Correction status:qualified
Teacher's comments:



博客已迁移至自建网站,此博客已废弃.请移步至:https://blog.ours1984.top/posts/dwbj/ 欢迎大家访问
文档流指的是什么呢?由于这是显示在浏览器上面的,显示在电脑屏幕前的。如果我们将屏幕的两侧想象成河道,将屏幕的上面作为流的源头,将屏幕的底部作为流的结尾的话,那我们就抽象出来了文档流 !
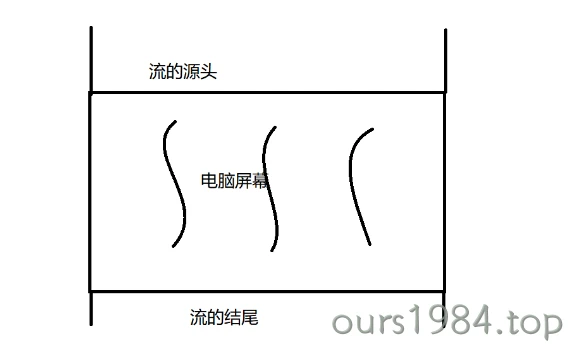
那文档流流动的又是什么呢?那就是元素!可以将屏幕中显示的内容都可以一一对应为文档中的一个元素,在这里就引出两个概念:内联元素与块级元素
块级: display: block / table / table-cell,td / list-item / form / p / h1-h6/…
内联/行内: 用来描述块级元素内部的内容/文本
可以将内联元素转为块级,使宽高生效, 这时后面的其它元素垂直排列display: block
如果不想让后面的元素换行显示/垂直排列,可以将它转为内联块/行内块
display: inline-block;/* 内联块/行内块: 即像内联一样水平排列,又像块级一样可以设置宽高 *//* 内联块的排列方式,仍然是水平的, 所以说, 内联块本质上仍是内联元素 *//* 内联块,可视为内联元素的一个特例/子集 */
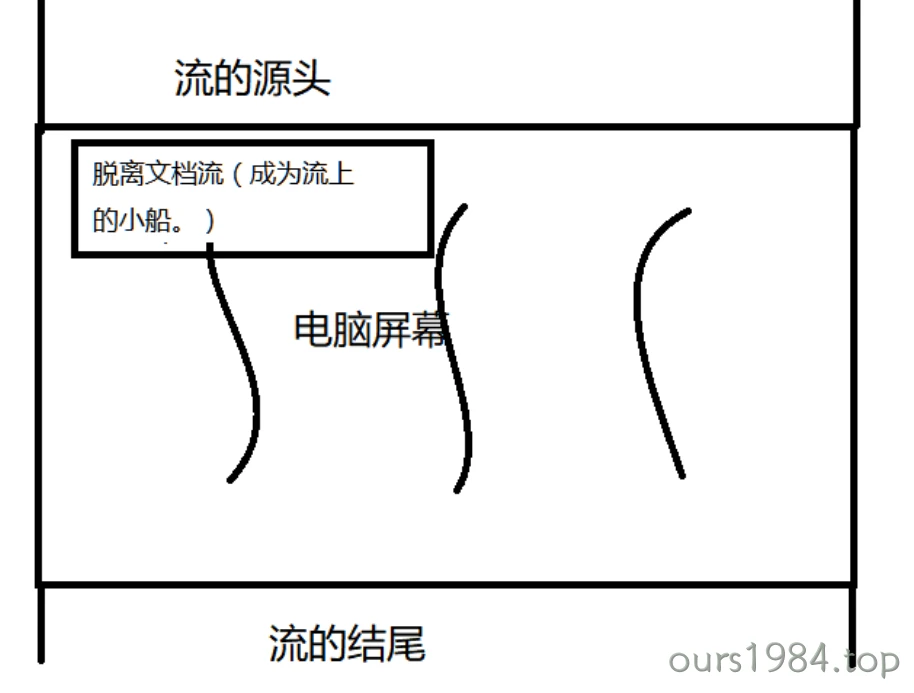
但是仅有的两种排版,就满足了我们的需求吗?肯定是不够的!!应该有一种更加自由的变换,从而满足多样的世界。有三种方式脱离文档流:
将文档流比作是河流的话,水就相当于文档流里面的元素。而脱离文档流就相当于脱离水跑到水的上面飘着,就像河流上的小船。
position属性取值含义如下
| 值 | 描述 | 参照物 | 定位规则 |
|---|---|---|---|
| absolute | 生成绝对定位的元素 | static定位以外的第一个父元素 | 通过”left”,”top”,”right”以及”bottom”属性进行规定 |
| fixed | 生成绝对定位的元素 | 浏览器窗口进行定位 | 通过”left”,”top”,”right”以及”bottom”属性进行规定 |
| relative | 生成相对定位的元素 | 自身在文档流中的位置 | “left:20”会向元素的LEFT位置添加20像素 |
| static | 默认值 | 没有定位 | 元素出现在正常的流中(忽略 top, bottom, left, right 或者 z-index 声明) |
| sticky | 粘性定位 = 静态定义 + 固定定位 | 浏览器窗口进行定位 | 当到了设置好的位置时,就自动悬停住了,采用固定定位 |
| inherit | 规定应该从父元素继承position属性的值 |
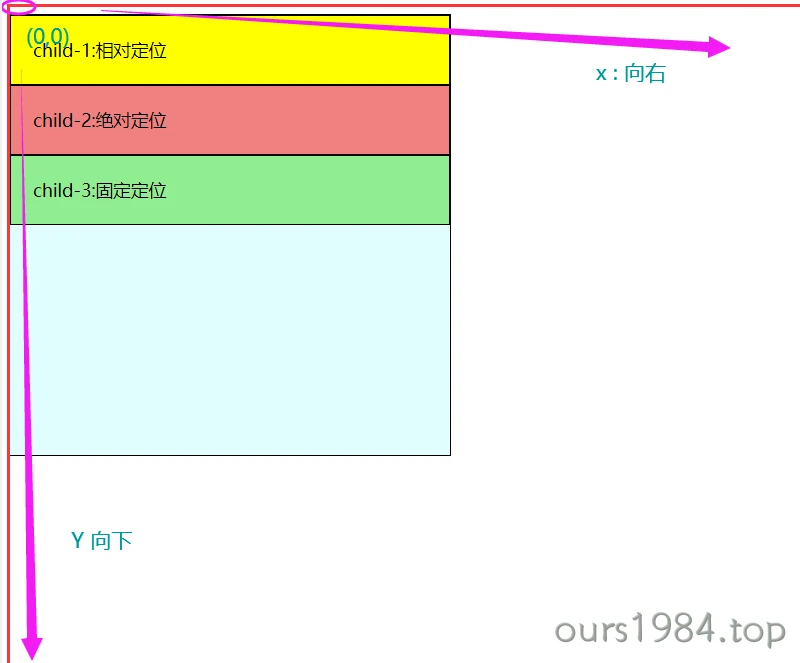
<div class="testPosition"><div class="box parent"><div class="box child one">child-1:相对定位相对定位相对定位相对定位</div><div class="box child two">child-2:绝对定位绝对定位绝对定位绝对定位</div><div class="box child three">child-3:固定定位固定定位固定定位</div><div class="box child four">child-4:粘性定位粘性定位粘性定位</div></div></div><style>.testPosition {height: 1000px;border: 2px solid blue;}.testPosition .box {border: 1px solid #000;}.testPosition .box.parent {width: 400px;height: 400px;background-color: lightcyan;}.testPosition .box.child {padding: 20px;}.testPosition .box.child.one {background-color: yellow;}.testPosition .box.child.two {background-color: lightcoral;}.testPosition .box.child.three {background-color: lightgreen;}.testPosition .box.child.four {background-color: rgb(144, 146, 238);}/* 1. 相对定位 */.testPosition .box.child.one {position: relative;top: 2px;left: 20px;}/* 2. 绝对定位 */.testPosition .box.child.two {position: absolute;top: 2px;right: 20px;}/* 3. 固定定位 */.testPosition .box.child.three {position: fixed;right: 50px;bottom: 100px;}/* 4. 粘性定位 */.testPosition .box.child.four {position: sticky;position: -webkit-sticky;top: 10px;}.testPosition {position: relative;}.testPosition .box.parent {position: static;}</style>