", "peach", "pear"]
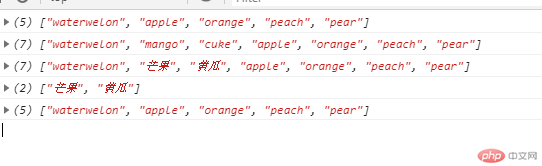
var fruits = ['waterwelon','apple','orange','peach','pear'];console.log(fruits); //["waterwelon", "apple", "orange", "peach", "pear"]// php中,splice(),可以实现数组插入,替换,删除fruits.splice(1,0,"mango","cuke");console.log(fruits); // ["waterwelon", "mango", "cuke", "apple", "orange", "peach", "pear"]fruits.splice(1,2,"芒果","黄瓜");console.log(fruits); //["waterwelon", "芒果", "黄瓜", "apple", "orange", "peach", "pear"]var res = fruits.splice(1,2);console.log(res); // ["芒果", "黄瓜"]console.log(fruits); //["waterwelon", "apple", "orange", "peach", "pear"]
// 对象,js中的数组类似php中的索引数组,js中对象也类似于php中的:关联数组var student ={id :1,name: 'xiaoming',email : 'admin@qq.com',"test scroe" :{php :22,html: 22,js:33,}}console.log(student);// 使用表格查看console.table(student);// 访问对象成员、属性,使用点操作符.console.log(student.email);console.log(student["test scroe"]);console.log(student["test scroe"]["php"]);console.log("-------------------");// 遍历/* for (对象的键名 in 对象){对象[键名]} */for ( key in student ){console.table(student[key]);}// 接祖数组中的forEach进行遍历console.log("-------------------");var keys= Object.keys(student);console.log(keys);keys.forEach(function (item,index ,arr){console.log(this[item]);},student);
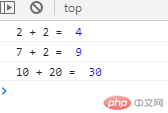
// 函数function f1(a,b){console.log(a + " + " + b +" = " , a+b );}f1(2,2);// 匿名函数var f2 = function f2(a,b){console.log(a + " + " + b +" = " , a+b );}f2(7,2);//立即调用(function f1(a,b){console.log(a + " + " + b +" = " , a+b );})(10,20);
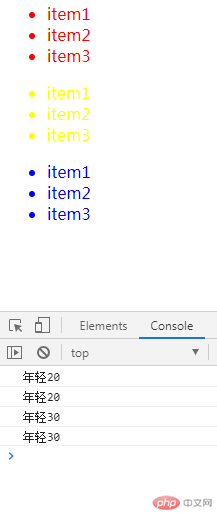
<body><ul><li>item1</li><li>item2</li><li>item3</li></ul><ul><li>item1</li><li>item2</li><li>item3</li></ul><ul><li>item1</li><li>item2</li><li>item3</li></ul><script>// 1.分支// 单分支var age = 20;if(age <= 30) console.log("年轻" +age );// 双分支if(age <= 30) console.log("年轻" +age );else console.log("中年了"+age );// 多分支var age = 30;if(age >=0 && age <= 30) console.log("年轻" +age );else if (age >30 && age <=50 ) console.log("中年了"+age );else if (age >50 && age <=70 ) console.log("老年了"+age );else console.log("不知多少年了"+age );// switchswitch(true){case age >=0 && age <= 30:console.log("年轻" +age )break;case age >30 && age <=50 :console.log("中年了"+age );break;case age >50 && age <=70 :console.log("老年了"+age );break;default:console.log("不知多少年了"+age );break;}// 循环var items = document.querySelectorAll("ul:first-of-type li");for(var i = 0; i< items.length; i++){items[i].style.color="red";};// whilevar items = document.querySelectorAll("ul:last-of-type li");var i =0while(i< items.length){items[i].style.color="blue";i++;};// do whilevar items = document.querySelectorAll("ul:nth-of-type(2) li");var i =0do {items[i].style.color="yellow"i++;}while(i< items.length);</script></body>
// 原生JS对象字面量var person = {name: 'Peter Zhu',age: 29};// 等价语法var person = {"name": "Peter Zhu","age": 29};// 以上内容用JSON对象表示{"name": "Peter Zhu","age": 29}// JSON对象与它相比有二处不同// 1. 没有变量声明: JSON中没有变量概念// 2. 没有分号: 因为JSON不是JS语句// 3. 属性名: 任何时候都必须添加双引号, 且必须是双引号// JSON属性值也支持复杂类型,如对象{"name": "Peter Zhu","age": 29,"course": {"name": "JavaScript","grade": 99}}
JSON 数组采用了原生 JS 中的数组字面量语法
// 原生JS数组var product = [101, "电脑", 9800];// JSON表示: 无变量和分号[101, "电脑", 9800][// 最常见场景是将数组与对象组合表示更加复杂的数据类型({id: 101,name: "电脑",price: 9800,},{id: 102,name: "手机",price: 4500,},{id: 103,name: "相机",price: 16800,})];// 许多软件的配置文件都是采用这种数据格式,如VSCODE
JSON 来源于 JS 对象,所以 JSON 下 JS 对象之间的转换非常方便
JSON.stringify(): 将原生 JS 对象,序列化为 JSON 字符串,用于存储与传输JSON.parse(): 将 JSON 字符串,解析为原生 JS 对象JSON.stringify(js对象,允许序列化的属性, 缩进字符数量)
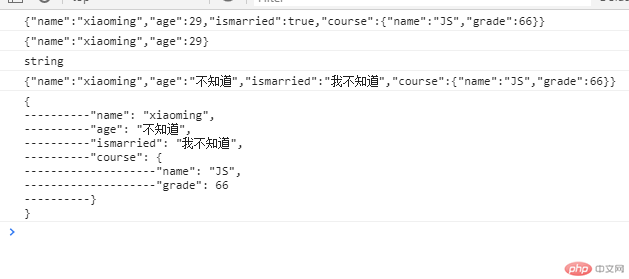
var person = {name : "xiaoming",age : 29,ismarried : true,course :{name : "JS",grade :66,},getName :function (){return this.name;},habby:undefined,tostring :function (){return "继承属性";},};// 1, 方法, 2,值为undefined的成员没有, 3, 原型对象成员也没有了// 将js对象 ===> 序列化为json字符串// 第二参数如果是数组,可以限制允许序列化的属性var jsonStr = JSON.stringify(person);console.log(jsonStr);var jsonStr = JSON.stringify(person,["name","age"]);console.log(jsonStr);console.log(typeof jsonStr);// 第二参数不是数组,是函数var jsonStr = JSON.stringify(person,function(key,value){switch(key){case 'age':return '不知道';break;case 'ismarried':return '我不知道';break;default :return value;}});console.log(jsonStr);var jsonStr = JSON.stringify(person,function(key,value){switch(key){case 'age':return '不知道';break;case 'ismarried':return '我不知道';break;default :return value;}},"----------");console.log(jsonStr);