Correction status:Uncorrected
Teacher's comments:



一、概述
这节课讲述了PHP在数据库连接和操作中的两种方法,一种是MYSQLI另外是PDO操作。
二、作业部分
1、PDO的优点:
通用接口,适用各种数据库 模块化,加载驱动快,运行速度快
轻型函数,PHP实现了抽象和兼容
2、获取结果集的正确数量
1.$stmt->num_rows(mysqli),
2.$stmt->rowCount()(PDO): 返回受影响的记录数量
3.PDO中select语句计数不能用rowCount(),因为不是“写"操作,用可能会报错。
只能先用count(*),再用fetchColum()获取第一行第一列的数字,也就是计数的个数。
3、编程部分
(1)mysqli
config.php
<?php $db = [ 'host' =>'127.0.0.1', 'user' => 'root', 'psw' => 'root', 'name' => 'php', 'charset' => 'utf8', ];
connect.php
<?php
require 'config.php';
error_reporting(E_ALL ^E_WARNING);
$mysqli = new mysqli($db[host],$db[user],$db[psw],$db[name]);
if ($mysqli->errno){
die($mysqli->errno.':'.$mysqli->connect_error);
}
//echo 'success';select.php
<?php
//连接数据库
require 'connect.php';
//准备sql语句
$sql = "select `staff_id`,`name`,`salary` from `staff` where `salary` > ? ; " ;
//$sql = "SELECT `name`,`salary` FROM `staff` WHERE `salary` > ? ;";
//创建预处理对象
$stmt = $mysqli -> stmt_init();
if ($stmt->prepare($sql)){
//参数绑定
$stmt->bind_param('i',$salary);
//设置参数值
$salary = 5000;
//执行
if($stmt->execute()){
//结果集存放缓存区
$stmt->store_result();
//将结果集绑定到数组
$stmt->bind_result($id,$name, $salary);
if ($stmt -> num_rows > 0){
//
while ($stmt->fetch()) {
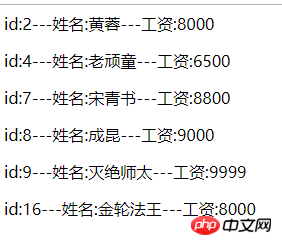
echo '<p>id:'.$id.'---姓名:' .$name.'---工资:'.$salary.'</p>';
}
}else {
exit('无数据');
}
//释放结果集
$stmt->free_result();
}else{
//执行阶段错误
exit('执行时'.$stmt->errno.':'.$stmt->error);
}
}else {
//检测SQL语句阶段错误
exit('SQL语句'.$stmt->errno . ':' . $stmt->error);
}
//注销释放预处理对象
$stmt->close();
//关闭连接
$mysqli->close();结果图:
(2)PDO
insert.php
<?php
//连接数据库
//$dsn = 'mysql:host=127.0.0.1; dbname=php';
$pdo = new PDO('mysql:host=127.0.0.1;dbname=php','root','root');
//准备SQL语句
$sql = "insert `user` set `user_name`= :name, `email`= :email, `password`=sha1(:password)";
//$sql = "INSERT `user` SET `user_name`= :name , `email`= :email, `password`= sha1(:password)";
//创建预处理对象
$stmt = $pdo->prepare($sql);
//绑定参数,PDO::PARAM_STR表示SQL中char、varchar或者其他字符串类型
$data = ['name'=>'杨过','email'=>'yg@wuxia.com','psw'=>'123'];
$stmt -> bindParam(':name',$data['name'],PDO::PARAM_STR);
$stmt -> bindParam(':email',$data['email'],PDO::PARAM_STR);
$stmt -> bindParam(':password',$data['psw'],PDO::PARAM_STR);
if ($stmt->execute()){
echo '<h3>成功添加了'.$stmt->rowCount().'条记录';
}else{
echo '<h3>未成功</h3>';
print_r($stmt->errorInfo());
exit();
}
$stmt = null;
$pdo = null;update.php
<?php
//链接数据库
$pdo = new PDO('mysql:host=127.0.0.1;dbname=php','root','root');
//$pdo = new PDO('mysql:host=127.0.0.1;dbname=php','root','root');
//准备sql语句
$sql = "UPDATE `user` SET `email`= :email WHERE `user_id`= :id";
//创建预处理对象
$stmt = $pdo->prepare($sql);
//绑定参数
$data = ['email'=>'yggg@qq.com','id'=>'9'];
$stmt -> bindParam(':email',$data['email'],PDO::PARAM_STR);
$stmt -> bindParam(':id',$data['id'],PDO::PARAM_STR);
//执行sql语句
if ($stmt->execute()){
echo '<h3>成功更新',$stmt->rowCount(),'记录';
}else{
echo print_r($stmt->errorInfo());
exit();
}
//释放预处理对象
$stmt = null;
//关闭数据库
$pdo = null;delete.php
<?php
//连接数据库
$pdo = new PDO('mysql:host=127.0.0.1;dbname=php','root','root');
//sql语句
$sql = "DELETE FROM `user` WHERE `user_id` = :id";
/*********************************sql语句``不是''**************************/
//创建预处理对象
$stmt = $pdo->prepare($sql);
//缩写绑定+执行命令
//if ($stmt -> execute(['id'=>2]))
if ($stmt->execute(['id'=>9])){
echo '成功删除',$stmt->rowCount(),'条数据';
}else{
//exit($stmt->errorInfo());
echo '<h3>无删除</h3>';
print_r($stmt->errorInfo());
exit();
}
//释放对象和关闭连接
$stmt = null;
$pdo = null;select.php
<?php
$pdo = new PDO('mysql:hos=127.0.0.1;dbname=php','root','root');
$sql = "select `user_name`,`email` from `user` where `user_id` > :id";
$stmt = $pdo->prepare($sql);
//PDO::FETCH_ASSOC 关联数组形式
if ($stmt->execute(['id'=>2])){
while ($row = $stmt->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC)){
echo var_export($row),'<br>';
}
}else{
echo print_r($stmt->errorInfo());
}
//$stmt = null;
echo '<hr>';
$sql = "select `name`,`age`,`salary` from `staff` where `salary` > :salary";
$stmt = $pdo->prepare($sql);
$stmt->execute(['salary'=>5000]);
while ($row = $stmt->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC)){
echo var_export($row),'<br>';
}
//select语句计数不能用rowCount(),因为不是“写"操作,用可能会报错。
//只能先用count(*),再用fetchColum()获取第一行第一列的数字,也就是计数的个数
$sql = "select count(*) from `staff` where `salary` > :salary";
$stmt = $pdo->prepare($sql);
$stmt->execute(['salary'=>5000]);
echo '工资大于5000的有',$stmt->fetchColumn(),'人。';
echo '<hr>';
//将结果集绑定到变量上
$sql = "select `name`,`age`,`salary` from `staff` where `salary` > :salary";
$stmt = $pdo->prepare($sql);
$stmt->execute(['salary'=>5000]);
$stmt->bindColumn('name',$name);
$stmt->bindColumn('age',$age);
while ($stmt->fetch(PDO::FETCH_BOUND)){
echo '姓名:',$name,',年龄:',$age,'。<br>';
}connect.php
<?php
//设置数据库类型,服务器,默认数据库
$dsn = 'mysql:host=127.0.0.1;dbname=php';
$user = 'root';
$psw = 'root';
try{
$pdo = new PDO($dsn,$user,$psw);
echo 'success';
}catch (PDOException $exception){
die('connect error :'.$exception->getMessage());
}
//关闭连接
$pdo = null;
//或
//unset($pdo);结果图:




3、总结
PDO::PARAM_STR表示SQL中char、varchar或者其他字符串类型
sql语句是``不是''
PDO::FETCH_ASSOC 关联数组形式
select语句计数不能用rowCount(),因为不是“写"操作,用可能会报错。
只能先用count(*),再用fetchColum()获取第一行第一列的数字,也就是计数的个数
预处理一定要有。