


1、html的页面中离不开各种模块的分布,以下是盒子模型的基本要素的介绍和学习,通过对具体的案例来熟练地掌握这些基本的元素的设置,主要包括内容(content)内边距(padding)边框(border)外边距(margin):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>盒模型</title>
<style>
.box1 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
/*内容区*/
/*content: */
/*内边距,外边距无颜色,无样式*/
/*内边距:上右下左顺时针顺序*/
/*padding-top:10px;
padding-right: 20px;
padding-bottom: 10px;
padding-left: 30px;*/
padding: 10px 20px 10px 30px;
/*边框*/
border-top-width: 5px;
border-top-style:solid;
border-top-color: black;
border-right: 5px solid green;
border-bottom: 5px dashed blue;
border-left-width: 5px;
border-left-style: dashed;
border-left-color: red;
/*外边距:上右下左顺时针顺序*/
margin-top: 10px;
margin-right: 20px;
margin-bottom: 30px;
margin-left: 10px;
/*margin: 10px;*/
}
.box2 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: coral;
/*padding的传递性,会撑开盒子*/
padding: 50px;
}
/*外边距在垂直方向上会塌陷,以数值大的为准,向大数值方向走,小的数值会被覆盖*/
.box3 {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: lightcoral;
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
.box4 {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: lightgreen;
margin-top: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<br>
<div class="box2">
<img src="images/1.jpg" width="200">
</div>
<br>
<div class="box3"></div>
<div class="box4"></div>
</body>
</html>点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

说明:通过简单的案例,进一步加深了对盒子模型的基本元素的使用,以及内外边距的规则,无颜色,无样式。
2、html中元素的对齐方式可以准确无误的控制每个模块的位置,以下主要介绍了html中的四种元素的对齐方式:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>元素对齐方式</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<h3 style="font-family: 楷体;color: green">元素对齐方式</h3>
<!-- 一共有四种常见的情况: -->
<!-- 1、子元素是单行行内元素:<a> ,<span> <br>等等
a:水平居中:在父元素使用:text-align: center;
b:垂直居中:在行内元素上设置行高与父元素等到即可:line-height:xxpx; -->
<style type="text/css">
.box1 {
width: 100px;
height: 80px;
background-color: skyblue;
text-align: center;
}
.box1 a {
font-family: 楷体;
font-weight: bolder;
line-height: 80px;
color: red;
text-decoration: none;
}
</style>
<div class="box1">
<a href="">php中文网</a>
</div>
<hr width="300" align="left">
<!-- 2、子元素为多行的内联文本 <br> <p>等
a:水平居中: 在父元素应用: text-align: center;
b:垂直居中: 在父元素: display:table-cell; -->
<style type="text/css">
.box2 {
width: 100px;
height: 80px;
background-color: lightcoral;
text-align: center; /*第一步水平居中*/
display: table-cell; /*第二部先转化为表格*/
vertical-align: middle; /*再垂直居中*/
}
.box2 span {
font-family: 楷体;
font-weight: bolder;
color: black;
}
</style>
<div class="box2">
<span>php中文网</span> <br>
<span>www.php.cn</span>
</div>
<hr width="300" align="left">
<!-- 3.子元素是块元素 <br>
a: 水平居中: 子元素设置左右外边距自动适应容器margin: auto;
b:垂直居中: 在父元素: display:table-cell; -->
<style type="text/css">
.box3 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightgreen;
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle; /*垂直居中*/
}
.box3 .child {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: pink;
margin: auto;
text-align: center;
}
.box3 .child a {
font-family: 楷体;
font-weight: bolder;
font-size: 20px;
line-height: 50px;
color: black;
text-decoration: none;
</style>
<div class="box3">
<div class="child"><a>福</a></div>
</div>
<hr width="300" align="left">
<!-- 4. 子元素是不定宽的块元素
a: 水平居中: 子元素转为行内元素,父级加: text-align:center
b: 垂直居中: 在父元素: display:table-cell; -->
<style type="text/css">
.box4 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightcoral;
text-align: center; /*水平居中*/
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: bottom; /*位于底部*/
}
ul {
margin: 0;
padding-left: 0;
padding-bottom: 5px;
}
.box4 li {
display: inline; /*将块元素转为行内元素*/
}
.box4 ul li a {
font-family: 楷体;
font-size: 10px;
font-weight: bolder;
color: black;
text-decoration: none;
}
</style>
<div class="box4">
<ul>
<li><a href=""><i>1</i></a></li>
<li><a href=""><i>2</i></a></li>
<li><a href=""><i>3</i></a></li>
<li><a href=""><i>4</i></a></li>
<li><a href=""><i>5</i></a></li>
</ul>
</div>
<hr width="300" align="left">
</body>
</html>点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
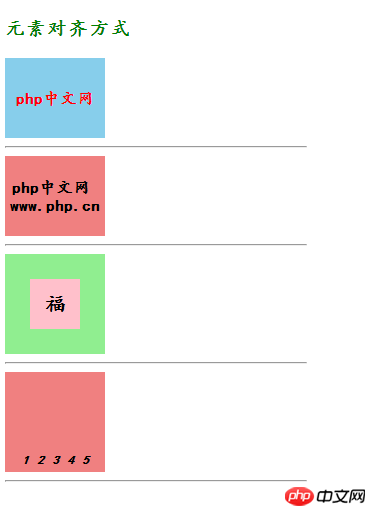
说明:以上通过四个案例实现了四种元素对齐的方式,主要有:
1、子元素是单行行内元素:<a> ,<span> <br>等等
2、子元素为多行的内联文本 <br> <p>等等
3、子元素是块元素 <br>等等
4.、子元素是不定宽的块元素
这四种对齐方式基本上包括了所有html中布局的需求
3,以下是通过相对定位实现的六色的十字架的小案例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>相对定位十字架</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<style type="text/css">
.box1 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: coral;
position: relative;
left: 100px;
}
.box2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
.box3 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
position: relative;
left: 100px;
top: -100px;
}
.box4 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightgreen;
position: relative;
left: 200px;
top: -200px;
}
.box5 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: grey;
position: relative;
left: 100px;
top: -200px;
}
.box6 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
position: relative;
left: 100px;
top: -200px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
<div class="box4"></div>
<div class="box5"></div>
<div class="box6"></div>
</body>
</html>点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
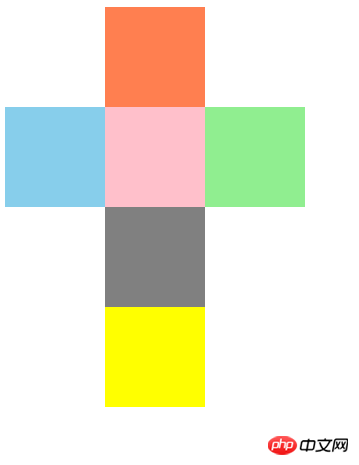
说明:通过相对定位技术,对模块进行准确的定位,定位是html中一个必不可少的技术,
1、相对定位:position: relative;
2、绝对定位:position: absolute;
3、固定定位:position:fixed;
总结:
(1)盒子模型的基本要素,包括内容(content)内边距(padding)边框(border)外边距(margin)分别分为上下左右四个方向,快捷的使用时,顺序排列为顺时针:上、右、下、左;外边距在垂直方向上会塌陷,以数值大的为准,向大数值方向走,小的数值会被覆盖,padding具有传递性,会撑开盒子;
(2)元素对齐的四种方式:
1、子元素是单行行内元素:<a> ,<span> <br>等等
a:水平居中:在父元素使用:text-align: center;
b:垂直居中:在行内元素上设置行高与父元素等到即可:line-height:xxpx;
2、子元素为多行的内联文本 <br> <p>等等
a:水平居中: 在父元素应用: text-align: center;
b:垂直居中: 在父元素: display:table-cell;
3、子元素是块元素 <br>等等
a: 水平居中: 子元素设置左右外边距自动适应容器margin: auto;
b:垂直居中: 在父元素: display:table-cell;
4、 子元素是不定宽的块元素
a: 水平居中: 子元素转为行内元素,父级加: text-align:center
b: 垂直居中: 在父元素: display:table-cell;
(3)模块定位主要包括三种:
1、相对定位:position: relative;
2、绝对定位:position: absolute;
3、固定定位:position:fixed;