通常情况下,Spring Boot 在启动时会将 resources 目录下的 application.properties 或 apllication.yml 作为其默认配置文件,我们可以在该配置文件中对项目进行配置,但这并不意味着 Spring Boot 项目中只能存在一个 application.properties 或 application.yml。
1、默认配置文件
Spring Boot 项目中可以存在多个 application.properties 或 apllication.yml。
Spring Boot 启动时会扫描以下 5 个位置的 application.properties 或 apllication.yml 文件,并将它们作为 Spring boot 的默认配置文件。
- file:./config/*/
- file:./config/
- file:./
- classpath:/config/
- classpath:/
注:file: 指当前项目根目录;classpath: 指当前项目的类路径,即 resources 目录。
以上所有位置的配置文件都会被加载,且它们优先级依次降低,序号越小优先级越高。其次,位于相同位置的 application.properties 的优先级高于 application.yml。
所有位置的文件都会被加载,高优先级配置会覆盖低优先级配置,形成互补配置,即:
- 存在相同的配置内容时,高优先级的内容会覆盖低优先级的内容;
- 存在不同的配置内容时,高优先级和低优先级的配置内容取并集。
示例
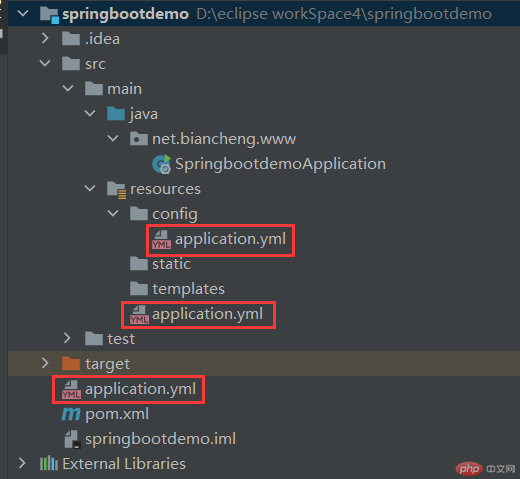
创建一个名为 springbootdemo 的 Spring Boot 项目,并在当前项目根目录下、类路径下的 config 目录下、以及类路径下分别创建一个配置文件 application.yml,该项目结构如下图。
项目根路径下配置文件 application.yml 配置如下。
#项目根目录下
#上下文路径为 /abc
server:
servlet:
context-path: /abc
项目类路径下 config 目录下配置文件 application.yml 配置如下。
#类路径下的 config 目录下
#端口号为8084
#上下文路径为 /helloWorld
server:
port: 8084
servlet:
context-path: /helloworld
项目类路径下的 application.yml 配置如下。
测试接口
package net.biancheng.
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class MyController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String hello() {
return "hello Spring Boot!";
}
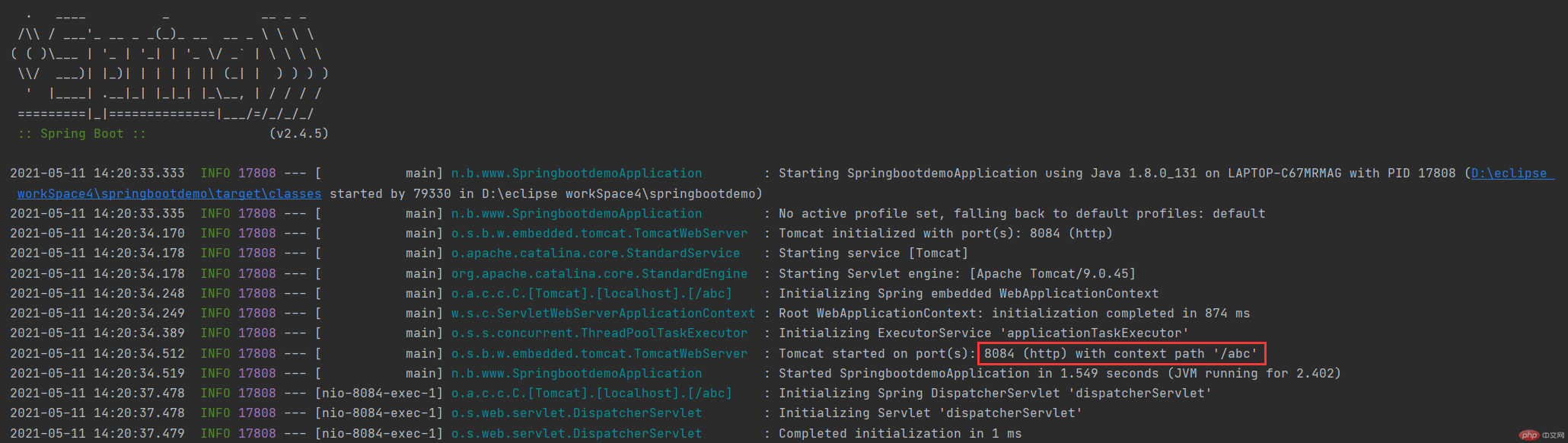
}启动 Spring Boot,查看控制台输出
根据 Spring Boot 默认配置文件优先级进行分析:
- 该项目中存在多个默认配置文件,其中根目录下 /config 目录下的配置文件优先级最高,因此项目的上下文路径为 “/abc”;
- 类路径(classpath)下 config 目录下的配置文件优先级高于类路径下的配置文件,因此该项目的端口号为 “8084”;
- 以上所有配置项形成互补,所以访问路径为“http://localhost:8084/abc”。
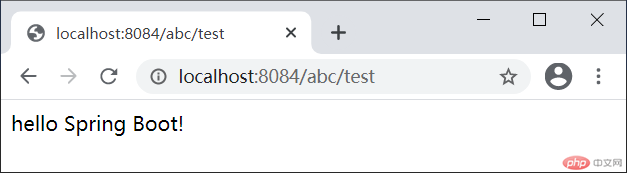
根据服务器端口和上下文路径,使用浏览器访问 http://localhost:8084/abc/test,结果如下图