Correction status:qualified
Teacher's comments:写的非常不错,继续加油!



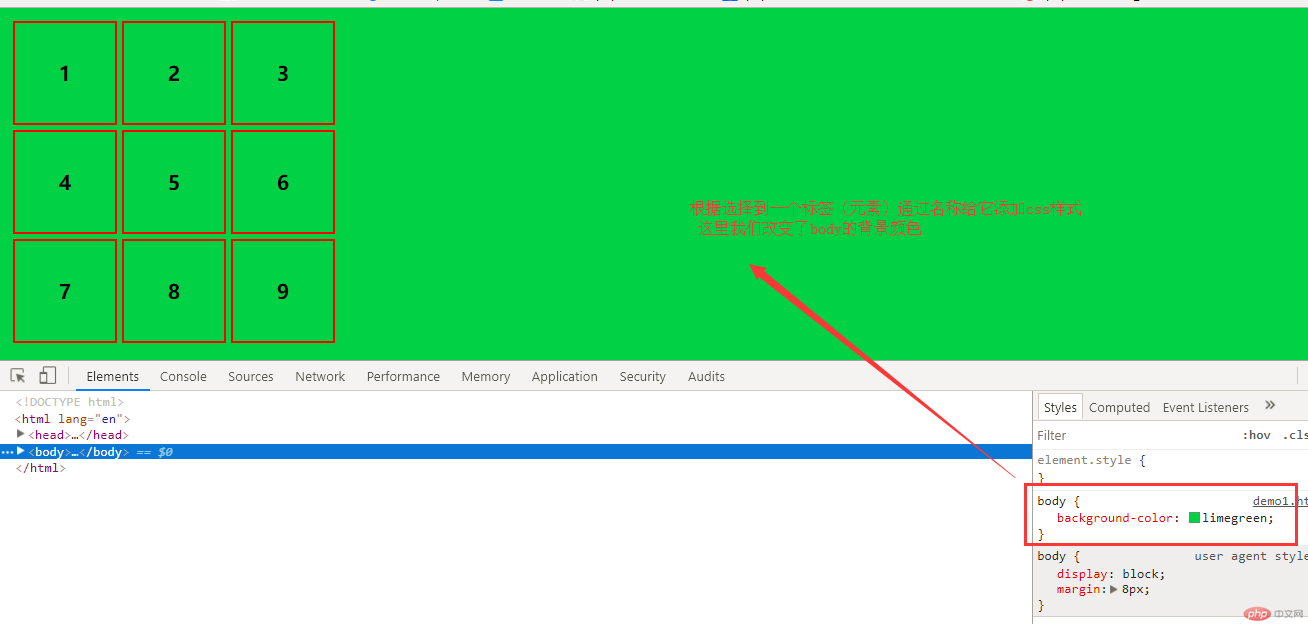
1.元素选择器 又叫标签选择器写法如: div{} body{} p{} span{}
例:改变body的背景颜色
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>选择器:简单选择器</title></head><style>.container {width: 400px;height: 400px;/* border: 1px solid black; */}.container .item {width: 100px;height: 100px;border: 2px solid red;float: left;text-align: center;line-height: 100px;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;margin-left: 5px;margin-top: 5px;}/* 1.元素选择器:标签选择器 */body {background-color: limegreen;}</style><body><!-- 简单选择器 --><div><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item">5</div><div class="item">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>
2.类选择器:对应着html标签中的class属性写法如: .item{} .container{}
例:给全部class属性为item的div加背景颜色 写法
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>选择器:简单选择器</title></head><style>.container {width: 400px;height: 400px;/* border: 1px solid black; */}.container .item {width: 100px;height: 100px;border: 2px solid red;float: left;text-align: center;line-height: 100px;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;margin-left: 5px;margin-top: 5px;}/* 2.类选择器:对应着html标签中的class属性 */.item {background-color: rosybrown;}</style><body><!-- 简单选择器 --><div class="container"><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item">5</div><div class="item">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>

3.类选择器之多个类复合应用写法如: .item.center{}
例:想给第五个div单独添加一个背景颜色
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>选择器:简单选择器</title></head><style>.container {width: 400px;height: 400px;/* border: 1px solid black; */}.container .item {width: 100px;height: 100px;border: 2px solid red;float: left;text-align: center;line-height: 100px;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;margin-left: 5px;margin-top: 5px;}/* 类选择器:对应着html标签中的class属性 */.item {background-color: rosybrown;}/*类选择器: 多个类复合应用 */.item.center {background-color: rgb(27, 210, 223);}</style><body><!-- 简单选择器 --><div class="container"><div class="item" id="first">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item center">5</div><div class="item">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>

4.id选择器 对应着html标签中的id属性写法如:#first{}
例:改变第一个div的背景颜色
注意:1.层叠样式表 相同元素 后面追加的样式回覆盖前面的样式
2.*号 id,class可以添加到任何元素上 所以可以省略
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>选择器:简单选择器</title></head><style>.container {width: 400px;height: 400px;/* border: 1px solid black; */}.container .item {width: 100px;height: 100px;border: 2px solid red;float: left;text-align: center;line-height: 100px;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;margin-left: 5px;margin-top: 5px;}/* id选择器 */#first {/* background-color: blue; */}*#first {/* background-color: orangered; */}/* 层叠样式表 相同元素 后面追加的样式回覆盖前面的样式 *//* * id,class可以添加到任何元素上 所以可以省略 *//* id选择器的应用场景目前只有两种场景 表单 锚点 */</style><body><!-- 简单选择器 --><div class="container"><div class="item" id="first">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item">5</div><div class="item">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>

1.后代选择器 重点加空格用法如:.container div{}
例:父级div下的所有子级div都加边框
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>上下文选择器</title></head><style>.container {width: 400px;height: 400px;/* border: 1px solid black; */}.container .item {width: 100px;height: 100px;/* border: 2px solid red; */float: left;text-align: center;line-height: 100px;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;margin-left: 5px;margin-top: 5px;}/*1. 后代选择器 空格*/.container div {border: 1px solid blue;}</style><body><div class="container"><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item center">5</div><div class="item">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>

2.父子选择器 写法如:body > div{}
例:给body下的子div的添加边框
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>上下文选择器</title></head><style>.container {width: 400px;height: 400px;/* border: 1px solid black; */}.container .item {width: 100px;height: 100px;/* border: 2px solid red; */float: left;text-align: center;line-height: 100px;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;margin-left: 5px;margin-top: 5px;}/* 2.父子选择器 */body > div {border: 1px solid green;}</style><body><div class="container"><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item center">5</div><div class="item">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>

3.同级相邻选择器 写法如:.item.center + .item{}
例:给第五个div后面相邻第六个div添加边框
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>上下文选择器</title></head><style>.container {width: 400px;height: 400px;/* border: 1px solid black; */}.container .item {width: 100px;height: 100px;/* border: 2px solid red; */float: left;text-align: center;line-height: 100px;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;margin-left: 5px;margin-top: 5px;}/* 3.同级相邻选择器 */.item.center + .item {border: 1px solid green;}</style><body><div class="container"><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item center">5</div><div class="item">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>
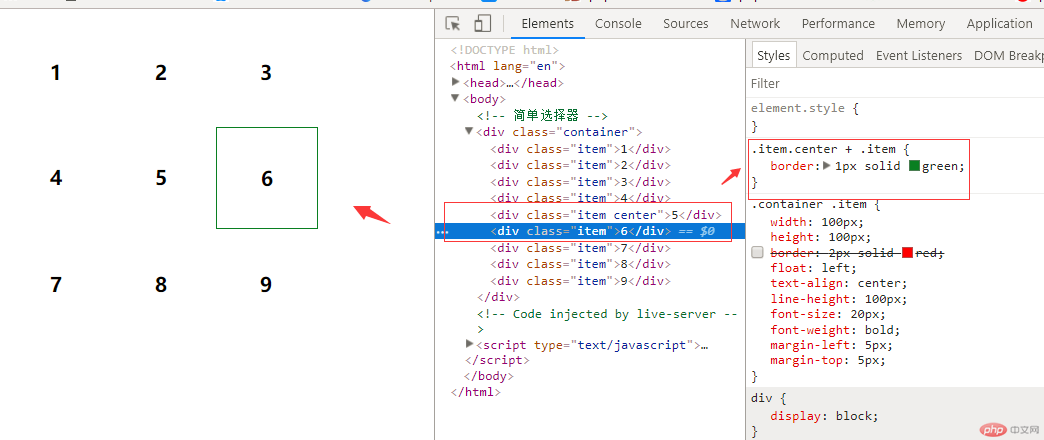
4.同级所有选择器写法如:.item.center ~ .item{}
例:给第五个div后面所有div添加边框
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>上下文选择器</title></head><style>.container {width: 400px;height: 400px;/* border: 1px solid black; */}.container .item {width: 100px;height: 100px;/* border: 2px solid red; */float: left;text-align: center;line-height: 100px;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;margin-left: 5px;margin-top: 5px;}/* 4.同级所有选择器 */.item.center ~ .item {border: 1px solid green;}</style><body><div class="container"><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item center">5</div><div class="item">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>
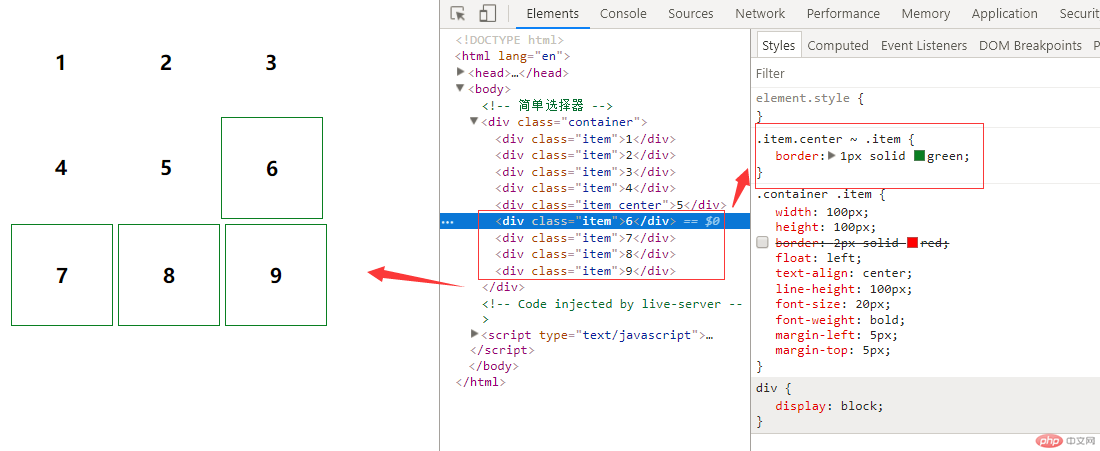
1.匹配第一个子元素 :first-child
注:如果前面不加类名 默认递归方式给html所有第一个元素添加样式写法如:.item:first-child{}
例:给第一个div添加背景颜色
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>结构伪类选择器:不分组 不区分元素类型</title></head><style>.container {width: 400px;height: 400px;/* border: 1px solid black; */}.container .item {width: 100px;height: 100px;/* border: 2px solid red; */float: left;text-align: center;line-height: 100px;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;margin-left: 5px;margin-top: 5px;}/* 匹配第一个子元素 *//* 注:如果不加类名.item 默认递归方式给html所有第一个元素添加样式 */.item:first-child {background-color: red;}</style><body><div class="container"><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item">5</div><div class="item">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>

2.匹配最后一个子元素 :last-child
注:如果前面不加类名 默认递归方式给html所有最后一个元素添加样式写法如:.item:last-child{}
例:给最后一个div添加背景颜色
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>结构伪类选择器:不分组 不区分元素类型</title></head><style>.container {width: 400px;height: 400px;/* border: 1px solid black; */}.container .item {width: 100px;height: 100px;/* border: 2px solid red; */float: left;text-align: center;line-height: 100px;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;margin-left: 5px;margin-top: 5px;}/* 匹配最后一个子元素 */.item:last-child {background-color: red;}</style><body><div class="container"><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item">5</div><div class="item">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>

3.匹配第几个子元素 :nth-child(n)
注:索引从1开始写法如:.item:nth-child(1){}
例:给第三个div添加背景颜色
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>结构伪类选择器:不分组 不区分元素类型</title></head><style>.container {width: 400px;height: 400px;/* border: 1px solid black; */}.container .item {width: 100px;height: 100px;/* border: 2px solid red; */float: left;text-align: center;line-height: 100px;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;margin-left: 5px;margin-top: 5px;}/* 选第三个 索引从1开始*/.item:nth-child(3) {background-color: red;}</style><body><div class="container"><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item">5</div><div class="item">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>
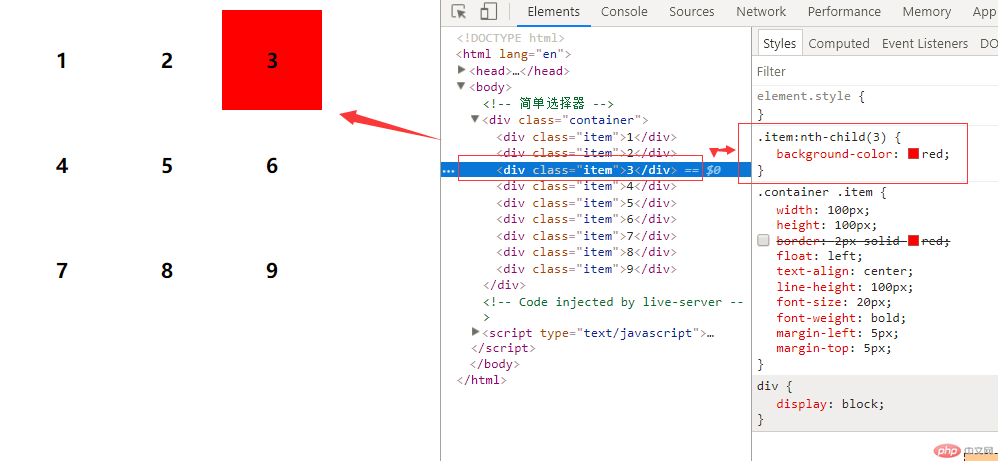
4.1.匹配偶数单元格 :nth-child(even) even为固定写法
注:索引从1开始写法如:.item:nth-child(even){}
例:给偶数div添加背景颜色
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>结构伪类选择器:不分组 不区分元素类型</title></head><style>.container {width: 400px;height: 400px;/* border: 1px solid black; */}.container .item {width: 100px;height: 100px;/* border: 2px solid red; */float: left;text-align: center;line-height: 100px;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;margin-left: 5px;margin-top: 5px;}/* 只选择偶数单元格 从1开始*/.item:nth-child(even) {background-color: red;}</style><body><div class="container"><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item">5</div><div class="item">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>

4.2.匹配奇数单元格 :nth-child(odd) odd为固定写法
注:索引从1开始写法如:.item:nth-child(odd){}
例:给奇数div添加背景颜色
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>结构伪类选择器:不分组 不区分元素类型</title></head><style>.container {width: 400px;height: 400px;/* border: 1px solid black; */}.container .item {width: 100px;height: 100px;/* border: 2px solid red; */float: left;text-align: center;line-height: 100px;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;margin-left: 5px;margin-top: 5px;}/* 只选奇数单元格 从1开始*/.item:nth-child(odd) {background-color: red;}</style><body><div class="container"><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item">5</div><div class="item">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>

4.3.从指定位置开始 选择剩下所有元素
注:索引从1开始 括号里位置不能变换写法如:.item:nth-child(n + 4){} 4为指定位置 随便写 n为指定位置后所有元素 固定写法
例:给指定第四个div起所有div添加背景颜色(包含第四个)
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>结构伪类选择器:不分组 不区分元素类型</title></head><style>.container {width: 400px;height: 400px;/* border: 1px solid black; */}.container .item {width: 100px;height: 100px;/* border: 2px solid red; */float: left;text-align: center;line-height: 100px;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;margin-left: 5px;margin-top: 5px;}/* 从指定位置开始 选择剩下所有元素 */.item:nth-child(n + 4) {background-color: red;}</style><body><div class="container"><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item">5</div><div class="item">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>
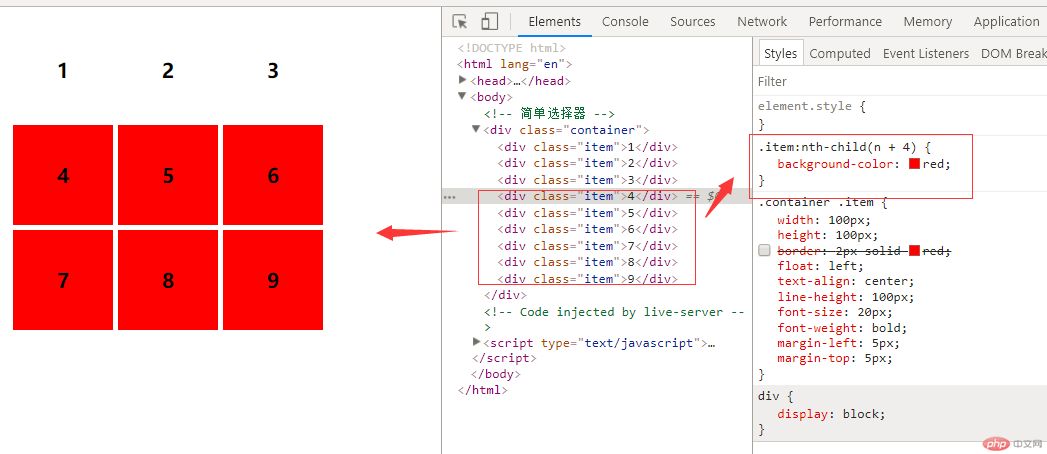
4.4.只取前几个元素
注:索引从1开始 括号里位置不能变换写法如:.item:nth-child(-n + 3){} 3为取几个 随便写 -n 固定写法
例:给前3个div添加背景颜色
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>结构伪类选择器:不分组 不区分元素类型</title></head><style>.container {width: 400px;height: 400px;/* border: 1px solid black; */}.container .item {width: 100px;height: 100px;/* border: 2px solid red; */float: left;text-align: center;line-height: 100px;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;margin-left: 5px;margin-top: 5px;}/* 只取前三个 */.item:nth-child(-n + 3) {background-color: red;}</style><body><div class="container"><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item">5</div><div class="item">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>

5.只取最后几个 :nth-last-child()
注:索引从1开始 括号里位置不能变换写法如:.item:nth-last-child(-n + 3){} 3为取几个 随便写 -n 固定写法
例:给最后3个div添加背景颜色
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>结构伪类选择器:不分组 不区分元素类型</title></head><style>.container {width: 400px;height: 400px;/* border: 1px solid black; */}.container .item {width: 100px;height: 100px;/* border: 2px solid red; */float: left;text-align: center;line-height: 100px;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;margin-left: 5px;margin-top: 5px;}/* 只取最后三个 */.item:nth-last-child(-n + 3) {background-color: red;}</style><body><div class="container"><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item">5</div><div class="item">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>
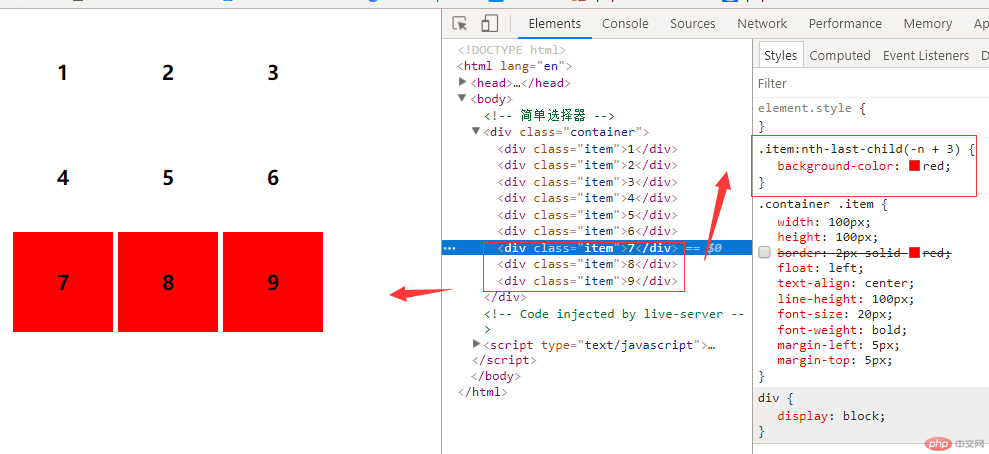
5.1.倒数第几个 :nth-last-child()
注:索引从1开始 括号里位置不能变换写法如:.item:nth-last-child(2){} 2为倒数第几个 随便写
例:给倒数第2个div添加背景颜色
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>结构伪类选择器:不分组 不区分元素类型</title></head><style>.container {width: 400px;height: 400px;/* border: 1px solid black; */}.container .item {width: 100px;height: 100px;/* border: 2px solid red; */float: left;text-align: center;line-height: 100px;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;margin-left: 5px;margin-top: 5px;}/* 倒数第二个 */.item:nth-last-child(2) {background-color: red;}</style><body><div class="container"><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item">5</div><div class="item">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>

分组结构伪类分两步
注:1.元素安类型进行分组
注:2.在分组中根据索引进行选择
1.在分组中匹配最后一个 :last-of-type
注:前面一定要加要匹配的元素写法如:.container span:last-of-type{} 匹配.container 下 span元素的最后一个
例:给.container 下 最后一个span添加背景颜色
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>结构伪类选择器:分组 不区分元素类型</title></head><style>.container {width: 400px;height: 400px;/* border: 1px solid black; */}.container .item {width: 100px;height: 100px;/* border: 2px solid red; */float: left;text-align: center;line-height: 100px;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;margin-left: 5px;margin-top: 5px;}/* 分组结构伪类分两步 *//* 1.元素安类型进行分组2.在分组中根据索引进行选择 *//* 在分组中匹配最后一个 */.container span:last-of-type {background-color: maroon;}</style><body><div class="container"><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><span class="item">4</span><span class="item">5</span><span class="item">6</span><span class="item">7</span><span class="item">8</span><span class="item">9</span></div></body></html>

2.在分组中匹配任何一个 :nth-of-type()
注:前面一定要加要匹配的元素写法如:.container span:nth-of-type(3){} 匹配.container 下 span元素的第三个
例:给.container 下 第三个span添加背景颜色
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>结构伪类选择器:分组 不区分元素类型</title></head><style>.container {width: 400px;height: 400px;/* border: 1px solid black; */}.container .item {width: 100px;height: 100px;/* border: 2px solid red; */float: left;text-align: center;line-height: 100px;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;margin-left: 5px;margin-top: 5px;}/* 分组结构伪类分两步 *//* 1.元素安类型进行分组2.在分组中根据索引进行选择 *//* 在分组中匹配任何一个 */.container span:nth-of-type(3) {background-color: maroon;}</style><body><div class="container"><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><span class="item">4</span><span class="item">5</span><span class="item">6</span><span class="item">7</span><span class="item">8</span><span class="item">9</span></div></body></html>

其他匹配方式类似 在 :nth-of-type()括号中添加匹配条件即可
如: /* 前三个 *//* .container span:nth-of-type(-n + 3) {background-color: maroon;} *//* 最后两个 *//* .container span:last-of-type(-n + 2) {background-color: maroon;} */
1.:target 选择器可用于选取当前活动的目标元素。
注:必须id配合 实现锚点操作
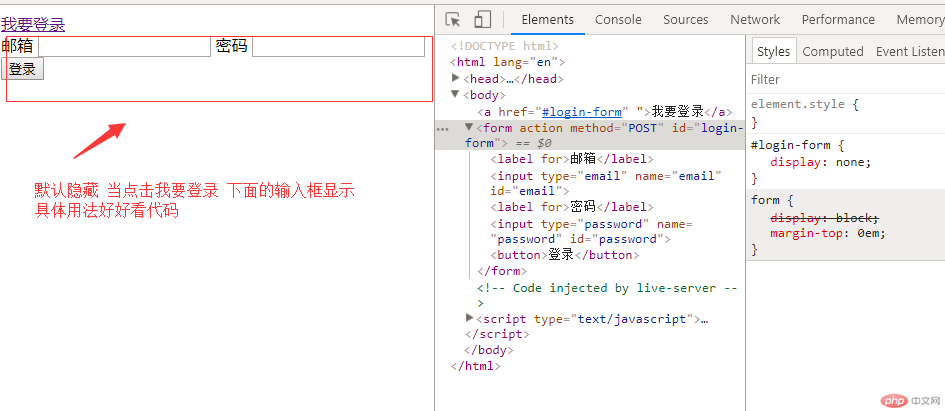
例:点击我要登录出现输入框demo
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>伪类和伪元素</title></head><style>#login-form {display: none;}/* :target :必须id配合 实现锚点操作 *//* 当前login-form的表单元素被a的锚点激活的时候执行 */#login-form:target {display: block;}/* 伪元素前面是双冒号 伪类前是单冒号 */</style><body><a href="#login-form"">我要登录</a><form action="" method="POST" id="login-form"><label for="">邮箱</label><input type="email" name="email" id="email" /><label for="">密码</label><input type="password" name="password" id="password" /><button>登录</button></form></body></html>
2.:focus 选择器当获取焦点的时候
例:点击输入框获取焦点时改变输入框样式
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>伪类和伪元素</title></head><style>/* :focus 当获取交点的时候 */input:focus {background-color: chocolate;}</style><body><!-- <a href="#login-form"">我要登录</a> --><form action="" method="POST" id="login-form"><label for="">邮箱</label><input type="email" name="email" id="email" /><label for="">密码</label><input type="password" name="password" id="password" /><button>登录</button></form></body></html>

其他类似方法有 自己练习一下
input::selection {} 设置选中文本的前景色和背景色:not(条件) 用于选择不满足条件元素::berore 在元素前创建伪元素::after 在元素后创建伪元素
1.元素选择器基本用法都是在设置元素样式是用到
2.动手实践掌握会更好