PHP Form Validation Basic Tutorial on PHP Development
1. PHP form verification
In this chapter we will introduce how to use PHP to verify the form data submitted by the client.
Note: We need to consider security when processing PHP forms. In this chapter we will demonstrate the secure processing of PHP form data. In order to prevent hackers and spam, we need to perform data security verification on the form.
The HTML form introduced in this chapter contains the following input fields: Must and optional text fields, radio buttons, and submit buttons.
2. Example display
The code is as follows:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>php.cn</title>
<style>
.error {color: #FF0000;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<?php
// 定义变量并默认设置为空值
$nameErr = $emailErr = $genderErr = $websiteErr = "";
$name = $email = $gender = $comment = $website = "";
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST")
{
if (empty($_POST["name"]))
{
$nameErr = "名字是必需的";
}
else
{
$name = test_input($_POST["name"]);
// 检测名字是否只包含字母跟空格
if (!preg_match("/^[a-zA-Z ]*$/",$name))
{
$nameErr = "只允许字母和空格";
}
}
if (empty($_POST["email"]))
{
$emailErr = "邮箱是必需的";
}
else
{
$email = test_input($_POST["email"]);
// 检测邮箱是否合法
if (!preg_match("/([\w\-]+\@[\w\-]+\.[\w\-]+)/",$email))
{
$emailErr = "非法邮箱格式";
}
}
if (empty($_POST["website"]))
{
$website = "";
}
else
{
$website = test_input($_POST["website"]);
// 检测 URL 地址是否合法
if (!preg_match("/\b(?:(?:https?|ftp):\/\/|www\.)[-a-z0-9+&@#\/%?=~_|!:,.;]*[-a-z0-9+&@#\/%=~_|]/i",$website))
{
$websiteErr = "非法的 URL 的地址";
}
}
if (empty($_POST["comment"]))
{
$comment = "";
}
else
{
$comment = test_input($_POST["comment"]);
}
if (empty($_POST["gender"]))
{
$genderErr = "性别是必需的";
}
else
{
$gender = test_input($_POST["gender"]);
}
}
function test_input($data)
{
$data = trim($data);
$data = stripslashes($data);
$data = htmlspecialchars($data);
return $data;
}
?>
<h2>PHP 表单验证实例</h2>
<p><span class="error">* 必需字段。</span></p>
<form method="post" action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]);?>">
名字: <input type="text" name="name" value="<?php echo $name;?>">
<span class="error">* <?php echo $nameErr;?></span>
<br><br>
E-mail: <input type="text" name="email" value="<?php echo $email;?>">
<span class="error">* <?php echo $emailErr;?></span>
<br><br>
网址: <input type="text" name="website" value="<?php echo $website;?>">
<span class="error"><?php echo $websiteErr;?></span>
<br><br>
备注: <textarea name="comment" rows="5" cols="40"><?php echo $comment;?></textarea>
<br><br>
性别:
<input type="radio" name="gender" <?php if (isset($gender) && $gender=="female") echo "checked";?> value="female">女
<input type="radio" name="gender" <?php if (isset($gender) && $gender=="male") echo "checked";?> value="male">男
<span class="error">* <?php echo $genderErr;?></span>
<br><br>
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<?php
echo "<h2>您输入的内容是:</h2>";
echo $name;
echo "<br>";
echo $email;
echo "<br>";
echo $website;
echo "<br>";
echo $comment;
echo "<br>";
echo $gender;
?>
</body>
</html>The output effect is as shown on the right
3. Practical explanation
1. Verification rules
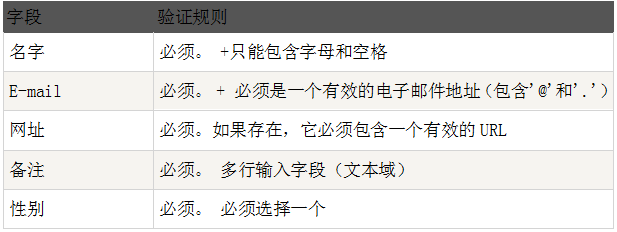
2. Text fields
The "Name", "E-mail", and "Website" fields are text input elements, and the "Remarks" field is a textarea. The HTML code is as follows:
"Name": <input type="text" name="name">
E-mail: <input type="text" name ="email">
Website: <input type="text" name="website">
Remarks: <textarea name="comment" rows="5" cols="40"></textarea>
3. Radio button
"Gender" The fields are radio buttons and the HTML code looks like this:
gender:
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="female">female
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="male">Male
4. Form elements
HTML form code is as follows:
<form method="post" action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF "]);?>">
This form uses method="post" method to submit data.
Note: What is the $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] variable?
$_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] is a super global variable that returns the file name of the currently executing script, and Document root related.
So, $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] will send the form data to the current page instead of jumping to a different page.
Note:
What is the htmlspecialchars() method?
htmlspecialchars() function converts some predefined characters into HTML entities.
The predefined characters are:
& (ampere) becomes &
" (double quotation marks) becomes "
' (single quotation mark) Quotes) become '
- ##5. What should we pay attention to in PHP forms?
The $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] variable may be used by hackers!
When hackers use cross-site scripting HTTP links to attack, the $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] server variable will also be embedded in the script. The reason is that cross-site scripting is appended to the path of the executable file, so the string $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] will contain the JavaScript program code behind the HTTP link.- Note: XSS is also called CSS (Cross-Site Script), a cross-site scripting attack. Malicious attackers insert malicious HTML code into a Web page. When a user browses the page, the HTML code embedded in the Web page will be executed, thereby achieving the special purpose of the malicious user.
##<form method="post" action="<? php echo $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"];?>">
Now, we use the URL to specify the submission address "test_form.php", the above code is modified as follows :
<form method="post" action="test_form.php">
- That's fine.
- However, consider that the user will enter the following address in the browser address bar:
http://www.php.cn/ test_form.php/%22%3E%3Cscript%3Ealert('hacked')%3C/script%3E
The above URL will be parsed into the following code and executed:
<form method="post" action="test_form.php/"><script>alert('hacked')</script>
A script tag has been added to the code, and an alert command has been added. This Javascript code will be executed when the page loads (the user will see a pop-up box). This is just a simple example of how the PHP_SELF variable can be exploited by hackers.
Please note that any JavaScript code can be added in the <script> tag! Hackers can use this to redirect the page to another server. The page code file can protect malicious code. The code can modify global variables or obtain the user's form data.
6. How to prevent $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] from being exploited?
- ## $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] can be passed htmlspecialchars() function to avoid being exploited.
- htmlspecialchars() Convert some predefined characters into HTML entities. Now if the user wants to utilize the PHP_SELF variable, the result will be output as follows:
7. Use PHP to validate form data
- First of all, we process all data submitted by users through PHP's htmlspecialchars() function
- This code will not is executed because it will be saved as HTML escaped code, as shown below: ##<script>location.href('http://www.php.cn') </script>
The above code is safe and can be displayed normally on the page or inserted into the email.
##When the user submits the form, we will do the following two things. Things:- Use the PHP stripslashes() function to remove backslashes (\) in user input data
- Next let us write these filtering functions in In a function we define ourselves, this can greatly improve the reusability of the code.
<?php
// 定义变量并默认设置为空值
$name = $email = $gender = $comment = $website = "";
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST")
{
$name = test_input($_POST["name"]);
$email = test_input($_POST["email"]);
$website = test_input($_POST["website"]);
$comment = test_input($_POST["comment"]);
$gender = test_input($_POST["gender"]);
}
function test_input($data)
{
$data = trim($data);
$data = stripslashes($data);
$data = htmlspecialchars($data);
return $data;
}
?>4. SummaryNote that when we execute the above script, we will use $_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] to detect whether the form has been submitted. If REQUEST_METHOD is POST, the form will be submitted - and the data will be validated. If the form is not submitted validation will be skipped and displayed blank. The use of input items in the above examples is optional, and it can be displayed normally even if the user does not enter any data. In the next chapter we will introduce how to verify the data entered by the user














