 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 CentOS
CentOS
 3. Installation and use of linux CentOS pagoda panel svn (graphic tutorial)
3. Installation and use of linux CentOS pagoda panel svn (graphic tutorial)
3. Installation and use of linux CentOS pagoda panel svn (graphic tutorial)
做程序员这么多年,放假或者出差的时候,偶尔需要改改代码,这个时候带一个笔记本电脑,太累赘了。
除了笔记本电脑,也用过远程连接台式机,能解决修改代码的问题,同时也会有其他的问题。
比如:偶尔连接不上,网络不好会卡,电脑不能关机。电费每月 100 多,后来搜到黑科技,使用 `bois` 定时任务,定时开机,省了一半的电费。
后来使用宝塔面板,觉得可以直接用服务器写代码,拿着 `ipad` 就能写了,在后来发现跟 `svn、git` 配合,那是更好了。所以就写了个服务器写代码的流程,给大家参考下。
一、安装 `svn`
1、安装命令
linux CentOS 自带 yum 命令
yum -y install subversion
2、指定 `svn` 版本库目录
创建新目录,目录放在哪里,根据自己需要
用 `svnserve` 命令指定版本库目录
mkdir /www/svndata svnserve -d -r /www/svndata

二、创建 svn 项目
1、创建版本库
www.ouyangke.cn 是 `svn` 项目的目录名称,也是客户端连接的项目名。
可以用域名作为 `svn` 目录名,一眼就知道这个 `svn` 对应哪个域名
svnadmin create /www/svndata/www.ouyangke.cn

2、配置 svnserve.conf 文件
进入项目里的 conf 目录
cd /www/svndata/www.ouyangke.cn/conf
打开 svnserve.conf 文件,vi 命令是系统自带的
vi svnserve.conf

以下配置放在 svnserve.conf 文件里的 20 行后面
anon-access=none auth-access=write password-db=passwd

保存就可以了,如果不会使用 vi 命令的,可以用宝塔面板,找到对应的文件修改

3、配置 passwd 文件
打开 passwd 文件,也在 conf 目录下
vi passwd
在后面一行输入账号=密码
ouyangke=ou123

4、客户端连接 svn


三、线上同步
同步的目的是:更新代码后,服务器中的项目自动更新同步
1、拷贝项目
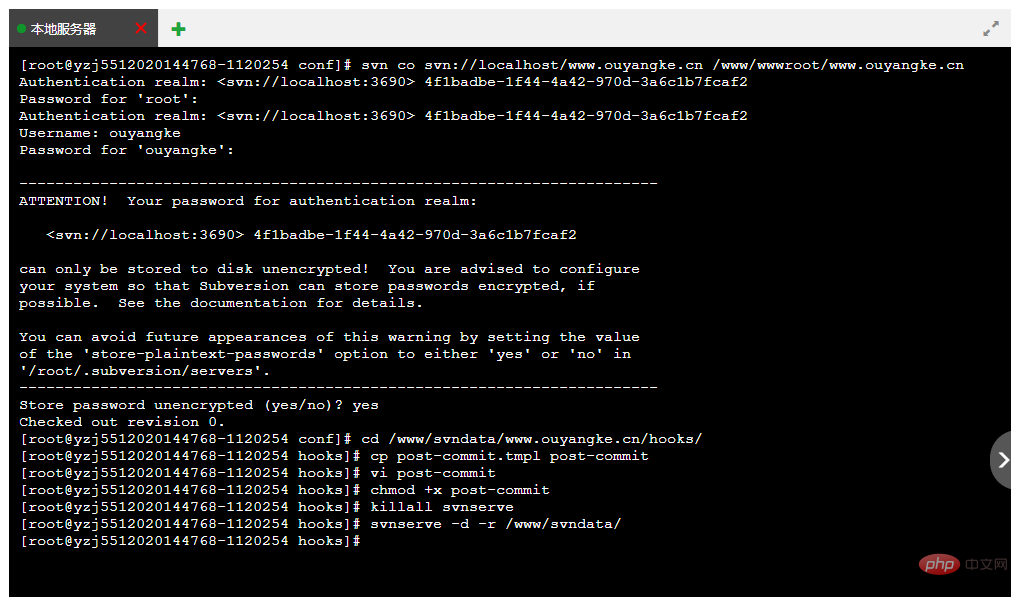
拷贝要同步的项目,到网站目录文件中。需要 root 密码和 svn 账户密码。
svn co svn://localhost/www.ouyangke.cn /www/wwwroot/www.ouyangke.cn
2、建立同步脚本
先复制一份同步脚本
cd /svndata/name/hooks/ cp post-commit.tmpl post-commit

3、编辑同步脚本
vi post-commit
REPOS="$1"REV="$2" BASEPATH=/www/wwwroot/ WEBPATH="$BASEPATH/" export LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8 svn update $WEBPATH --username ouyangke --password ou123 --no-auth-cache
`BASEPATH` 是拷贝的项目目录

4、脚本
执行脚本
chmod +x post-commit
关闭 svn
killall svnserve
开启 svn
svnserve -d -r /www/svndata

5、上传文件
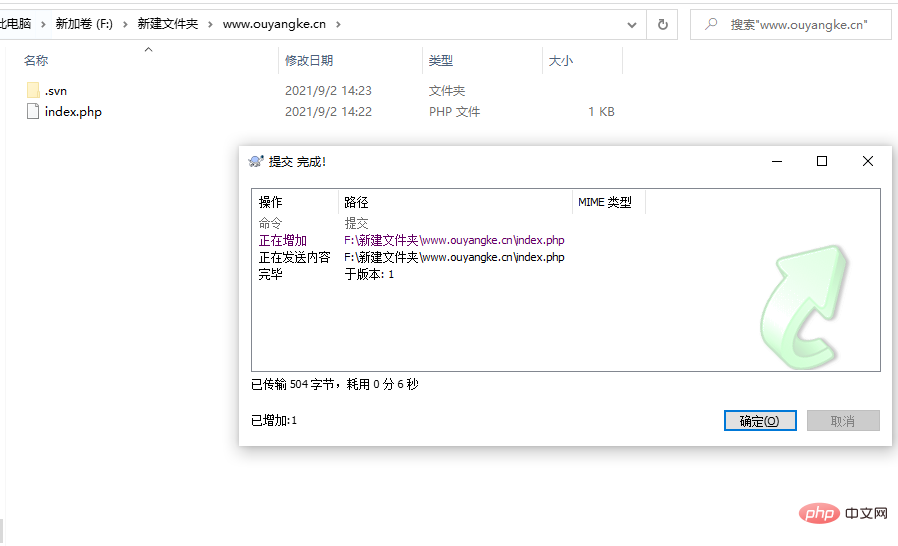
五、宝塔编辑项目
1、连接 svn
svn checkout svn://localhost/www.ouyangke.cn /www/wwwroot/www.ouyangke.cn.edit
2、更新文件
在 www.ouyangke.cn.edit 目录下
svn update
3、新增文件
在 www.ouyangke.cn.edit 目录下
svn add 文件名
4、上传文件
在 www.ouyangke.cn.edit 目录下
svn commit -m `备注` 文件名
如果是新文件,必须先新增文件
如果上传文件失败,执行 linux 命令,改变环境变量:
export SVN_EDITOR=vim
如果 `svn` 服务器不是你管理,那可以直接从第五步开始。
配置好后,在给项目创建个域名,就可以随时随地用 `ipad` 来写代码了。
【专题:Linux CentOS服务器PHP运营环境搭建使用】
四、外网访问数据库
五、宝塔面板 FTP
推荐学习:php培训
The above is the detailed content of 3. Installation and use of linux CentOS pagoda panel svn (graphic tutorial). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
Improve HDFS performance on CentOS: A comprehensive optimization guide to optimize HDFS (Hadoop distributed file system) on CentOS requires comprehensive consideration of hardware, system configuration and network settings. This article provides a series of optimization strategies to help you improve HDFS performance. 1. Hardware upgrade and selection resource expansion: Increase the CPU, memory and storage capacity of the server as much as possible. High-performance hardware: adopts high-performance network cards and switches to improve network throughput. 2. System configuration fine-tuning kernel parameter adjustment: Modify /etc/sysctl.conf file to optimize kernel parameters such as TCP connection number, file handle number and memory management. For example, adjust TCP connection status and buffer size
 What files do you need to modify in HDFS configuration CentOS?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
What files do you need to modify in HDFS configuration CentOS?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
When configuring Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) on CentOS, the following key configuration files need to be modified: core-site.xml: fs.defaultFS: Specifies the default file system address of HDFS, such as hdfs://localhost:9000. hadoop.tmp.dir: Specifies the storage directory for Hadoop temporary files. hadoop.proxyuser.root.hosts and hadoop.proxyuser.ro
 CentOS Stream 8 troubleshooting methods
Apr 14, 2025 pm 04:33 PM
CentOS Stream 8 troubleshooting methods
Apr 14, 2025 pm 04:33 PM
CentOSStream8 system troubleshooting guide This article provides systematic steps to help you effectively troubleshoot CentOSStream8 system failures. Please try the following methods in order: 1. Network connection testing: Use the ping command to test network connectivity (for example: pinggoogle.com). Use the curl command to check the HTTP request response (for example: curlgoogle.com). Use the iplink command to view the status of the network interface and confirm whether the network interface is operating normally and is connected. 2. IP address and gateway configuration verification: Use ipaddr or ifconfi
 CentOS HDFS performance tuning tips
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:00 PM
CentOS HDFS performance tuning tips
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:00 PM
CentOS Platform Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) Performance Optimization Guide Optimizing HDFS Performance is a multi-faceted issue, and multiple parameters need to be adjusted for specific situations. The following are some key optimization strategies: 1. Memory management adjusts the NameNode and DataNode memory configuration: reasonably configure the HADOOP_NAMENODE_OPTS and HADOOP_DATANODE_OPTS environment variables according to the actual memory size of the server to optimize memory utilization. Enable large page memory: For high memory consumption applications (such as HDFS), enabling large page memory can reduce memory page allocation and management overhead and improve efficiency. 2. Disk I/O optimization uses high-speed storage
 Troubleshooting methods for Zookeeper on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 04:30 PM
Troubleshooting methods for Zookeeper on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 04:30 PM
ZooKeeper troubleshooting guide for CentOS Systems This article provides a step-by-step guide to help you effectively troubleshoot ZooKeeper faults on CentOS systems. 1. Verify the status of ZooKeeper service: First, use the following command to check the status of ZooKeeper service: sudosystemctlstatuszookeeper If the service is not running, use the following command to start: sudosystemctlstartzookeeper To enable it to start by starting: sudosystemctlenablezookeeper2. Analyze the ZooKeeper log to check Z
 What is the CentOS MongoDB backup strategy?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
What is the CentOS MongoDB backup strategy?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
Detailed explanation of MongoDB efficient backup strategy under CentOS system This article will introduce in detail the various strategies for implementing MongoDB backup on CentOS system to ensure data security and business continuity. We will cover manual backups, timed backups, automated script backups, and backup methods in Docker container environments, and provide best practices for backup file management. Manual backup: Use the mongodump command to perform manual full backup, for example: mongodump-hlocalhost:27017-u username-p password-d database name-o/backup directory This command will export the data and metadata of the specified database to the specified backup directory.
 How to configure slow query log in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
How to configure slow query log in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
Enable Redis slow query logs on CentOS system to improve performance diagnostic efficiency. The following steps will guide you through the configuration: Step 1: Locate and edit the Redis configuration file First, find the Redis configuration file, usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Open the configuration file with the following command: sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Step 2: Adjust the slow query log parameters in the configuration file, find and modify the following parameters: #slow query threshold (ms)slowlog-log-slower-than10000#Maximum number of entries for slow query log slowlog-max-len
 How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Complete Guide to Checking HDFS Configuration in CentOS Systems This article will guide you how to effectively check the configuration and running status of HDFS on CentOS systems. The following steps will help you fully understand the setup and operation of HDFS. Verify Hadoop environment variable: First, make sure the Hadoop environment variable is set correctly. In the terminal, execute the following command to verify that Hadoop is installed and configured correctly: hadoopversion Check HDFS configuration file: The core configuration file of HDFS is located in the /etc/hadoop/conf/ directory, where core-site.xml and hdfs-site.xml are crucial. use



)
)
)
)
)
