class methods
1. Class-specific methods
When a class is created, it will contain some methods, mainly the following methods:
Proprietary methods of the class :
##__init__ Constructor, call __del__ when generating the object Destructor, use # when releasing the object ##__repr__ __setitem__ __getitem__ __len__ __cmp__ __call__ __add__ __sub__ __mul__ ##__div__ Division operation__mod__ Remainder operation__pow__ PowerOf course, sometimes we need to obtain relevant information about the class. We can use the following methods:
type(obj): to obtain the corresponding type of the object;
isinstance(obj, type ): Determine whether the object is an instance of the specified type;
hasattr(obj, attr): Determine whether the object has the specified attributes/methods;
getattr(obj, attr[, default] ) Get the value of the attribute/method. If there is no corresponding attribute, the default value is returned (provided that default is set), otherwise an AttributeError exception will be thrown;
setattr(obj, attr, value): Set the The value of the attribute/method, similar to obj.attr=value;
dir(obj): You can get a list of all attributes and method names of the corresponding object:
2. Method Access control
In fact, we can also regard methods as attributes of the class. Then the access control of methods is the same as attributes, and there is no actual private method. Everything relies on programmers to consciously abide by Python programming standards.
The example is as follows, the specific rules are the same as the attributes,
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- class User(object): def upgrade(self): pass def _buy_equipment(self): pass def __pk(self): pass
3. Method decorator
@classmethod uses the class directly when calling Name class call, not an object
@property You can call the method just like accessing properties
See the example for specific usage:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
class UserInfo(object):
lv = 5
def __init__(self, name, age, account):
self.name = name
self._age = age
self.__account = account
def get_account(self):
return self.__account
@classmethod
def get_name(cls):
return cls.lv
@property
def get_age(self):
return self._age
if __name__ == '__main__':
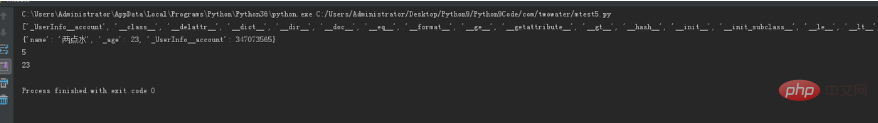
userInfo = UserInfo('两点水', 23, 347073565);
# 打印所有属性
print(dir(userInfo))
# 打印构造函数中的属性
print(userInfo.__dict__)
# 直接使用类名类调用,而不是某个对象
print(UserInfo.lv)
# 像访问属性一样调用方法(注意看get_age是没有括号的)
print(userInfo.get_age)The result of running:
- Course Recommendations
- Courseware download
-

ElementaryPython programming introductory series of graphic tutorials
35709 people are watching -

ElementaryScala Tutorial
13357 people are watching -

ElementaryCSS Online Manual
81804 people are watching -

ElementarySVG Tutorial
12818 people are watching -

ElementaryAngularJS Chinese Reference Manual
24273 people are watching -

ElementaryGo language tutorial manual
27059 people are watching -

ElementaryRedis command operation Chinese manual
57560 people are watching -

ElementaryPython 3 Tutorial
87254 people are watching -

ElementaryXML DOM tutorial
20790 people are watching -

ElementaryMemcached command operation manual
17536 people are watching -

ElementaryXSLT tutorial
9614 people are watching -

ElementaryXQuery Tutorial
8942 people are watching
Students who have watched this course are also learning
- Let's briefly talk about starting a business in PHP
- Quick introduction to web front-end development
- Large-scale practical Tianlongbabu development of Mini version MVC framework imitating the encyclopedia website of embarrassing things
- Getting Started with PHP Practical Development: PHP Quick Creation [Small Business Forum]
- Login verification and classic message board
- Computer network knowledge collection
- Quick Start Node.JS Full Version
- The front-end course that understands you best: HTML5/CSS3/ES6/NPM/Vue/...[Original]
- Write your own PHP MVC framework (40 chapters in depth/big details/must read for newbies to advance)
| Method | Description |
| Print, convert | |
| Assign value according to index | |
| Get the value according to the index | |
| Get the length | |
| Comparison operation | |
| Function call | |
| Addition operation | |
| Subtraction operation | |
| Multiplication operation | |


